Hematology focuses on diseases of the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
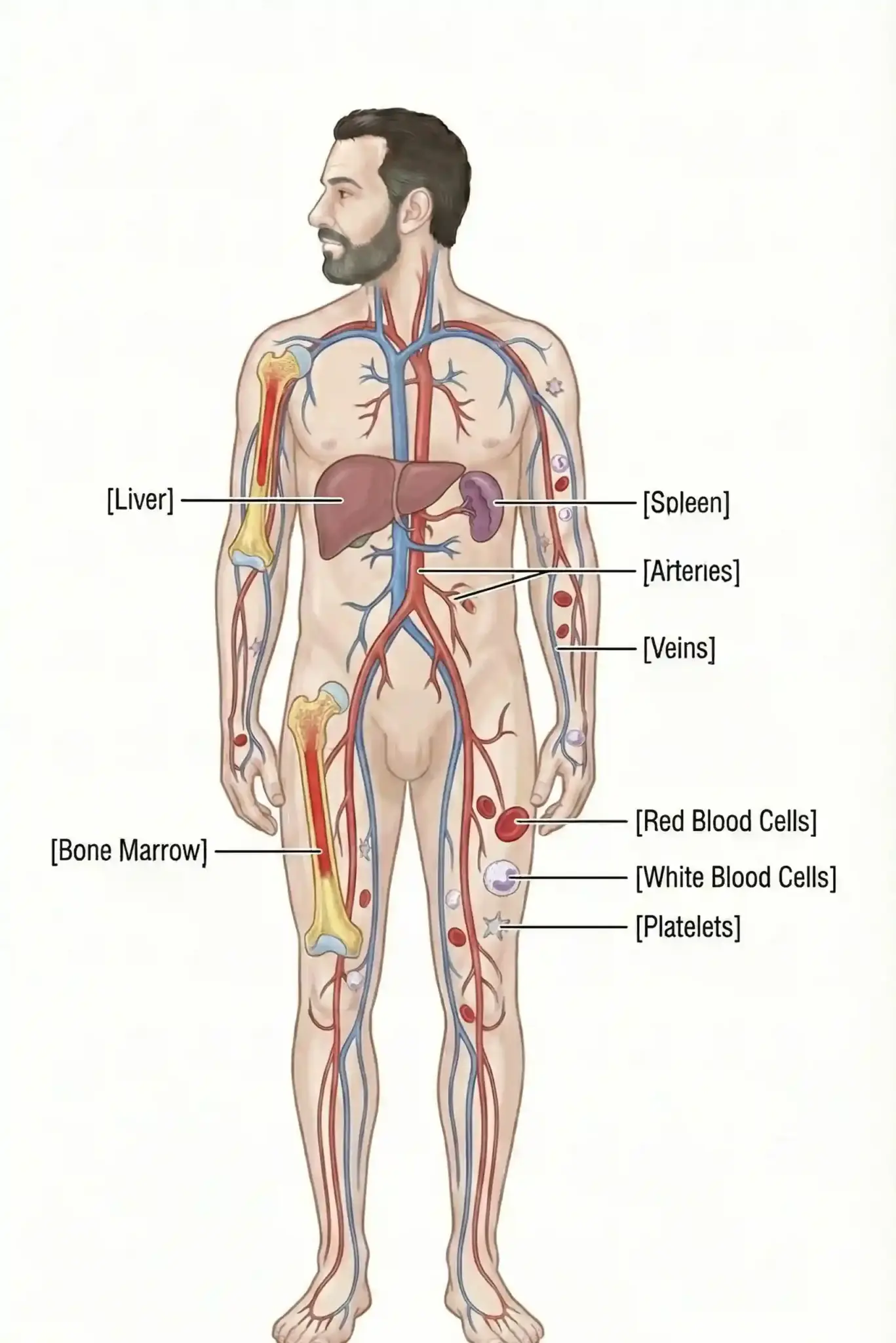
Hematology is the branch of medicine focused on studying, diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases of the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic system. Blood is vital for carrying oxygen and nutrients, fighting infections, and helping wounds heal. This field deals with conditions that affect red blood cells (which carry oxygen), white blood cells (which fight infection), and platelets (which help with clotting). Hematologists care for both non-cancerous conditions like anemia and hemophilia, and cancerous diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Since blood travels throughout the body, good blood health is essential for survival and a strong immune system.
Blood disorders happen when the body does not make or use blood cells properly. This can lead to too few cells (cytopenia), too many cells (cytosis), or blood cells that are shaped or work differently, as in sickle cell disease.

The Bone Marrow Transplant Unit has special HEPA-filtered rooms to keep patients with weak immune systems safe. There is also an advanced Apheresis Unit for collecting stem cells and a Flow Cytometry Lab that quickly and accurately identifies blood cancers.
Here’s an interesting fact: bone marrow makes about 500 billion blood cells every day. Because so many new cells are made so quickly, the blood system is very sensitive to treatments like chemotherapy that target dividing cells.

Blood diseases can affect the whole body. Anemia means there is not enough oxygen in the tissues, which causes tiredness and shortness of breath. Low platelets (thrombocytopenia) make bruising and internal bleeding more likely. Low white blood cell counts (neutropenia) leave the body open to serious infections. Cancerous cells can take over the bone marrow, stopping it from making healthy blood cells.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Several factors can increase the risk of blood disorders. Genetics is important, as in Thalassemia and Hemophilia. Exposure to chemicals like benzene or high levels of radiation can cause leukemia. Not getting enough iron or vitamin B12 can lead to anemia. Age also matters—some types of leukemia are more common in children, while others affect older adults.
Diagnosing blood conditions usually begins with a Complete Blood Count (CBC) and a Peripheral Blood Smear, where doctors look at blood cells under a microscope. If more information is needed, a Bone Marrow Biopsy is done to check the source of blood cell production. Genetic tests can also help find the exact mutation causing the disease.
A hematologist is both a pathologist and a clinician. They study blood cells under a microscope to diagnose diseases and then create treatment plans. Their job is to destroy cancer cells while helping the patient’s body make healthy new blood.
Treatments can be as simple as taking iron or vitamin supplements, or as complex as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. For some people with blood cancers or bone marrow failure, a stem cell or bone marrow transplant may be the only way to cure the disease.
The treatment journey depends on the condition. Chronic diseases often need regular check-ups. For cancers, treatment is more intense, starting with “induction” therapy to fight the disease, then “consolidation” therapy or a transplant. This process can mean long hospital stays, with support from blood transfusions and antibiotics.

Multidisciplinary approach: Highlight the collaboration. Hematologists work with Transfusion Medicine specialists, Radiation Oncologists, and Infectious Disease experts (critical during periods of low immunity). Psychologists provide support for the mental strain of long-term isolation and treatment.
Before treatment, patients should know about neutropenia, which means having low immunity. They need to follow strict hygiene rules, like wearing masks and avoiding crowds or raw foods, to prevent infections. It’s also important to talk about fertility options before starting chemotherapy. Support from family is key during recovery.
The success of hematologic treatment, especially bone marrow transplantation, relies heavily on the physical environment.
Liv Hospital adheres to the rigorous standards set by international hematology organizations. The center performs both autologous and fully matched/haploidentical allogeneic transplants. By combining cutting-edge therapies such as targeted agents and immunotherapy with world-class infection control and nursing care, Liv Hospital provides a sanctuary of healing for patients facing the most challenging blood disorders.
A hematologist treats a wide range of blood disorders, including anemia, clotting issues, bleeding disorders like hemophilia, and blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Anemia can range from mild to life-threatening. In contrast, mild cases often cause fatigue, and severe anemia can strain the heart and other organs, requiring prompt medical investigation to find the underlying cause.
A white blood cell count measures only immune cells, whereas a complete blood count (CBC) measures red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit.
The procedure involves local anesthesia to numb the area, so sharp pain is minimized, but patients often report feeling pressure or a dull ache during the extraction of the marrow sample.
Blood type is generally permanent, but in sporadic cases, such as after a bone marrow transplant or due to certain infections or cancers, a person’s blood type can appear to change.

Researchers are making big strides in understanding MDS. They’ve found out how normal bone marrow cells turn into myelodysplastic cells. This knowledge has led to
Myelodysplastic syndromes are disorders where blood cells don’t form right. Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) happens when the bone marrow can’t make healthy blood cells. It’s key
Myelodysplastic syndrome, or MDS, is a group of disorders that affect thousands worldwide. A diagnosis can be life-altering, and managing the condition requires a complete
In 2012, Robin Roberts, the famous anchor of Good Morning America, was diagnosed with Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS). This is a rare blood disorder that can
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) affects thousands of people worldwide. About 1 in 3 patients will develop acute myeloid leukemia. Knowing what to avoid is key to
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are disorders that affect how our bodies make healthy blood cells. They impact thousands of people globally. A diagnosis of MDS is

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)