Asking how do doctors test for asthma? Read our step-by-step guide on spirometry, challenge tests, and clinical evaluation.
Are you or a loved one worried about asthma but don’t know how to find out? It’s important to understand asthma diagnosis to get the right treatment and manage symptoms well.
We take a detailed approach to diagnose . This includes both clinical checks and objective tests. Spirometry is key, measuring how much and fast air is exhaled.
Other tests, like FeNO and methacholine challenge, might also be needed. Knowing about these tests helps you manage your health better and get the care you need.
Key Takeaways
- A detailed method is used for asthma diagnosis, mixing clinical checks and objective tests.
- Spirometry is the main test for checking lung function.
- More tests like FeNO and methacholine challenge might be used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Understanding the diagnostic process helps patients take charge of their health.
- Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment and symptom control.
Understanding Asthma and Its Symptoms
Getting to know asthma starts with spotting its signs and what might lead to it. It’s a long-term lung issue that causes swelling, blocks airways, and tightens bronchial tubes. This can lead to many symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms differ from person to person. But common ones include wheezing, coughing, feeling short of breath, and tightness in the chest. Wheezing, a high-pitched sound when breathing out, is very noticeable.
Coughing, often at night or when exercising, is another common symptom. Feeling short of breath or having trouble breathing is alarming. It’s usually what makes people go to the doctor.
These symptoms can come and go or stick around. How bad they are can vary a lot. Asthma symptoms can be set off by many things, like allergens, colds, exercise, and stress.
Risk Factors for Developing Asthma
There are many things that can make someone more likely to get asthma. Having a family history of asthma or allergies is a big risk. Allergies can also trigger asthma symptoms.
Other risks include getting sick with a respiratory infection as a kid, being around tobacco smoke, and pollution. Some jobs can also expose people to chemicals or dust, raising the risk of occupational asthma.
Knowing these risks can help spot asthma early and manage it better.
When to Seek Medical Evaluation
If you or your child has asthma symptoms, seeing a doctor is key. Early treatment can make life better and stop problems from getting worse. If you have wheezing, coughing, or trouble breathing often, or if these symptoms get worse, you should see a doctor.
A doctor can figure out if you have asthma by looking at your medical history, doing a physical check, and running tests. They can then make a plan to help manage your symptoms and keep asthma under control.
The Diagnostic Process: What to Expect

The journey to diagnose asthma starts with a first meeting with your doctor. This meeting is key for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan. We’ll help you understand each step, making sure you’re ready.
Initial Consultation with Healthcare Provider
Your doctor will talk with you to learn about your symptoms and worries. This is your chance to ask questions and for your doctor to check your health. It’s important to share your symptoms, medical history, and what makes your symptoms better or worse.
Medical History Assessment
Knowing your medical history is essential for diagnosing asthma. Your doctor will ask about:
- Your symptoms and when they happen
- If anyone in your family has asthma or allergies
- Any past lung problems or illnesses
- Things that might make your symptoms worse, like smoke or allergens
This info helps your doctor understand your situation and find what might be causing your symptoms.
Physical Examination Procedures
A physical check-up is a big part of figuring out if you have asthma. Your doctor will listen to your breathing with a stethoscope and might do other tests to see how well your lungs work. They might find signs of breathing trouble or other health issues that could be causing your symptoms.
By using what they learn from talking to you, looking at your medical history, and doing a physical check-up, your doctor can start to figure out if you have asthma. They’ll also start planning for more tests and treatment.
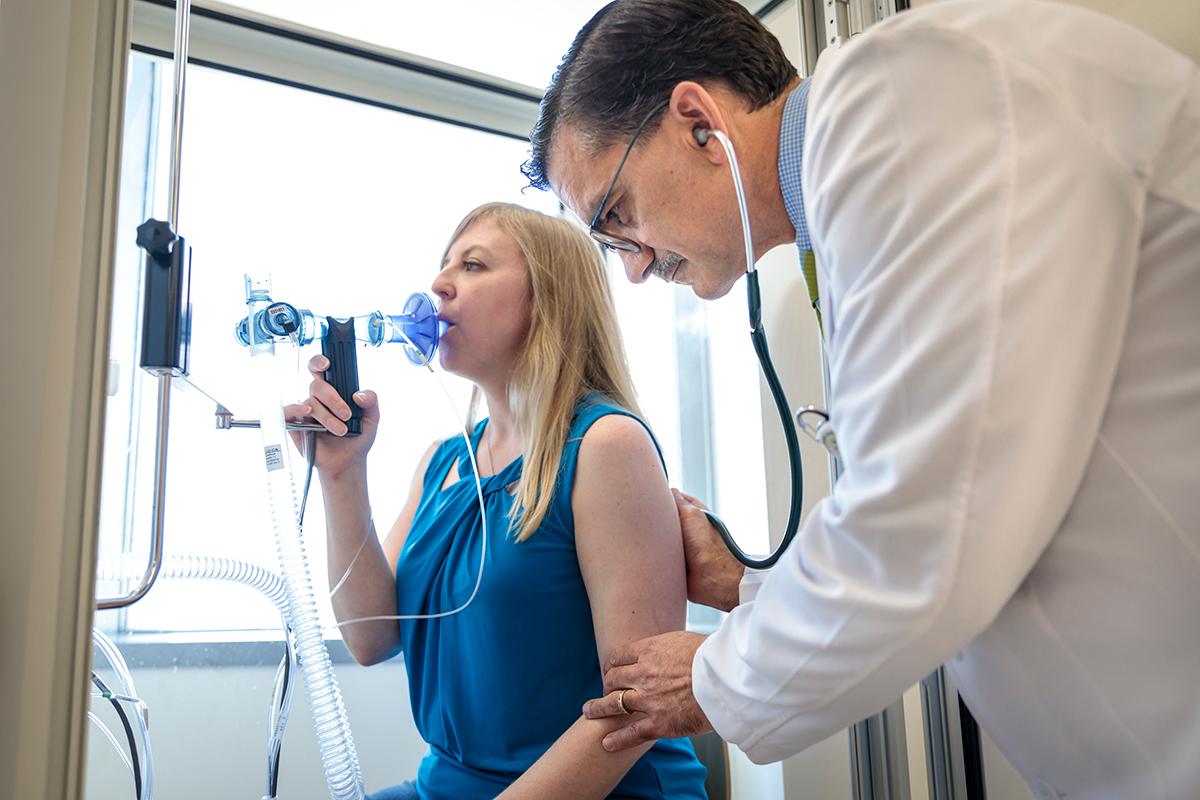
Spirometry: The Primary Diagnostic Test
If you think you might have asthma, spirometry is a key first step. It’s a simple, non-invasive test that checks how well your lungs work. It looks at how much air you can breathe out and how fast you can do it.
How Spirometry Works
During a spirometry test, you take a deep breath and then blow into a tube. This tube is connected to a spirometer, a device that measures lung function. The test looks at things like Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC). These are important for finding out if you have airflow problems.
Preparing for Your Spirometry Test
To get the best results from your spirometry test, it’s important to prepare well. We recommend that you:
- Don’t take bronchodilator medications for a while before the test, as your doctor tells you.
- Wear loose, comfy clothes that don’t get in the way of your breathing.
- Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking.
Understanding Your Spirometry Results
After the test, your doctor will look at the results. They’ll check for signs of breathing problems and see if your lung function gets better with medicine. This helps figure out if you have asthma and what treatment you need.
Key results to look out for include:
- A lower FEV1/FVC ratio means you might have breathing problems.
- If FEV1 goes up after a bronchodilator, it shows your lungs can get better, which helps confirm asthma.
Peak Flow Monitoring: Tracking Lung Function
For those with asthma, peak flow monitoring is a simple way to check lung function. It’s a tool that shows how well your lungs are working. It’s key in managing asthma symptoms.
Using a Peak Flow Meter Correctly
To get accurate readings, using a peak flow meter right is key. Stand or sit up straight to give your lungs room. Take a deep breath and then blow out hard and fast into the meter. The highest number on the meter is your peak flow. Take three readings and record the highest one.
Establishing Your Personal Best Value
Your personal best peak flow value is the highest reading when your asthma is well-controlled. Take peak flow readings twice a day for two to three weeks when you’re feeling well. Record all your readings to find your highest value. This value is a reference for future readings, showing if your asthma is worsening.
Interpreting Peak Flow Readings
After finding your personal best value, compare it to your daily readings. This helps you understand your asthma status. Readings are divided into three zones:
- Green zone: 80-100% of your personal best. You’re in good control.
- Yellow zone: 50-79% of your personal best. Caution is needed; your asthma might be getting worse.
- Red zone: Below 50% of your personal best. This indicates a serious problem; you should take action according to your asthma action plan.
Knowing these zones helps you make better decisions about managing your asthma.
By making peak flow monitoring a part of your daily routine, you can better control your asthma. Regular monitoring, with the help of a healthcare provider, leads to better asthma management.
How Do Doctors Test for Asthma in Challenging Cases
Diagnosing asthma can be easy in many cases. But when symptoms are unclear or test results are not clear, doctors use more tools. Asthma is complex and can show up differently, making it hard to diagnose when it doesn’t act like typical asthma.
Bronchoprovocation Testing
Bronchoprovocation Testing, or a methacholine challenge test, is a key test for tough cases. It checks how sensitive the airways are to certain things. The patient breathes in methacholine in increasing amounts, and lung function is checked after each breath. If the airways get too tight at a low amount, it might mean asthma.
Key aspects of Bronchoprovocation Testing include:
- Assessing airway sensitivity
- Measuring lung function after methacholine inhalation
- Determining the concentration of methacholine that causes a 20% drop in lung function (PC20)
When Standard Tests Are Inconclusive
Standard tests like spirometry might not always give a clear answer. This can happen for many reasons, like mild symptoms, asthma that comes and goes, or other lung problems that look like asthma. When this happens, doctors might suggest more tests or watch the patient closely to confirm the diagnosis.
The following table summarizes the scenarios where additional testing might be considered:
|
Scenario |
Possible Additional Tests |
|---|---|
|
Symptoms suggest asthma, but spirometry is normal |
Bronchoprovocation Testing, Peak Flow Monitoring |
|
Patient has a history of allergies |
Allergy Testing (Skin Prick or Blood Tests) |
|
Presence of other respiratory conditions |
Chest X-ray, Sputum Analysis, FeNO Testing |
By using these extra tests, doctors can better diagnose asthma, even when it’s hard. This ensures patients get the right treatment.
Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) Testing
FeNO testing is a key tool in managing asthma. It shows how much airway inflammation there is. This test is non-invasive and measures nitric oxide in the breath.
What FeNO Measures and Why It Matters
FeNO testing looks at the nitric oxide in your breath. Nitric oxide shows airway inflammation, a sign of asthma. Doctors use it to see how bad the inflammation is.
This helps them diagnose asthma and check if treatments are working. It also guides changes to treatment plans.
The amount of nitric oxide in your breath shows how much inflammation there is. More nitric oxide means more inflammation. This could mean asthma is not controlled well or there’s another inflammation issue.
The Testing Procedure
The FeNO test is easy and doesn’t hurt. You breathe slowly into a device that checks nitric oxide levels. The test is quick, and you get results right away. Preparation is simple, but you might need to avoid some foods or meds.
Interpreting FeNO Results
Understanding FeNO results means looking at the nitric oxide level and the patient’s overall health. High levels often mean eosinophilic inflammation, common in asthma. Low FeNO levels suggest asthma might not be caused by eosinophilic inflammation or that treatment is working well.
FeNO testing is very useful for asthma diagnosis and management. It gives direct info on airway inflammation. This helps doctors create better treatment plans for their patients, improving asthma control and life quality.
Allergy Testing for Asthma Triggers
Allergy testing is key in diagnosing and managing asthma. It helps patients know what causes their symptoms. Healthcare providers can then create specific treatment plans to help patients feel better.
Skin Prick Tests
Skin prick tests are a common way to find allergies. A small amount of an allergen is placed on the skin and pricked with a needle. The skin’s reaction is then checked. This test is quick, relatively painless, and gives immediate results.
We use these tests to find common allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. These can make asthma symptoms worse in some people.
Blood Tests for Specific Allergens
Blood tests check for allergy-related antibodies in the blood. They are useful when skin prick tests can’t be done or if a patient has a condition that makes skin testing hard.
Blood tests can find specific allergens that might be causing asthma symptoms. This helps doctors create a treatment plan that’s just right for the patient.
|
Test Type |
Purpose |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Skin Prick Test |
Detects immediate allergic reactions |
Quick results, relatively painless |
|
Blood Test |
Measures allergy-related antibodies |
Useful when skin testing is not feasible |
Patch Testing for Contact Allergens
Patch testing finds contact allergens that can cause skin reactions. While it’s not directly for asthma, it can help with skin conditions that might go with asthma.
Small amounts of possible allergens are put on the skin with patches. The skin is watched for reactions over a few days.
Understanding how allergy testing helps manage asthma is important. It helps us find what triggers symptoms and create better treatment plans. Whether it’s through skin prick tests, blood tests, or patch testing, it gives us valuable info to improve patient care.
Additional Diagnostic Procedures
Healthcare providers use many tests to diagnose asthma. These tests help rule out other conditions that might look like asthma. They give a full picture of the patient’s health.
Chest X-rays and Imaging
Chest X-rays help find other lung problems that might look like asthma. These include pneumonia or something stuck in the airway. Even if a chest X-ray looks normal, it can spot other issues.
Blood Tests for Inflammatory Markers
Blood tests check for inflammation markers like eosinophils. These markers are often high in asthma patients. The tests help doctors understand how severe the inflammation is and what treatment to use.
|
Inflammatory Marker |
Normal Range |
Elevated in Asthma |
|---|---|---|
|
Eosinophils |
0-500 cells/μL |
Often above 500 cells/μL |
|
IgE |
Varies by age and lab |
Frequently elevated |
Sputum Analysis
Sputum analysis looks at sputum under a microscope. It checks for inflammatory cells like eosinophils. This test helps confirm asthma and understand the inflammation.
“Sputum analysis can be very helpful in telling different airway diseases apart and guiding treatment.” – Medical Expert, Pulmonologist
Using these extra tests, doctors can better understand a patient’s asthma. This leads to more effective treatment plans.
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
Asthma diagnosis changes a lot with age. We need to tailor our approach for each age group. This helps us diagnose and manage asthma better.
Diagnosing Asthma in Children Under 5
It’s hard to diagnose asthma in kids under 5 because they can’t do lung tests. We look at symptoms, medical history, and how they react to treatment. Signs like wheezing, coughing, and trouble breathing are important.
We might try asthma medicine to see if it helps. This can help us figure out if they have asthma.
Testing Approaches for School-Age Children
Kids in school can have spirometry tests. This test checks how much air they can breathe out and how fast. It’s key for diagnosing asthma in this age.
We also look at symptoms, medical history, and how they react to asthma meds. Allergy tests might be suggested to find out what triggers their asthma.
Adult-Onset Asthma Evaluation
Adults who get asthma need a thorough check-up. This includes looking at their medical history, doing a physical exam, and lung function tests like spirometry. We also think about their job, smoking history, and other lung problems.
Allergy tests might help find out what causes their asthma.
Elderly Patient Assessment
Diagnosing asthma in older adults can be tricky because of other health issues. We use a mix of clinical checks, lung tests, and sometimes more tests like bronchoprovocation or FeNO testing. We also look at their overall health and what medicines they take.
Knowing these age-specific details helps us diagnose asthma more accurately. This way, we can create better treatment plans for each patient.
Conclusion: After Your Diagnosis
Getting an asthma diagnosis is just the start of your journey. We’ve shown you how to get diagnosed, from first visits to tests like spirometry. This helps find out if you have asthma.
After you know you have asthma, making a personal action plan is key. This plan includes your treatment and lifestyle changes. We help you make a plan that fits your life and needs.
Managing asthma is a long-term job. You need to keep an eye on your treatment and make changes when needed. We stress the importance of regular check-ups and talking openly about your asthma. This way, you can control your asthma better.
Knowing how asthma is tested and managed can make you feel more in control. With the right help, you can live a full and active life even with asthma.
FAQ
What is the primary diagnostic test for asthma?
Spirometry is the main test for asthma. It checks how much air you can breathe out and how fast.
How is asthma diagnosed in adults?
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and tests like spirometry and peak flow monitoring to diagnose asthma in adults.
What is peak flow monitoring, and how is it used in asthma management?
Peak flow monitoring uses a meter to measure how fast you can exhale. It helps manage asthma by tracking lung function.
What is FeNO testing, and what does it measure?
FeNO testing checks the level of nitric oxide in your breath. It helps diagnose and manage asthma by measuring airway inflammation.
How do doctors test for asthma in challenging cases?
In tough cases, doctors might use tests like bronchoprovocation testing (e.g., methacholine challenge) to diagnose asthma.
What is bronchoprovocation testing?
Bronchoprovocation testing involves inhaling a substance that can make airways constrict. It checks airway responsiveness.
Can allergy testing help diagnose asthma?
Yes, allergy testing can find asthma triggers. Tests include skin prick tests, blood tests, and patch testing.
Are there special considerations for diagnosing asthma in different age groups?
Yes, diagnosing asthma varies by age. Children under 5, school-age kids, adults, and the elderly need special testing approaches.
What additional diagnostic procedures may be used to diagnose asthma?
More tests might include chest X-rays, blood tests for inflammation, and sputum analysis. They help rule out other conditions.
What happens after being diagnosed with asthma?
After a diagnosis, creating an asthma action plan is key. It outlines how to manage symptoms and adjust medications.
How can I prepare for a spirometry test?
To prepare for spirometry, avoid bronchodilator meds, wear loose clothes, and follow your doctor’s instructions.
How do I use a peak flow meter correctly?
To use a peak flow meter, stand up, take a deep breath, and blow out hard and fast. Record the reading and repeat for accuracy.
What is the role of FeNO testing in managing asthma?
FeNO testing helps check airway inflammation. It guides treatment and monitors asthma management.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/asthma_qrg.pdf







