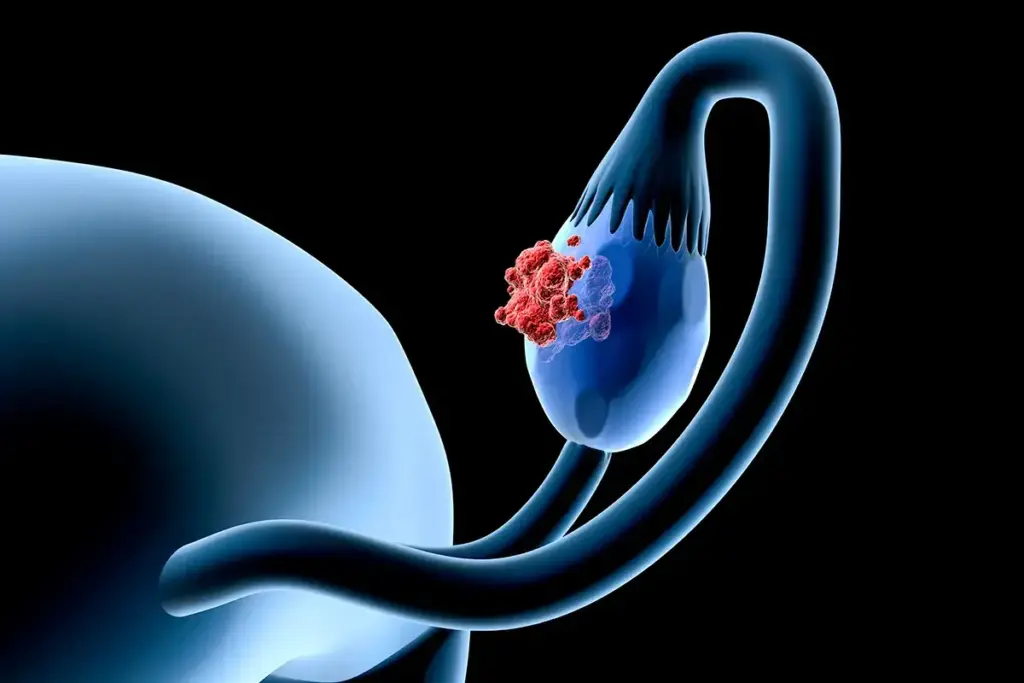
Testicular cancer is rare but common in young men, as studies show. This makes it key to know who’s at risk. We’ve found that some things can make a man more likely to get it.
Testicul cancer risk factors revealed. Learn amazing insights into who is at the highest risk and how to stay safe with early checks.
Being between 15 and 35 is a big risk factor. A family history of testicular cancer also matters a lot. Plus, having certain health issues can raise your risk too.
Key Takeaways
- Testicular cancer is most common in young men.
- Age is a significant risk factor for testicular cancer.
- A family history can increase the risk.
- Certain medical conditions are associated with a higher risk.
- Understanding risk factors is key for early detection.
Understanding Testicular Cancer and Its Impact

It’s important to know about testicular cancer for early detection and treatment. While testicular cancer is relatively uncommon overall, it is frequently diagnosed in men aged 15-35. We’ll look at what it is, its statistics, and why catching it early is key.
What is Testicular Cancer?
Testicular cancer happens when abnormal cells grow in the testicles. These testicles make sperm and testosterone. Testicular tumors can be harmless or dangerous, needing quick medical help.
There are different types of testicular cancer. Seminomas grow slowly and respond well to radiation. Non-seminomas grow faster and are more varied.
Key Statistics on Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer makes up about 1% of male cancers. In the U.S., hundreds of new cases are found each year. The survival rate for testicular cancer is high if caught early, showing why awareness and self-exams are important.
- Testicular cancer is most common in men aged 15-35.
- The incidence of testicular cancer has been rising over the past few decades.
- Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of testicular cancer is key for better treatment and survival. Men should do regular self-examinations to spot any unusual lumps or swelling. Prompt medical evaluation is vital if you notice any changes.
Knowing the symptoms of testicular cancer is important. Look out for a painless lump, swelling, or pain in the testicle or scrotum. This helps men take care of their health.
Common Risk Factors for Testicular Cancer
Knowing the common risk factors for testicular cancer helps men and doctors prevent and catch it early. Testicular cancer, like many cancers, is influenced by several factors.
Age and Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer often affects young and middle-aged men. It’s a top cancer in men aged 15 to 35, though it can happen at any age.
The American Cancer Society says the risk is highest in men aged 20 to 34. The risk slightly drops after 40.
Ethnicity and Genetic Factors
Ethnicity affects the risk of testicular cancer. Men of European descent face a higher risk than those of African or Asian descent.
Genetics also play a part. Certain genetic conditions, like Klinefelter syndrome, raise the risk of testicular cancer.
Family History and Hereditary Influences
A family history of testicular cancer is a big risk factor. Men with a father or brother who had testicular cancer are at higher risk.
|
Risk Factor |
Description |
Relative Risk |
|---|---|---|
|
Age |
Men between 20 and 34 years old |
Higher |
|
Ethnicity |
Men of European descent |
Higher |
|
Family History |
Having a father or brother with testicular cancer |
Significantly Higher |
It’s key to understand these risk factors for early detection and management of testicular cancer. Men with known risk factors should talk to their healthcare provider about their risk and screening options.
The Role of Cryptorchidism in Testicular Cancer Risk
It’s important to understand how cryptorchidism, or undescended testis, affects testicular cancer risk. This condition, where one or both testes don’t move down into the scrotum, is linked to a higher risk of testicular cancer in men.
Definition and Impact of Undescended Testis
Cryptorchidism is a birth defect that affects many male babies. Studies show that men with this condition are more likely to get testicular cancer. The exact reason for this increased risk is not clear, but it might be related to how the testes develop.
About 3% of full-term male babies have cryptorchidism, and up to 30% of premature males do. This condition can be one-sided or both-sided and often comes with other genital issues. While it often fixes itself by the first year, some cases need medical help.
Treatment and Surveillance Options
For cryptorchidism, doctors usually recommend surgery, called orchiopexy. This surgery moves the undescended testis into the scrotum. It’s usually done between 6 to 12 months old.
The surgery has many benefits:
- It lowers the risk of testicular torsion
- It can improve fertility
- It makes it easier to check for testicular problems through self-examination
Men with a history of cryptorchidism should also do regular testicular self-exams and see their doctor yearly. Some research suggests they might also benefit from ultrasound checks, but this isn’t always recommended.
—Oncologist
|
Condition |
Relative Risk of Testicular Cancer |
|---|---|
|
Cryptorchidism |
2.5-3 times higher |
|
Normal Testicular Development |
Baseline risk |
How Hormonal Factors Influence Risk
It’s important to know how hormonal imbalances can lead to testicular cancer. Hormonal factors, like testosterone levels and certain conditions, play a big role. They can increase the risk of getting testicular cancer.
Testosterone Levels and Their Effects
Testosterone is key for male reproductive health. Studies show that abnormal levels might raise the risk of testicular cancer. High levels of testosterone have been linked to a higher risk, but scientists are trying to understand why.
Testosterone is vital for the testes to work right. But, an imbalance can cause problems. Changes in testosterone, like during puberty, might affect the risk of testicular cancer.
Hormone-Related Conditions
Some hormone-related conditions can also change the risk of testicular cancer. For example, issues like hypogonadism or androgen insensitivity can affect the risk.
To understand how hormonal factors and testicular cancer risk are linked, let’s look at some data:
|
Hormonal Factor |
Association with Testicular Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
|
High Testosterone Levels |
Increased Risk |
|
Hormone-Related Conditions (e.g., Hypogonadism) |
Altered Risk Profile |
|
Androgen Insensitivity Disorders |
Increased Risk |
While there’s evidence that hormonal factors can increase testicular cancer risk, more research is needed. Scientists are working to understand how hormonal imbalances and related conditions contribute to testicular cancer.
Testicular Cancer in Young Men
Testicular cancer is most common in young men. Knowing its symptoms is key for early detection and treatment. It’s the most common cancer in men aged 15 to 35. Being aware of symptoms can greatly improve treatment outcomes.
Incidence Rates Among Adolescents
Medical research has focused on testicular cancer in young people. The rates have stayed relatively the same, with some changes in different groups.
Here are some key statistics:
|
Age Group |
Incidence Rate per 100,000 |
|---|---|
|
15-19 |
2.1 |
|
20-24 |
11.4 |
|
25-29 |
13.6 |
|
30-34 |
9.3 |
|
35-39 |
5.5 |
Symptoms to Watch For
It’s important for young men to know the symptoms of testicular cancer. Common signs include:
- A lump or swelling in the testicle
- A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- Pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum
- A sudden collection of fluid in the scrotum
Seek medical help if you notice any of these symptoms or if they worry you.
The Genetic Links to Testicular Cancer
Understanding the genetic roots of testicular cancer is key for early detection and treatment. We are starting to uncover how genetics and this disease interact.
Testicular cancer is shaped by both genetics and the environment. Some genetic mutations raise the risk of getting this cancer.
Specific Genetic Mutations
Research has found specific genetic mutations linked to testicular cancer. For example, changes in the KitLG gene are tied to germ cell tumors in the testicles. These are the most common type of testicular cancer.
Other genes, like DMRT1 and TERT, also play a role in testicular cancer. These discoveries help us understand the disease better. They also lead to new treatments.
Genetic Counseling and Testing
For those with a family history of testicular cancer or who have been diagnosed, genetic counseling and testing are helpful. We suggest men with a family history or risk factors get genetic counseling. It helps them understand their risks.
Genetic testing can spot specific mutations that raise testicular cancer risk. This info is key for making choices about monitoring, prevention, and treatment.
Genetic counseling also helps people grasp their test results. It lets them talk about what it means for their family. It explores ways to manage the situation.
Testicular Cancer and Infertility
Research shows a strong link between infertility and testicular cancer in men. This connection is key to understanding both conditions.
Correlation Between Infertility and Cancer Risk
Studies suggest men with infertility issues face a higher risk of testicular cancer. The exact reasons are unclear, but genetics and hormones are thought to play a part. Infertility and testicular cancer may share common underlying causes, like genetic mutations or testicular development issues.
“The connection between infertility and testicular cancer is a growing concern,” saysa leading researcher. “Understanding this link can help us identify at-risk men and reduce their risk through early intervention.”
Fertility Preservation Options
For men with testicular cancer, preserving fertility is a top concern. Several options are available, including sperm banking. Fertility preservation techniques have evolved significantly, giving hope to men who want to father children after cancer treatment.
- Sperm banking: A straightforward process where sperm is frozen and stored.
- Cryopreservation of testicular tissue: An emerging technique that may offer future fertility options.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): Techniques such as IVF and ICSI can help achieve pregnancy using preserved sperm.
We know a testicular cancer diagnosis is tough, both physically and emotionally. Knowing about fertility preservation options can help men make informed choices about their reproductive health.
Environmental Factors and Testicular Cancer
Environmental exposures are now seen as possible risk factors for testicular cancer. Looking into this disease, we find that some environmental elements might greatly affect its development.
Impact of Chemicals and Pesticides
Research shows that chemicals and pesticides might raise the risk of testicular cancer. Studies have shown that people exposed to these substances, either at work or in their environment, might face a higher risk of getting the disease.
Some pesticides can disrupt hormones, which could harm testicular health. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but research links certain chemical exposures to testicular cancer.
Occupational Exposure Risks
Certain jobs might increase the risk of testicular cancer due to harmful substance exposure. Workers in jobs involving pesticides, heavy metals, and certain industrial chemicals might be at higher risk.
- Agricultural workers exposed to pesticides
- Industrial workers handling chemicals and heavy metals
- Workers in environments with poor air quality or high levels of pollution
Knowing these occupational risks is key to creating ways to lower exposure. This could help reduce testicular cancer cases among workers in high-risk jobs.
Lifestyle Choices That May Affect Risk
Our daily habits and lifestyle choices can greatly affect our risk of testicular cancer. Some choices can help lower this risk, while others can increase it.
Diet and Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet is key for health, and it may also help lower testicular cancer risk. Foods rich in antioxidants, like fruits and veggies, are very beneficial.
Research shows that a diet lacking nutrients can raise the risk. So, it’s important to get enough vitamins and minerals.
Nutritional Elements to Consider:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
|
Nutritional Component |
Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Antioxidants (e.g., Vitamin C, E) |
Reduces oxidative stress |
|
Omega-3 fatty acids |
Anti-inflammatory effects |
|
Folate |
Essential for DNA synthesis and repair |
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and drinking too much alcohol are linked to many cancers. Studies are looking into how they affect testicular cancer risk. But, avoiding or limiting these habits can help keep you healthy and might lower cancer risk.
Smoking is bad for health and quitting can help lower cancer risk.
Impact of Smoking and Alcohol:
- Smoking: Associated with increased risk of various cancers
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: May increase cancer risk and impact overall health
By living a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding harmful habits, you can lower your risk of testicular cancer.
Screening and Prevention Strategies
Screening and prevention are key in fighting testicular cancer. Regular check-ups and self-exams can lower the risk of advanced cancer. This is important for men’s health.
Seeing a doctor regularly is vital for early detection. A doctor can check for testicular issues during these visits. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Guidelines for Regular Check-Ups
Men, even those at lower risk, should get regular check-ups. The timing depends on individual risk factors. But, an annual check-up is usually a good start.
- Talk to your doctor about your risk factors to set up check-up times.
- Make sure your doctor does a thorough testicular exam during your visit.
Self-Examinations: How to Perform Them
Self-exams are a simple way to check testicular health. Men should do these monthly to know their testicles’ normal feel.
- Do the self-exam after a warm bath or shower when your scrotum is relaxed.
- Gently roll each testicle between your thumb and fingers to check for any lumps, swelling, or pain.
- If you find any issues, see your healthcare provider right away.
Medical experts say, “Regular self-exams and check-ups can help detect testicular cancer early” (Source: Medical research papers). By following these steps, men can protect their health.
Conclusion: Reducing Your Risk
Knowing the risks of testicular cancer is key to catching it early and treating it well. We’ve looked at what can increase your risk, like family history, hormones, and the environment.
Being aware and educated helps lower your risk of testicular cancer. By knowing the risks and acting early, you can greatly reduce your chance of getting it. Regular self-checks and doctor visits are important steps to prevent it.
Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
Learning about your health is powerful. By understanding testicular cancer, its risks, and the need for early detection, men can lower their risk and get better results.
Accessing Support and Information
If you want more info or support, there are many places to turn. Groups like the American Cancer Society offer lots of help. They have info on self-checks, treatments, and stories from survivors.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of testicular cancer?
Symptoms include a painless lump or swelling on the testicle. You might also feel a heavy feeling in the scrotum. Or, there could be a dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin.
What does a testicular cancer lump feel like?
A testicular cancer lump is usually painless. It feels like a hard, smooth mass inside the testicle. It can be small or quite large.
Is it normal for one testicle to be larger than the other?
Yes, it’s normal for one testicle to be slightly bigger. But, a big size difference or a new lump could mean a problem.
What is cryptorchidism, and how does it relate to testicular cancer?
Cryptorchidism, or undescended testis, is when a testicle doesn’t move into the scrotum. Men with this condition are at higher risk for testicular cancer.
Can testicular cancer be inherited?
There’s no clear inheritance pattern. But, men with a family history of testicular cancer are at higher risk. Certain genetic mutations can also increase the risk.
How can I reduce my risk of testicular cancer?
There’s no sure way to prevent testicular cancer. But, knowing the risk factors, doing regular self-exams, and getting check-ups can help find it early.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help reduce the risk of testicular cancer?
Eating well, not smoking, and drinking less alcohol can help your overall health. But, their direct effect on testicular cancer risk is being studied.
How often should I perform self-examinations for testicular cancer?
Do self-exams monthly, best after a warm bath or shower. This is when the scrotum is relaxed, making it easier to check for abnormalities.
What should I do if I find a lump or abnormality during a self-examination?
If you find a lump or abnormality, see a healthcare professional right away. They can evaluate and advise you.
Can testicular cancer be treated if caught early?
Yes, testicular cancer is highly treatable if caught early. Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer.
What are the treatment options for testicular cancer?
Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. These are used alone or together, based on the cancer’s stage and type.
Will having testicular cancer affect my fertility?
Testicular cancer and its treatment can affect fertility. Talk to a healthcare provider about preserving fertility before treatment.
Are there any resources available for men with testicular cancer?
Yes, there are many resources. These include support groups, counseling services, and online information. They help men with testicular cancer and their families.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10145700/























