Clinical Immunology focuses on the immune system’s health. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of allergies, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition

Immunology is the branch of medicine and biology that studies the immune system, which is the body’s complex defense network against infection and disease. This system works to find and destroy “foreign” invaders like bacteria, viruses, and fungi, while protecting the body’s own cells. The field includes a wide range of disorders, usually grouped into three types: hypersensitivities (allergies), autoimmunity (when the body attacks itself), and immunodeficiencies (when the defense system is weak or missing). Immunologists look at how white blood cells, antibodies, and chemical messengers communicate. Learning how these parts work together is important for treating infections, helping with organ transplants, making vaccines, and using immunotherapy to treat cancer.
Immune disorders happen when the immune system does not work as it should. Sometimes it becomes overactive and attacks harmless things like pollen or even healthy tissue. Other times, it is too weak to fight off infections, which can cause long-term health problems.
Information about facilities: Highlight the specialized Allergy and Immunology Clinic. Mention the advanced diagnostic capabilities, including Flow Cytometry for analyzing immune cell subsets and Molecular Genetic Testing for diagnosing primary immunodeficiencies. Describe the dedicated Infusion Center where patients receive immunoglobulin replacement therapy (IVIG) or biologic treatments in a safe, monitored environment.
Here’s an interesting fact: The immune system has a kind of memory. After it fights off a certain germ or after you get a vaccine, B cells and T cells can remember that invader for many years. This helps your body respond faster and more strongly if it comes back.

Immune disorders can affect the whole body. In autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, ongoing inflammation can harm organs, joints, and skin, leading to tiredness and pain. People with immunodeficiencies often get serious infections, such as pneumonia or sinus infections, that are hard to treat. Severe allergies can cause a dangerous reaction called anaphylaxis, which can make it hard to breathe and cause shock.
Who is at risk: Identify risk factors. Primary Immunodeficiencies are often genetic and appear in childhood. Autoimmune diseases affect women more frequently than men and often have a hereditary component. Environmental factors such as hygiene, diet, and exposure to pollutants contribute to the rising rates of allergies and asthma.
Doctors use several tests to diagnose immune conditions. For allergies, they use Skin Prick Tests and special blood tests to find out what causes reactions. For immune deficiencies, they check levels of different antibodies (IgG, IgA, IgM) and see how the body responds to vaccines. Rare disorders may require genetic sequencing to find the cause.
An immunologist is like a detective for hidden problems in the body. They figure out if someone’s frequent infections are normal or a sign of a real immune issue. They also manage allergy treatments and adjust medicines for autoimmune diseases to help prevent organ damage.
Treatment for immune disorders is about bringing the immune system back into balance. For deficiencies, doctors replace missing antibodies. For autoimmune diseases, they use medicines like corticosteroids or biologics to calm the immune response. For allergies, treatment includes avoiding triggers and using allergy shots to help the immune system react less strongly.
The path to treatment often starts with a detailed medical history. Most immune conditions need ongoing care. For example, someone with a primary immunodeficiency might need regular infusions under the skin or into a vein every few weeks for life. Blood tests are done regularly to make sure these long-term treatments are working and safe.

Immunologists often work together with other specialists. They team up with rheumatologists for joint problems, pulmonologists for lung issues like asthma, and dermatologists for skin conditions such as eczema or hives. This teamwork helps make sure all aspects of immune disorders are treated thoroughly.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Before starting treatment, patients should know that boosting the immune system is not always the goal, especially for autoimmune diseases. Good hygiene, like washing hands and staying away from people who are sick, is very important. People taking immunosuppressant medicines need to be careful with live vaccines.
Innate immunity is the rapid, non-specific defense you are born with, while adaptive immunity is the specialized response that develops over time and remembers specific pathogens.
Specialists have advanced training to diagnose complex immune system disorders, such as recurrent infections, severe allergies, or autoimmune conditions, that primary care may not be equipped to manage.
No, the immune system is a network of cells, tissues, and organs spread throughout the body, including the spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
Yes, if the immune system is overactive, it can mistake harmless substances for threats, leading to allergies, or attack the body’s own tissues, causing autoimmune diseases.
Vaccines stimulate the adaptive immune system to produce memory cells specific to a pathogen, without causing the disease, preparing the body to fight the actual infection if exposed later.

The Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) is called the ‘everything’ blood test. It gives a wide view of a person’s metabolic health. This tool includes many
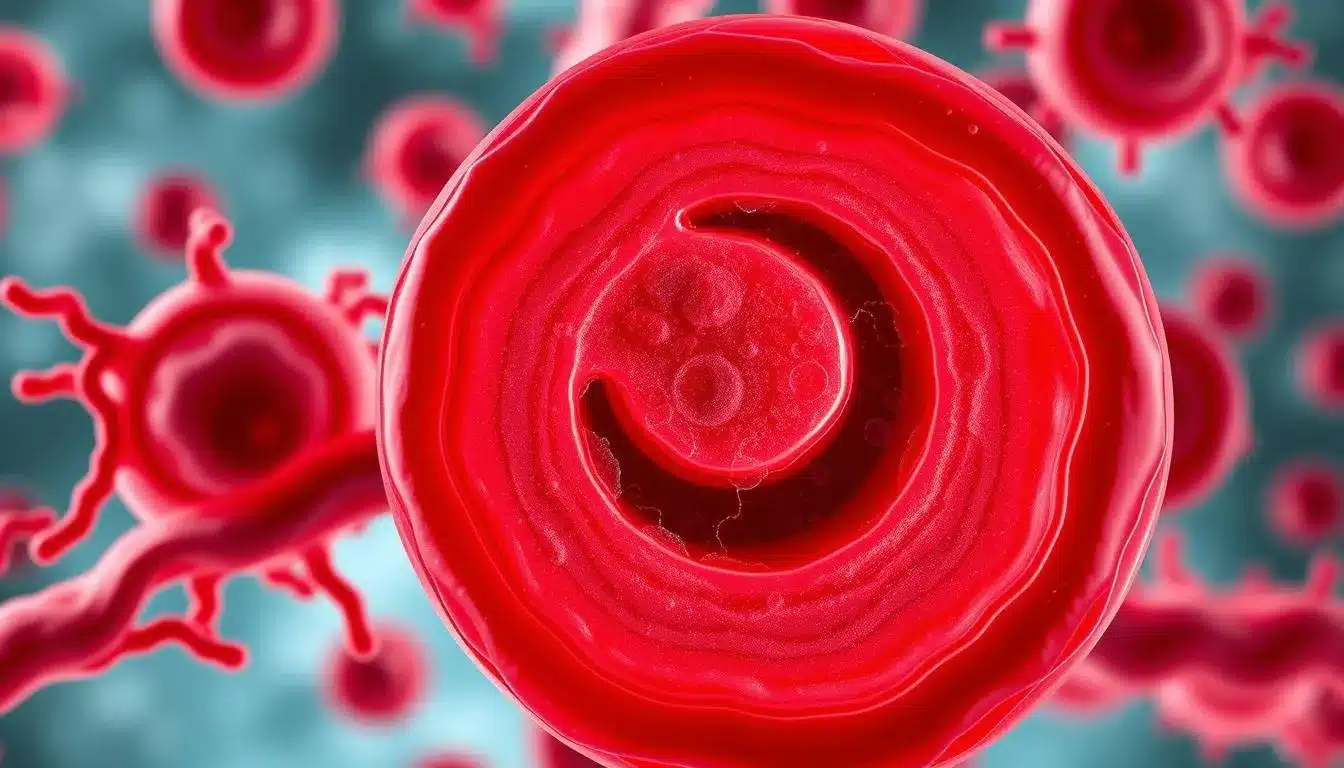
Sickle cell anemia is a major health problem worldwide. It affects the body’s ability to carry oxygen because of abnormal red blood cells. This issue
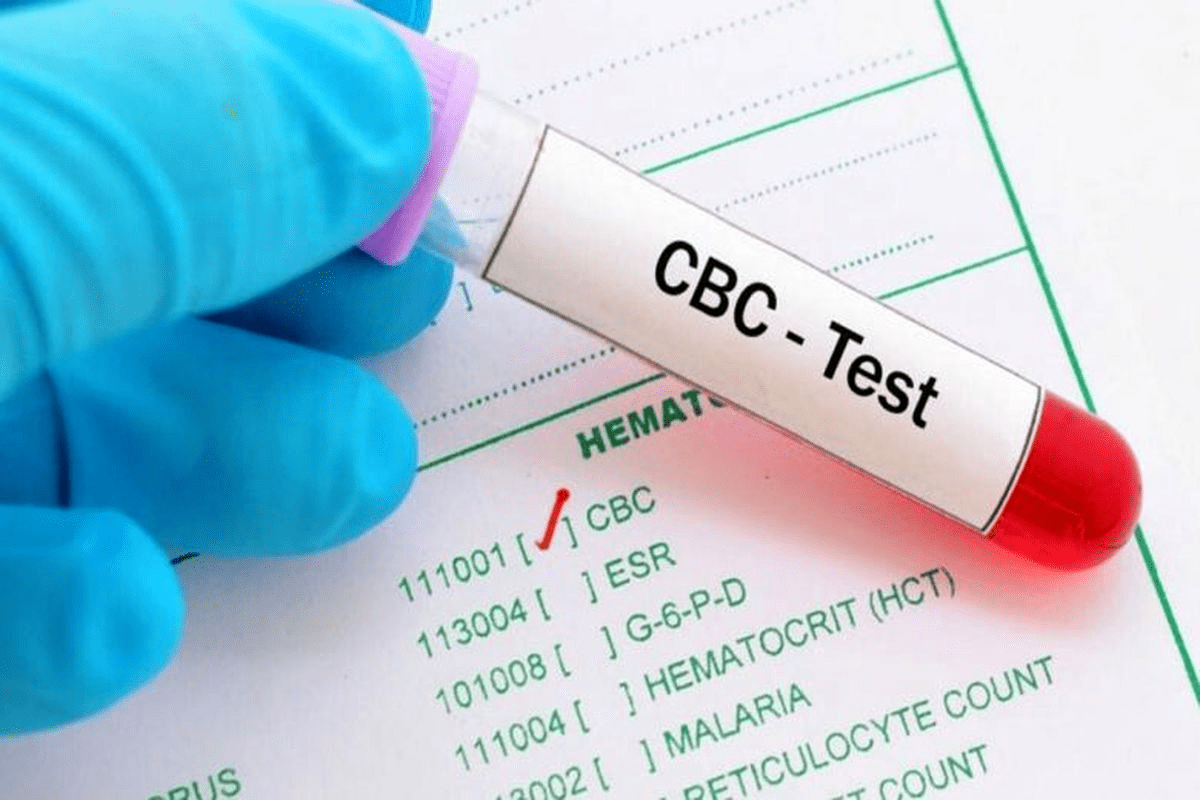
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a common blood test. It gives important information about the blood’s different parts, like red and white blood cells

Ischemic stroke is a serious medical issue. It happens when a brain artery gets blocked, cutting off blood flow, oxygen, and glucose to parts of

Bone marrow transplants are lifesaving for many blood-related diseases. The thought of getting or giving a bone marrow transplant can be scary. People worry a
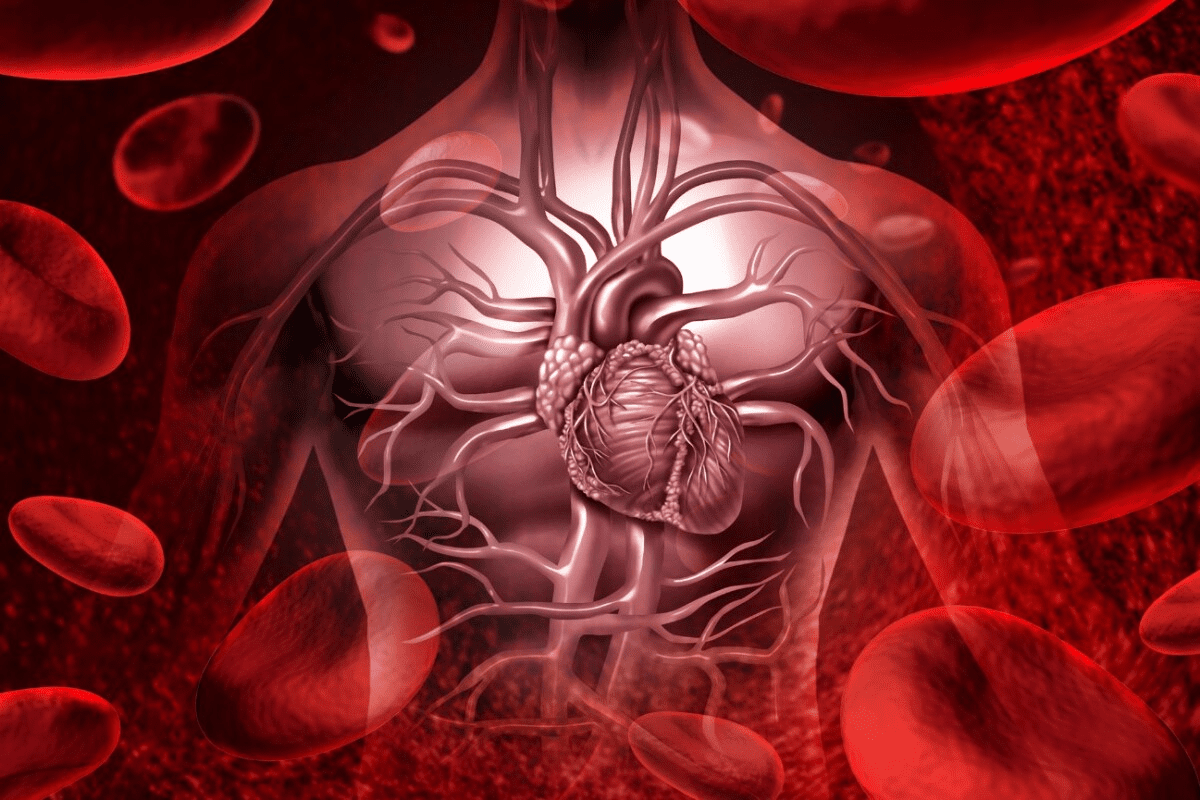
What are some blood diseases that can affect your health? Blood disorders impact the red and white blood cells, platelets, plasma, and bone marrow. These

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)