Understand Hematology Symptoms and Risk Factors, including early warning signs of blood disorders, genetic risks, and environmental factors you can control.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Blood disorders are often called “invisible illnesses” in their early stages. Unlike a broken bone that causes immediate, localized pain, or a skin rash that is clearly visible, problems within the blood and bone marrow often manifest as vague, systemic changes.
A patient with Leukemia might just feel “tired” for weeks. A patient with Lymphoma might think they have a stubborn flu. A patient with Anemia might attribute their shortness of breath to getting older.
At Liv Hospital, we believe that awareness is the most powerful diagnostic tool. Recognizing the subtle signals your body is sending and distinguishing them from everyday stress or minor infections is the key to early intervention. When blood cancers or severe anemias are caught early, treatment is often less aggressive and more successful.
This guide outlines the specific symptoms associated with the three main components of blood: Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets, as well as the Lymphatic System.
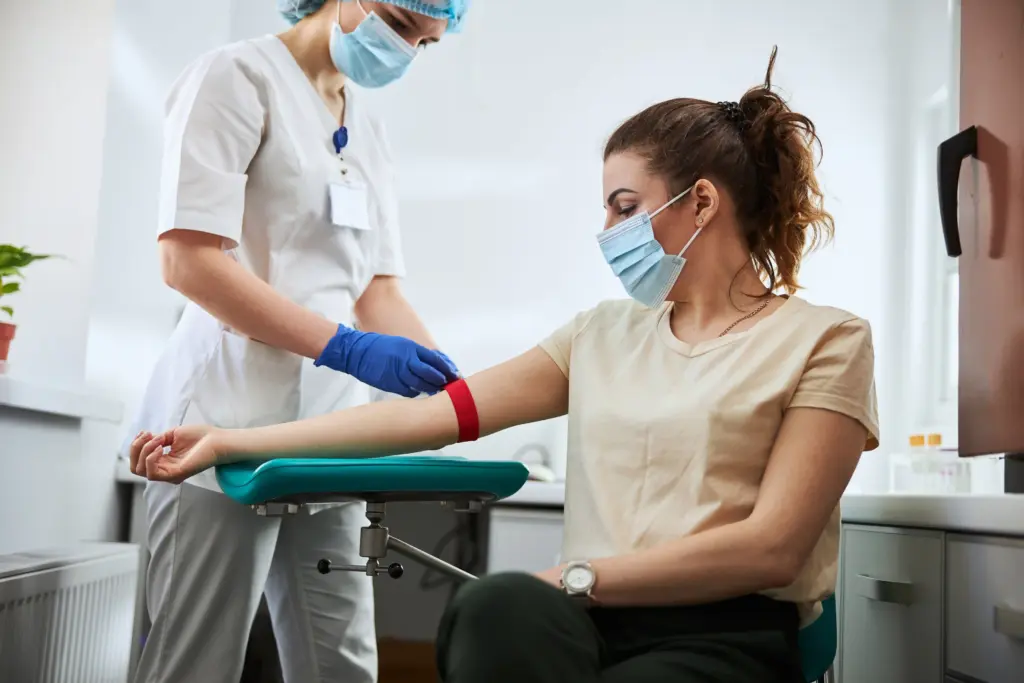
In Hematology, doctors pay close attention to a specific triad of systemic symptoms known as “B-Symptoms.” These signs indicate that the body is fighting a high-grade internal battle, consuming vast amounts of energy and releasing inflammatory chemicals. They are classic “Red Flags” for Lymphoma and aggressive Leukemias.

Red blood cells carry oxygen. When their numbers drop (Anemia) or their function is impaired (Sickle Cell), the body enters a state of oxygen starvation.
Platelets are the tiny cells that plug holes in blood vessels. When they are low (Thrombocytopenia) or don’t work (Von Willebrand Disease), you bleed too easily.

Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
White blood cells fight infection. In Leukemia, the bone marrow makes billions of useless white cells that crowd out the healthy ones. Paradoxically, even though the white cell count is high, the patient has no immunity.
The lymphatic system is the body’s drainage network. In Lymphoma, cancer cells congregate in the lymph nodes.
Multiple Myeloma is a cancer of the plasma cells (antibody factories). It typically affects older adults. Doctors use the acronym CRAB to identify its specific damage:
Most hematologic cancers arise from random genetic mutations (bad luck) rather than lifestyle choices. However, certain factors increase the statistical risk.
Certain viruses can alter the DNA of blood cells, triggering cancer.
You should consult a specialist at Liv Hospital if you experience:

No. There is no scientific evidence that emotional stress, grief, or physical injury causes Leukemia. Leukemia is caused by DNA mutations in the bone marrow cells. While chronic stress can weaken the immune system, it does not directly mutate DNA to cause blood cancer.
Usually, no. The vast majority of anemia cases are caused by Iron Deficiency (from diet or heavy periods) or B12 deficiency. However, unexplained anemia especially in an older adult can be the first sign of a gastrointestinal tumor (slow bleeding) or a bone marrow disorder (Myelodysplastic Syndrome). It always requires investigation.
Malignant Node (Lymphoma): Usually painless, hard (like a rock), fixed in place, and continues to grow slowly over months.
No. Night sweats are common in menopause, thyroid disorders, and infections like Tuberculosis. However, if they are “drenching” (requiring you to change clothes) and accompanied by weight loss or fever, they are a significant Red Flag for Lymphoma and must be checked.
This has been studied extensively. While some hair dyes used before 1980 contained carcinogenic chemicals, modern hair dyes are generally considered safe. Current research shows no conclusive link between personal hair dye use and an increased risk of Leukemia or Lymphoma.

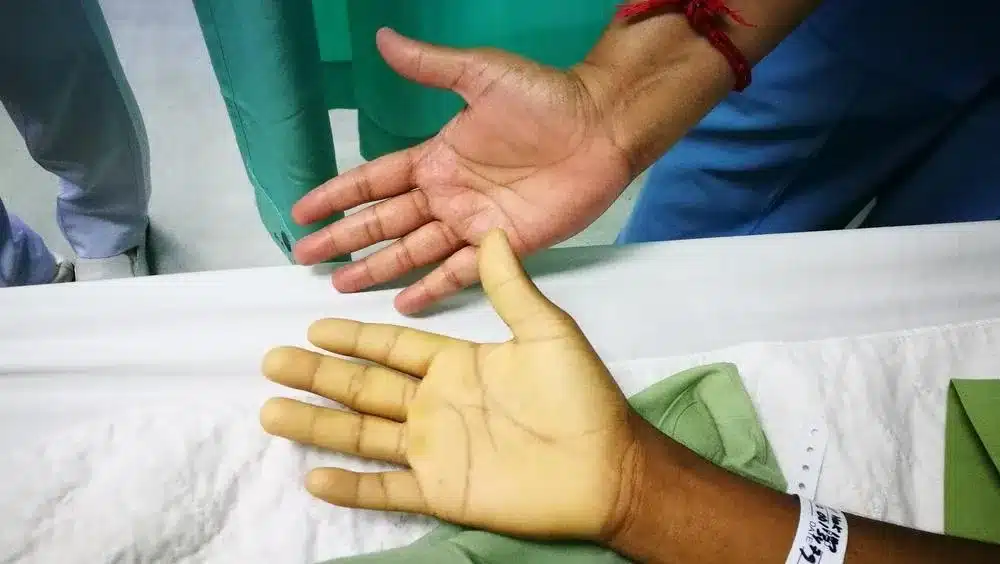
Are you always tired, dizzy, or have brittle nails? Poor iron absorption might be the reason. It’s a common issue that affects millions of people

The Rule of Three is key in hematology. It helps labs check if a complete blood count (CBC) is right. It says that if you
Iron deficiency affects nearly two billion people worldwide. It quietly harms health by reducing energy, thinking skills, and immune function. Unresolved deficiency can cause many

Iron deficiency is a common issue that can harm your health if not treated. Fixing it is complex, and how long it takes varies. This

Iron supplements are a common treatment for iron deficiency anemia. They can cause stomach problems. We will look into how iron supplementation and constipation are
The top 3 most common genetic diseases are sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, and thalassemia. Sickle cell disease alone impacts about 20-25 million people globally.

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)