Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Prevention in immunology is about resilience. While we cannot always prevent the onset of genetic disorders, we can optimize the body’s ability to handle stress and infection. This starts with the fundamentals of health.
There is a common myth that you can “boost” your immune system. In reality, a hyperactive system is an allergic or autoimmune one. The goal is balance, or homeostasis.
Daily habits accumulate to create this balance. Regular care involves a combination of medical surveillance and lifestyle discipline.
Sleep is the regenerative phase for the immune system. During sleep, cytokines are released that fight infection. Chronic sleep deprivation reduces the production of these protective proteins and antibodies.
Lack of sleep increases cortisol, which suppresses immune function. Adults should aim for 7 to 9 hours, while children need more.
Prioritizing sleep hygiene—dark rooms, consistent schedules—is a direct investment in immune defense.

The immune system requires energy and micronutrients to function. Deficiencies in Zinc, Selenium, Iron, Copper, Folic Acid, and Vitamins A, B6, C, and E can alter immune responses.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins provides these nutrients naturally. The gut microbiome, fueled by fiber, regulates immune tolerance.
Processed foods and high sugar intake can promote inflammation. Nutritional care focuses on whole, nutrient-dense foods.
Moderate exercise mobilizes immune cells. It increases blood flow, allowing white blood cells to patrol the body more effectively. It also reduces inflammation and the levels of stress hormones.
However, extreme, prolonged exertion without rest can temporarily suppress the immune system. The key is consistency and moderation.
Regular physical activity is associated with a lower incidence of infections and better vaccine responses in the elderly.
Vaccines are the single most effective tool for preventing infectious diseases. They train the adaptive immune system to recognize pathogens without the danger of the actual disease.
Keeping up with the vaccination schedule protects the individual and the community through herd immunity. This is vital for those who cannot be vaccinated.
Specialists often manage vaccination schedules for immunocompromised patients, ensuring they receive safe (non-live) vaccines at the correct times.

Chronic stress is an immunosuppressant. It keeps the body in a fight mode, diverting resources away from immune maintenance. This increases susceptibility to colds and reactivates latent viruses.
Mindfulness, meditation, and therapy are preventative tools. They lower the physiological stress burden.
Managing stress is particularly important for patients with autoimmune conditions, as stress is a common trigger for flares.

Simple hygiene practices prevent the introduction of pathogens. Hand washing remains the gold standard. Avoiding close contact with sick individuals protects those with weak immune systems.
However, the “hygiene hypothesis” suggests that some exposure to microbes in early childhood is necessary to train the immune system. A balance is needed.
For immunocompromised patients, stricter protocols, such as wearing masks in crowded areas or avoiding raw foods, may be necessary.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
In the world of high-level medical care, the quality of research matters. Journals like Frontiers in Immunology publish cutting-edge studies. The frontiers in immunology impact factor reflects the significance of this research.
Similarly, the Nature Immunology Impact Factor and Science Immunology Impact Factor serve as benchmarks for the scientific community. High impact factors suggest that the research is rigorous and influential.
Clinicians use this hierarchy to determine which new treatments are ready for patient care. It ensures that prevention strategies are based on the best available science.
Clean air and water are foundational. Reducing exposure to indoor pollutants such as smoke, mold, and harsh chemicals relieves the immune system’s burden.
For allergy sufferers, creating a “safe zone” in the bedroom is key. This prevents the immune system from fighting allergens all night, allowing it to rest.
Awareness of outdoor air quality helps patients plan activities to avoid high-pollen or high-pollution days.
Smoking damages the cilia in the lungs, the first line of innate defense. It also alters immune cell function, promoting inflammation and autoimmunity.
Excessive alcohol impairs the ability of white blood cells to migrate to infection sites. Avoiding these toxins allows the immune barriers to function correctly.
Vaping and secondhand smoke are also detrimental. Cessation is a primary preventative intervention.
Uncontrolled diabetes or kidney disease impairs immunity. High blood sugar paralyzes white blood cells. Prevention involves tight control of these comorbid conditions.
Regular check-ups ensure that underlying health issues do not undermine the immune defense.
Medication reviews help avoid drugs that might inadvertently suppress immunity unless necessary.
The skin is the fortress wall. Keeping it intact prevents pathogens from entering. For patients with eczema, daily moisturizing is a medical necessity, not cosmetic.
Treating cuts and scrapes promptly prevents bacterial entry. Sun protection prevents UV-induced immune suppression in the skin.
Gentle skincare preserves the skin’s natural microbiome, which aids in defense.
Loneliness has been linked to poorer immune responses. Social connection reduces stress and promotes positive hormonal balance.
Maintaining strong relationships and a sense of community is a protective factor. It encourages adherence to medical advice and provides support during illness.
For older people, social engagement is correlated with better health outcomes.
No, supplements cannot replicate the complex synergy of nutrients and fiber found in whole foods; they are meant to fill gaps, not replace the foundation of a healthy diet.
Over-sterilization of the home environment can limit the immune system’s exposure to harmless microbes it needs to learn from, but basic hygiene, like handwashing, is essential to prevent disease.
No, vaccines strengthen the immune system by teaching it how to fight specific threats without the risk of severe illness; they do not “overload” the system.
Cold weather itself does not cause low immunity or the flu; however, people spend more time indoors in proximity during winter, which facilitates the spread of viruses.
Chronic stress produces cortisol, a hormone that, over time, suppresses the immune system and reduces the number of lymphocytes available to fight infection.


At Liv Hospital, we know how hard it is to diagnose and treat anemia of chronic disease (ACD). This condition affects people with chronic infections,

A blood clot in the hand can cause a lot of pain and serious problems if not treated quickly. It’s important to know the signs
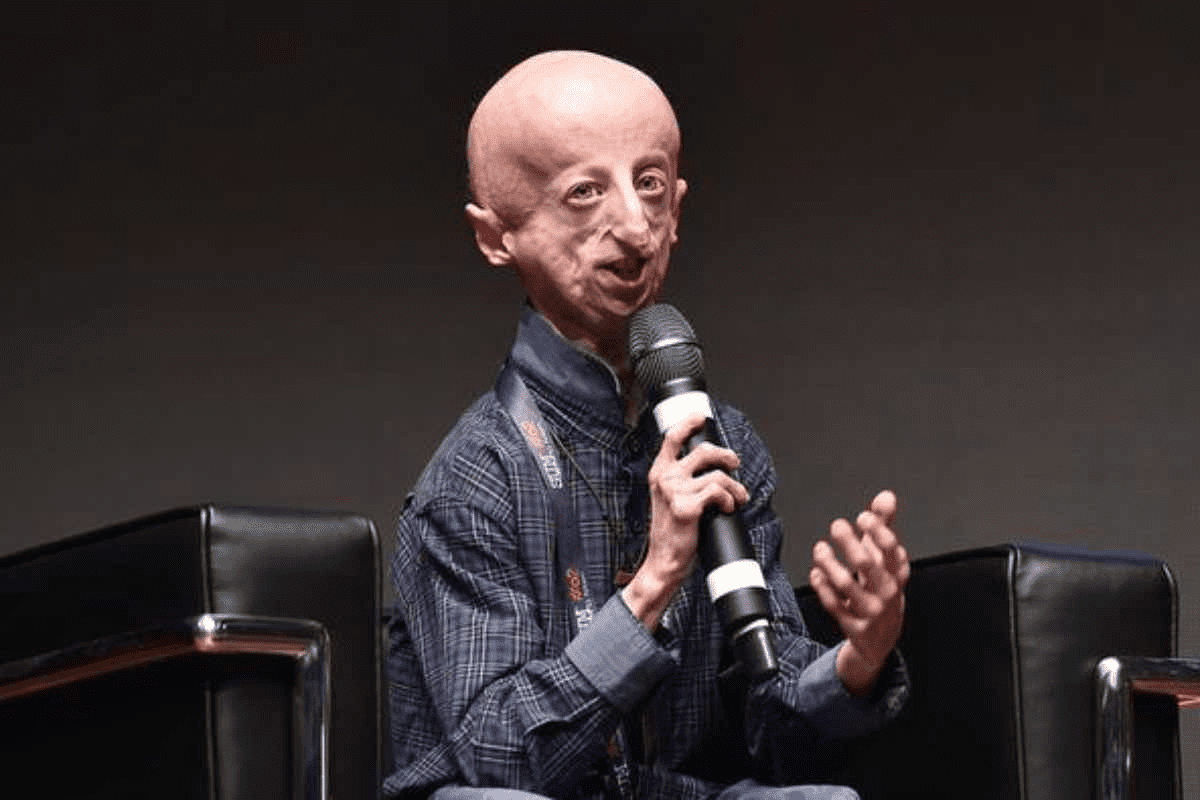

Progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder. It affects about 1 in 4 million children worldwide and causes them to

Folic acid is a key part of folate (vitamin B9). It’s vital for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and cellular growth. While it’s famous

3 types of blood cells play a vital role in keeping our bodies healthy. At Liv Hospital, we understand how important these cells are for
About 100,000 people in the U.S. live with sickle cell anemia. Many think it’s an autoimmune disorder, but the truth lies in sickle cell anemia genetics.

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)