Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Most heart attacks and strokes are linked to risk factors we can influence, such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, excess weight, and inactivity. Research suggests that a cluster of healthy habits—heart-friendly eating, regular physical activity, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight—can reduce cardiovascular risk by more than 80% in some groups. Working with your cardiology team, you can combine lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring to prevent heart disease or stop it from getting worse.
Daily habits strongly influence blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar, weight, and inflammation, which are key drivers of cardiovascular disease. Large cohort studies show that people who do not smoke, are physically active, eat a healthy diet, and maintain a normal body weight have dramatically lower rates of heart disease and diabetes than those who do not follow these habits. Global organizations estimate that up to 80% of cardiovascular disease could be prevented by addressing modifiable risk factors.
Heart-healthy eating patterns emphasize whole, minimally processed foods and limit salt, added sugars, and unhealthy fats. Guidelines often highlight Mediterranean- or DASH-style diets rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts, fish, and unsaturated oils, with less red and processed meat, refined carbohydrates, and trans fats.
These patterns help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol, support weight management, and reduce overall cardiovascular risk.
Regular physical activity makes the heart and circulatory system more efficient, helps control blood pressure and cholesterol, and supports weight and blood sugar control. Major organizations recommend at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, or 75 minutes of vigorous activity, plus muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days weekly.
Even small increases in daily movement can improve cardiovascular health, especially for people who were previously inactive.
Tobacco use is one of the most powerful and preventable risk factors for heart disease and stroke. Smoking damages blood vessels, raises blood pressure, promotes clotting, and interacts with other risk factors such as diabetes and hypertension to multiply cardiovascular risk. Stopping smoking at any age reduces heart risk, and the benefit grows over time.
Regarding alcohol, many guidelines advise avoiding heavy drinking and limiting or abstaining from alcohol for heart health, emphasizing that any potential benefits are outweighed by risks in many people. Discuss safe limits or whether you should avoid alcohol altogether with your doctor.
Excess body weight—especially around the waist—is linked to high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol, diabetes, and inflammation, all of which increase cardiovascular risk. Modest weight loss of 5–10% of body weight can significantly improve blood pressure and metabolic risk factors. Sleep and stress also matter: short or poor-quality sleep and chronic stress have been associated with higher blood pressure, weight gain, and unhealthy behaviors.
These factors are often addressed within comprehensive lifestyle and cardiac rehabilitation programs.
Primary prevention focuses on people who have risk factors but no diagnosed cardiovascular disease, aiming to prevent a first heart attack or stroke. Secondary prevention targets those who already have heart disease or have had events, using intensive strategies to prevent recurrence and complications.
Both levels of prevention typically involve:
Guidelines stress that lifestyle changes and medications work together—not as alternatives—to reduce future cardiovascular events.
Effective prevention is a partnership between you and your healthcare providers. Your care team helps you understand your individual risk, set realistic goals, choose appropriate medications, and access support services such as dietitians, smoking-cessation programs, or cardiac rehabilitation.
Practical steps include:
International patients can often combine medical evaluation with lifestyle counselling during a focused visit, then continue prevention plans with local providers.
Explore specific risk factors further on cardiology symptoms and risk factors and see how rehab programs support prevention on cardiology treatment and rehabilitation.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil, is consistently ranked as the best diet for cardiovascular health.
Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, per week, plus muscle-strengthening activities on 2 days.
Staying properly hydrated helps the heart pump blood more efficiently and can prevent blood from thickening, but water alone is not a cure for chronic hypertension.
Yes, the benefits begin within minutes of quitting; heart rate drops, and within a year, the added risk of coronary heart disease is cut in half compared to a smoker’s risk.
Absolutely, chronic stress releases hormones that increase blood pressure and inflammation, directly contributing to arterial damage and heart disease over time.

What is RFR? Resting Full Cycle Ratio. Get best vital definitions. This new index helps spot dangerous artery issues fast. Amazing tech for you. Radio

Every year, over 1 million heart catheterizations are done in the U.S. This makes it a common way to check and treat heart problems. If

Recent studies show that taking aspirin every day can lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes. This has made people curious about aspirin’s heart-protective
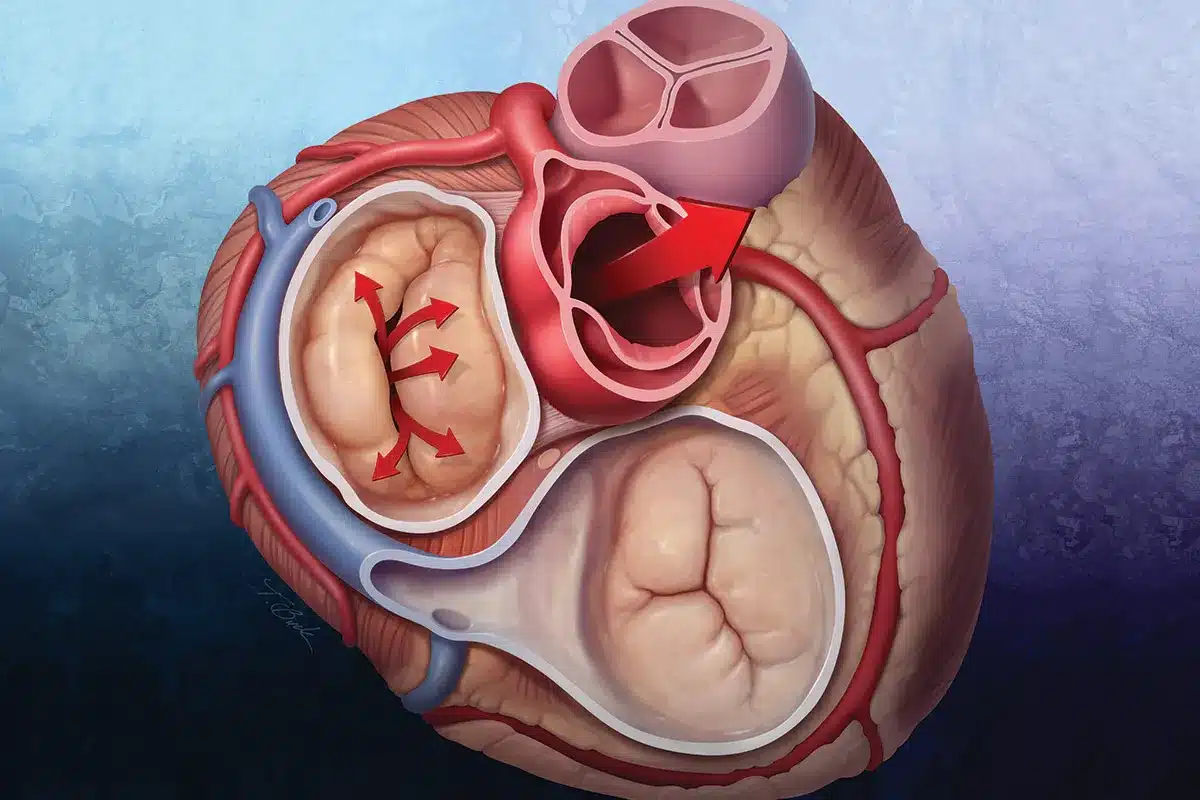
It’s important to know about rare heart conditions to help patients. We look into these uncommon diseases, their traits, and the help available for those

Did you know the National Institutes of Health (NIH) gives out billions in grants each year? Knowing when Federal Financial Reports (FFRs) are due is
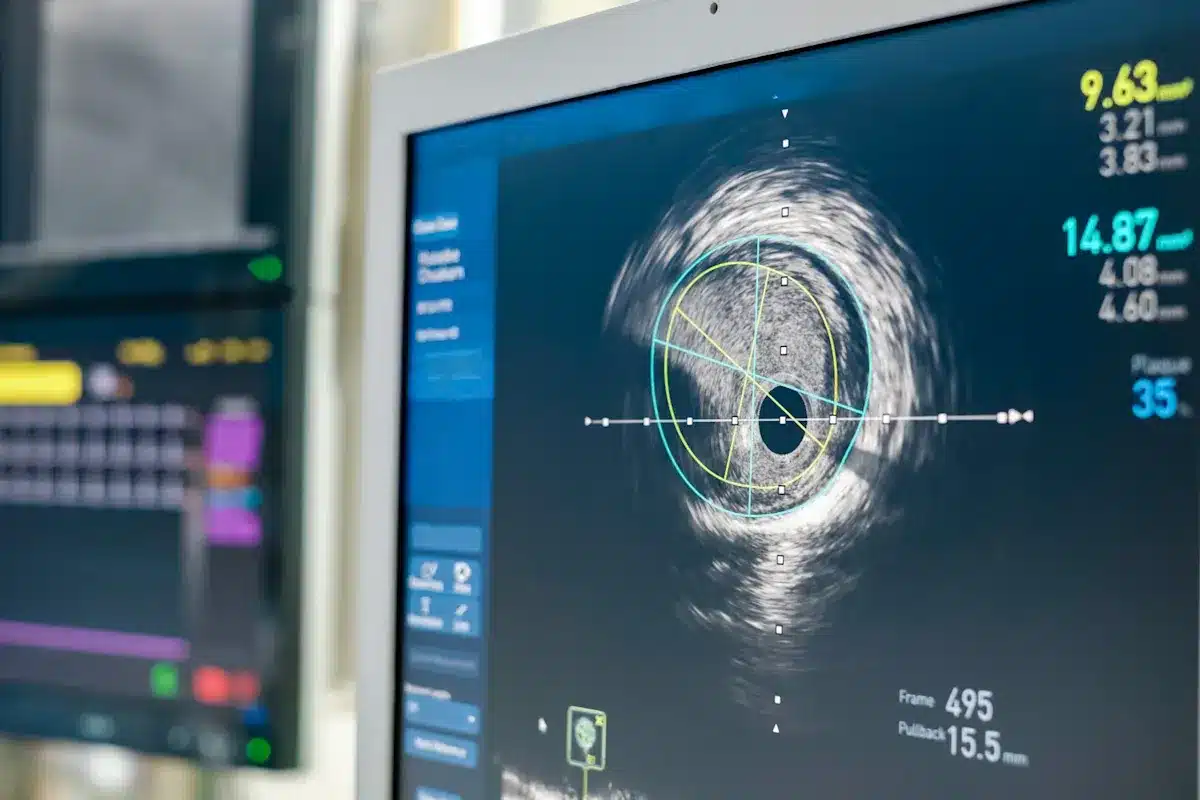
A resting heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute is seen as normal for adults. Yet, research shows that a lower resting heart rate links

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)