Clinical Immunology focuses on the immune system’s health. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of allergies, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
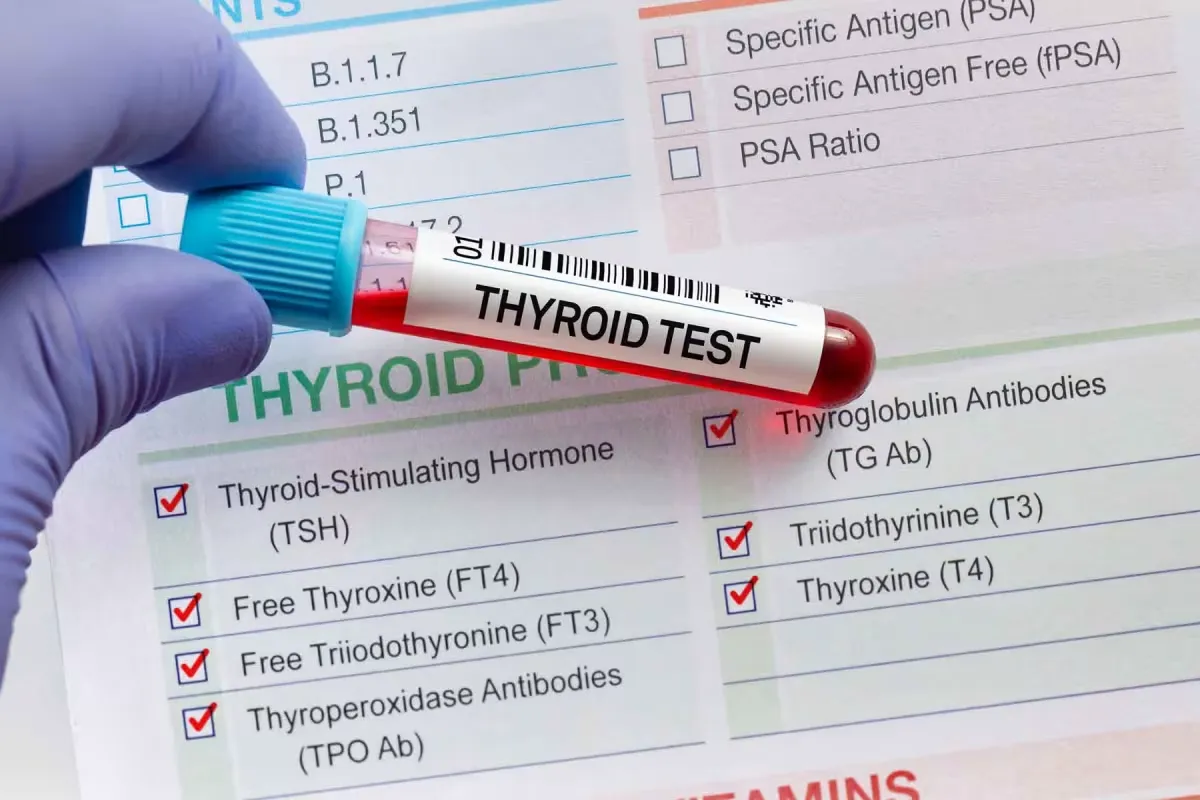
Diagnosing Hashimoto thyroiditis begins with routine blood tests to evaluate how well the thyroid gland is functioning. Because symptoms like fatigue and weight gain are non-specific, these tests are essential for establishing a medical cause.
While TSH and T4 show how the thyroid is functioning, advanced tests determine why it is failing. Identifying the autoimmune nature of the disease distinguishes Hashimoto’s from other forms of hypothyroidism.

An ultrasound is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of the thyroid gland. It does not use radiation.
Proper preparation helps ensure your test results are accurate.
Interpreting thyroid panels involves looking at the relationship between pituitary signals (TSH) and thyroid output (T4).
Routine imaging is not always necessary if blood tests clearly confirm the diagnosis. However, an ultrasound is recommended if:
While blood tests tell us how the thyroid is functioning, imaging tells us what the thyroid looks like. This structural assessment is vital for ruling out nodules or cancer.
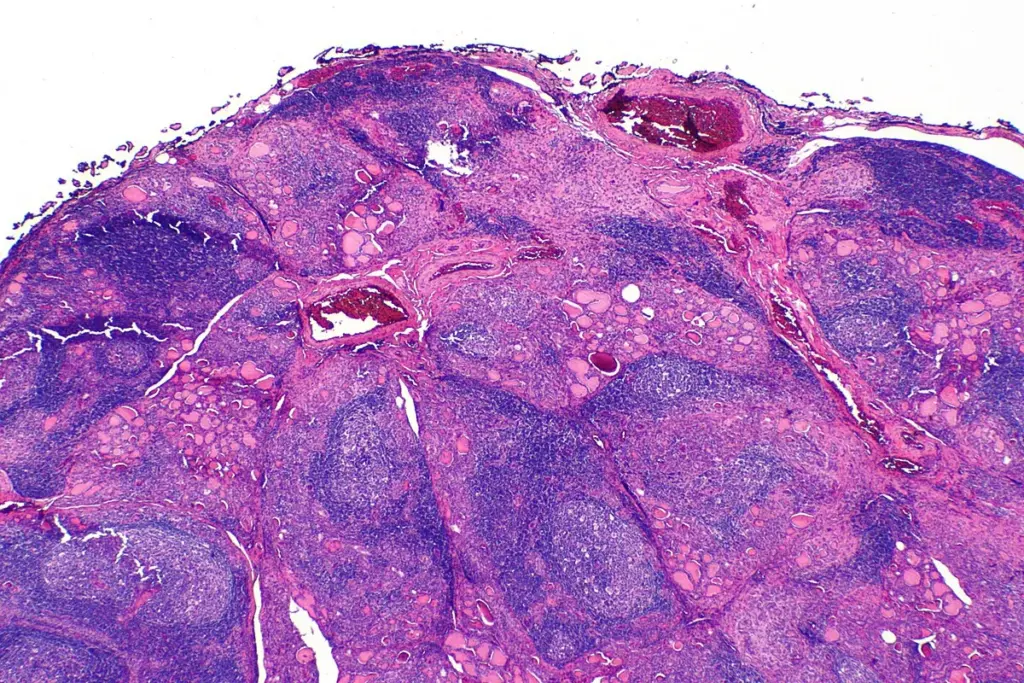
This is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create a picture of the thyroid gland. It is painless and radiation-free. In a healthy person, the thyroid appears smooth and uniform gray on the screen. In a patient with Hashimoto’s, the texture appears heterogeneous (patchy) and hypoechoic (darker).
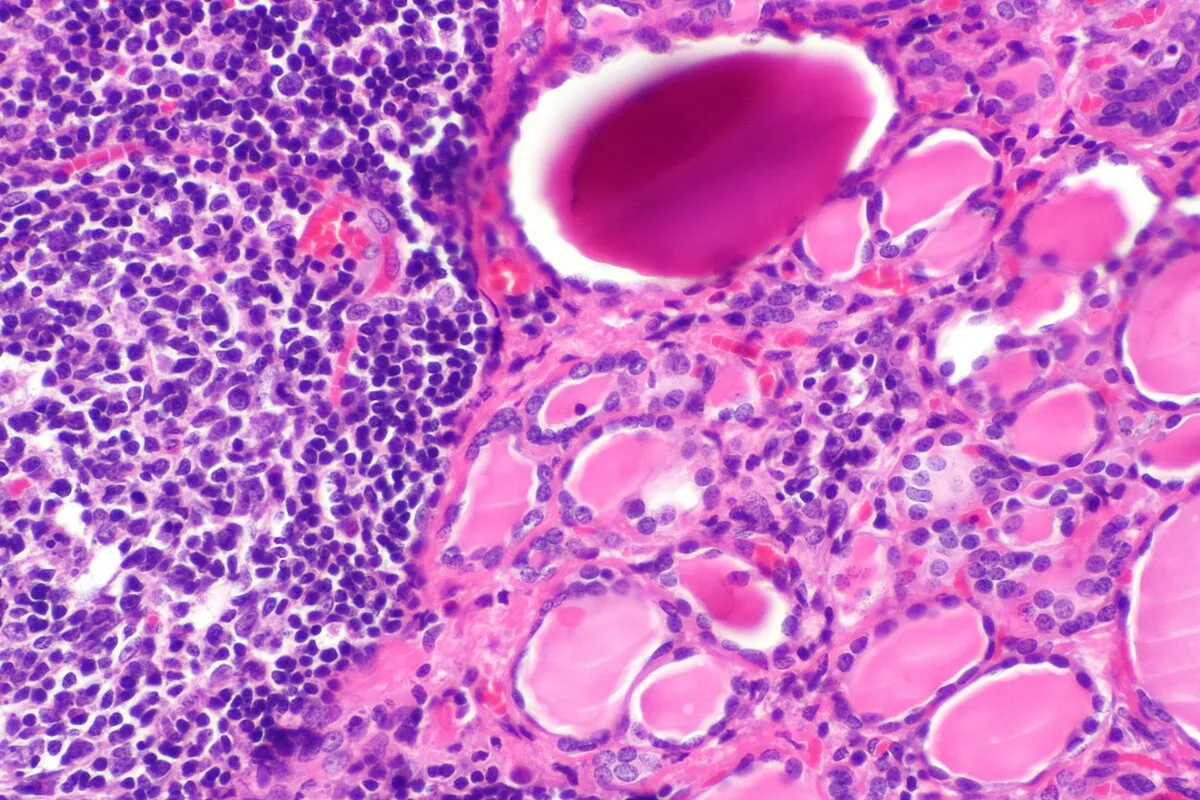
Radiologists often describe the appearance as moth-eaten or pseudonodular. This patchiness represents areas of lymphocytic infiltration (white blood cells invading the tissue) and fibrosis (scarring). An ultrasound can strongly suggest Hashimoto’s even if antibodies are negative. It is also critical for measuring the size of the gland to check for a goiter (enlargement) or atrophy (shrinkage).
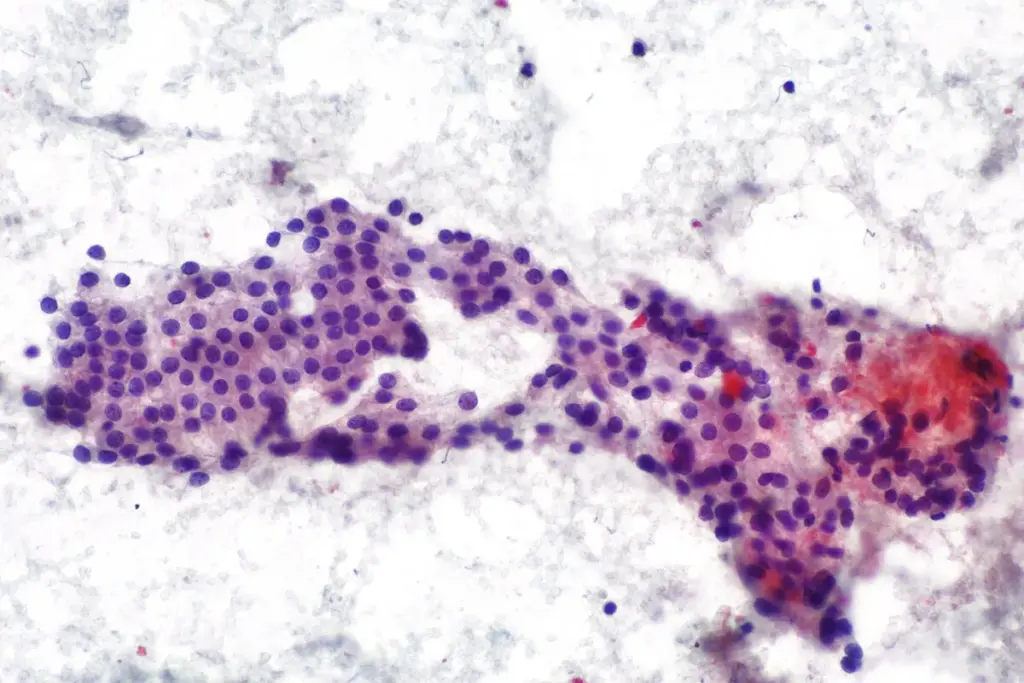
Biopsy is not routinely required to diagnose Hashimoto Thyroiditis. However, because Hashimoto’s increases the risk of developing thyroid nodules, an FNA may be performed if an ultrasound detects a suspicious lump. During this procedure, a very thin needle is inserted into the nodule to extract cells for microscopic examination to rule out thyroid cancer or lymphoma.


Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The primary tests are blood tests for TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) and Free T4 to check function, plus TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase) antibodies to confirm the autoimmune cause. Ultrasound is used to check for physical changes in the gland.
You generally do not need to fast. However, it is critical to stop taking biotin supplements (often found in hair and nail vitamins) at least 48 hours before the test, as biotin can distort the lab results.
No, a thyroid ultrasound is completely painless and non-invasive. It involves a probe gliding over the skin of your neck with some gel. There is no radiation involved.
The combination of high TSH and positive TPO antibodies is extremely accurate for diagnosing Hashimoto’s. About 90-95% of patients with Hashimoto’s will test positive for TPO antibodies.
A biopsy is usually not needed to diagnose Hashimoto’s itself. It is only required if an ultrasound finds a nodule (a distinct lump) within the thyroid that looks suspicious, to make sure it is not cancer.




Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)