Sickle cell disease is known as the most painful blood disorder. It affects millions of people around the world. This genetic condition changes the shape of red blood cells, causing them to get stuck in small blood vessels. This leads to episodes of intense pain, known as pain crises. Sickle cell anemia causes intense pain. Explore proven relief methods and treatment options to help manage this difficult blood disorder.
Living with sickle cell disease is tough, with severe pain episodes happening often. The says over 100,000 people in the U.S. have this condition. This shows how important it is to have good care and support.
Key Takeaways
- Sickle cell disease is identified as the most painful blood disorder.
- It is a genetic condition affecting red blood cells.
- Over 100,000 people in the U.S. live with this condition.
- Recurring episodes of severe pain are a hallmark of the disease.
- Comprehensive care and support are key for managing it.
The Nature of Pain in Blood Disorders
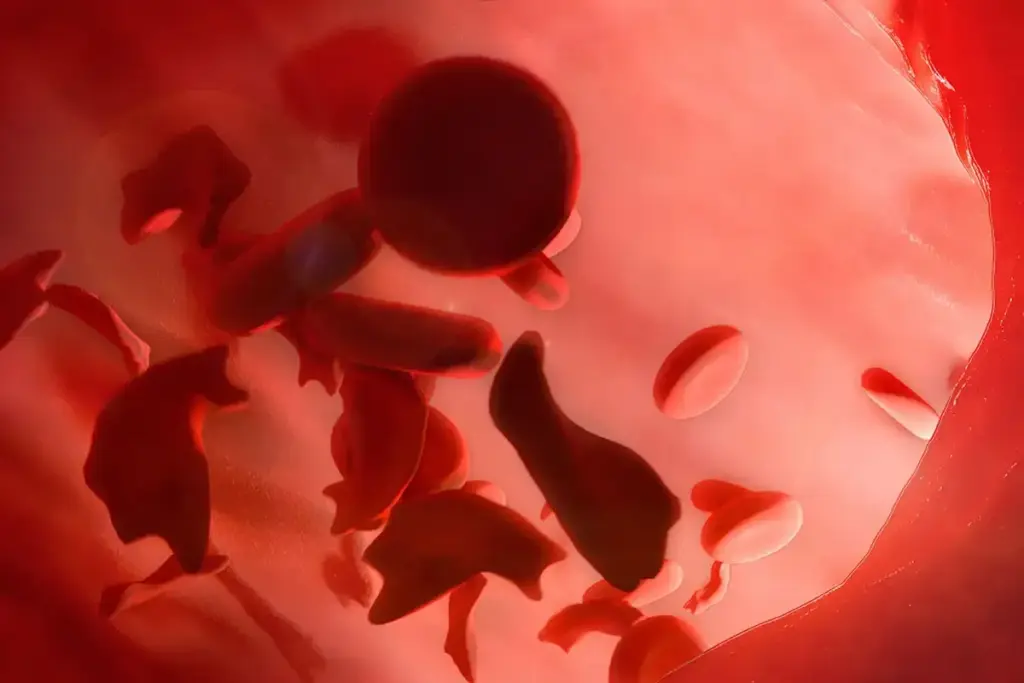
It’s key to understand pain in blood disorders to manage it well. Blood disorders are many and each has its own pain pattern.
How Blood Disorders Cause Pain
Pain in blood disorders comes from different sources. This includes the clotting process, blockages in blood vessels, and inflammation. For example, sickle cell disease causes pain because sickle-shaped red blood cells block small blood vessels. This leads to tissue not getting enough blood and pain.
Measuring and Comparing Pain Severity
Measuring pain is hard because it’s personal. But, tools and scales help us understand pain levels. Below, we compare pain levels in different blood disorders.
|
Blood Disorder |
Pain Severity |
Characteristics of Pain |
|---|---|---|
|
Sickle Cell Disease |
Severe |
Acute episodes of pain due to vaso-occlusion |
|
Polycythemia Vera |
Moderate |
Headaches, fatigue, and itching |
|
Aplastic Anemia |
Variable |
Pain due to bone marrow failure and associated complications |
Understanding the extent and sources of pain caused by blood disorders is essential for doctors in creating effective treatment plans. They can then create better treatments to help patients.
Sickle Cell Anemia: The Most Painful Blood Condition
Sickle cell anemia is a very painful blood disorder. We will look at what it is and how it works. We’ll also talk about the sickled red blood cells that make it so bad.
Definition and Basic Mechanism
Sickle cell anemia comes from a gene problem. It affects the beta-globin part of hemoglobin. This leads to sickle hemoglobin, or HbS, which changes when it’s not full of oxygen.
When HbS changes, red blood cells turn into a crescent moon shape. These cells are stiff and break down easily. This causes pain, anemia, and more infections because the spleen doesn’t work right.
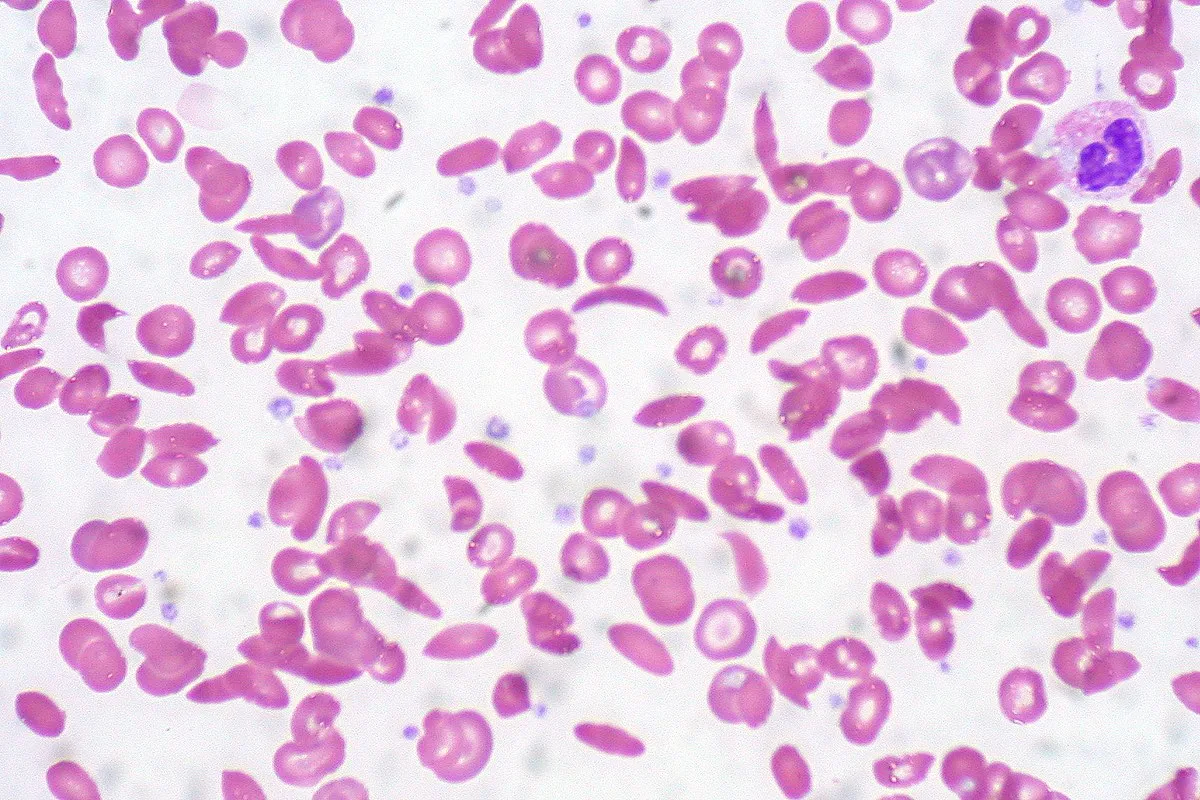
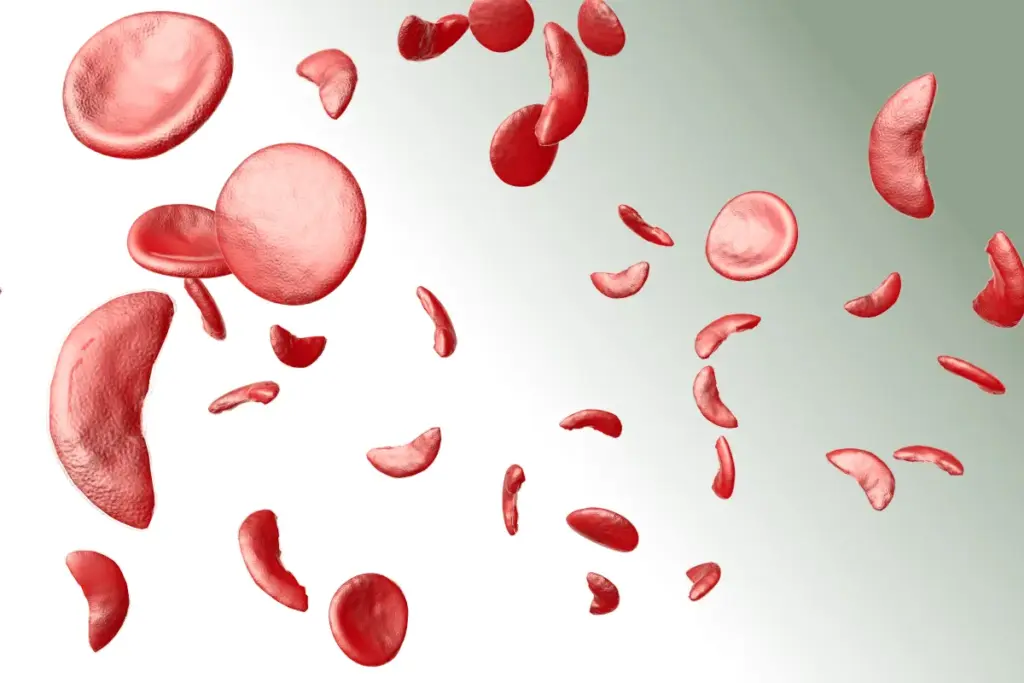
The Crescent Moon Shape of Sickled Cells
The crescent moon shape of sickled cells is key to sickle cell anemia. It happens when HbS changes under low oxygen. These cells can’t move well and get stuck in small blood vessels.
This causes blockages and damage to tissues. It’s a big part of why sickle cell anemia is so painful.
|
Characteristics |
Normal Red Blood Cells |
Sickled Red Blood Cells |
|---|---|---|
|
Shape |
Disk-shaped |
Crescent moon shape |
|
Flexibility |
Highly flexible |
Less flexible |
|
Hemoglobin |
Normal hemoglobin (HbA) |
Abnormal hemoglobin (HbS) |
Vaso-Occlusive Crises: Understanding the Excruciating Pain
Vaso-occlusive crises are a key part of sickle cell disease, causing severe pain. These episodes happen when sickled red blood cells block blood vessels. This blockage leads to tissue ischemia and pain. We will look into the details of these crises, including what triggers them, how long they last, and how intense they are.
What Happens During a Pain Crisis
During a vaso-occlusive crisis, sickled red blood cells pile up in small blood vessels. This blocks blood flow, causing tissue ischemia and severe pain. The pain can spread across the body, hitting areas like the back, chest, and limbs. A patient once said,
“The pain is like nothing I’ve ever experienced before; it’s as if my bones are being crushed.”
Duration and Intensity of Pain Episodes
The length of a vaso-occlusive crisis can vary, lasting from hours to days. The pain is often very intense, needing hospital care and strong pain management. We know managing these episodes is key, and for more info, visit and resources.
These crises come and go, making life unpredictable for those with sickle cell disease. Knowing when and how long a crisis will last is hard. Effective management strategies are vital to lessen the impact of these episodes.
Triggers That Initiate Pain Crises
Several things can start a vaso-occlusive crisis, like dehydration, infection, and extreme temperatures. Knowing these triggers is key to preventing or reducing pain crises. By managing these triggers, people with sickle cell disease can cut down on how often and how bad these episodes are.
For instance, drinking enough water is important, as dehydration can trigger a crisis. Also, quickly treating infections and avoiding extreme temperatures can help prevent these episodes. We stress the need for proactive care in managing sickle cell disease.
The Unique Pain Experience of Sickle Cell Patients
Patients with sickle cell disease have a unique pain experience. This pain is complex and affects both their physical and mental health. It’s different from other blood disorders.
Acute vs. Chronic Pain Patterns
Sickle cell disease causes both acute and chronic pain. Acute pain happens when sickled red blood cells block blood vessels. This leads to tissue ischemia and pain.
Chronic pain comes from ongoing inflammation and organ damage. The mix of acute and chronic pain makes managing pain a challenge. It needs a treatment plan that covers both immediate and long-term needs.
Patient Testimonials About Pain Severity
Patient stories give us a glimpse into the pain of sickle cell disease. Many say their pain is unbearable and interferes with their daily life. It affects their quality of life greatly.
“The pain is like nothing I’ve ever experienced before. It’s as if someone is tightening a vice around my bones.” – Anonymous Patient
The Cyclical Nature of Sickle Cell Pain
The pain from sickle cell disease comes in cycles. Patients have periods of acute pain followed by calm times. This cycle makes it hard to predict when pain will strike again. It causes anxiety and stress.
|
Pain Characteristics |
Acute Pain |
Chronic Pain |
|---|---|---|
|
Cause |
Vaso-occlusive crises |
Ongoing inflammation and organ damage |
|
Duration |
Variable, often sudden onset |
Long-term, persistent |
|
Impact |
Immediate, severe pain |
Ongoing discomfort, reduced quality of life |
It’s important to understand the cyclical nature of sickle cell pain. Using technology, like mobile health apps, can help. Healthcare providers can then monitor patients closely and act early to lessen pain crises.
Comparing Sickle Cell to Other Painful Blood Disorders
<image4>
Sickle cell disease is known for its pain, but it’s not alone. Other conditions like aplastic anemia, polycythemia vera, and Castleman disease also cause pain. Learning about these can help us understand pain in blood disorders better.
Aplastic Anemia Pain Profile
Aplastic anemia makes it hard for the bone marrow to make blood cells. This leads to fatigue, infections, and bleeding. While pain isn’t the main symptom, some people might feel pain from infections or bleeding. Managing pain in aplastic anemia usually means treating the cause, like infections or bleeding.
Polycythemia Vera and Pain Symptoms
Polycythemia vera makes too many red blood cells, making blood thick and prone to clotting. Pain can come from clots or an enlarged spleen. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, and itching, along with pain.
Castleman Disease Pain Manifestations
Castleman disease is rare and involves too many immune cells, causing lymph nodes to grow. Pain happens when these nodes press on nearby things. Treatment aims to shrink the nodes to ease pain and other symptoms.
The Clotting Cascade and Pain in Various Blood Disorders
The clotting process is key in pain for many blood disorders. Conditions like polycythemia vera and sickle cell disease affect clotting, causing pain. Knowing about the clotting cascade helps manage pain in these disorders. Circle Medical and others are finding new ways to handle pain in these complex cases.
The Genetic Basis of Sickle Cell Disease
<image5>
Sickle cell disease comes from a mutation that changes hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is key for carrying oxygen in red blood cells.
This change makes abnormal hemoglobin, or sickle hemoglobin. It causes red blood cells to bend into a sickle shape under stress.
Inheritance Patterns and Gene Flow
Sickle cell disease follows an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a person needs two copies of the HBB gene defect to have the disease.
Gene flow of the sickle cell trait is shaped by migration and malaria. The trait helps protect against malaria.
Gene flow is key in spreading the sickle cell trait among different groups.
Homozygous Definition and Implications
Being homozygous for the sickle cell gene means having two mutated HBB genes.
This leads to full sickle cell disease symptoms.
Those homozygous for the sickle cell gene often face severe symptoms and complications.
Sickle Cell Traits vs. Full Disease
Carrying the sickle cell trait is different from having the full disease.
Carriers have one normal and one mutated HBB gene. They usually don’t show full disease symptoms but can pass the mutated gene to their kids.
- Carriers are mostly healthy but might face health issues under certain conditions.
- Those with full disease experience frequent pain and serious health problems.
Epidemiology and Economic Impact of Sickle Cell Disease
<image6>
Sickle cell disease is a big problem worldwide. It affects how our bodies make hemoglobin, leading to sick red blood cells. This can cause a lot of health problems, like pain and damage to organs.
The number of people with sickle cell disease varies a lot. In the United States, about 100,000 people are affected.
Prevalence in the United States
In the U.S., sickle cell disease hits African Americans hard. It affects about 1 in 365 of them. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says thousands of babies are screened for it every year.
For more info on blood disorders, like sickle cell disease, check out.
Global Distribution Patterns
Worldwide, sickle cell disease is a big problem. It’s common in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, and parts of India. The World Health Organization (WHO) says hundreds of thousands of kids are born with it every year, mostly in Africa.
Healthcare Costs Exceeding $1.7 Million Per Patient
Most of this money goes to hospital stays for pain and other problems.
A study found that caring for sickle cell disease costs a lot. It shows we need better care and ways to prevent more problems to save money.
“The economic burden of sickle cell disease is not just a financial issue; it’s also a significant emotional and social burden on families and communities.”
It’s important to understand sickle cell disease to make better healthcare plans. This can help lessen its impact on people and the economy.
Comprehensive Sickle Cell Disease Symptoms Beyond Pain
Sickle Cell Disease is more than just pain. It affects many areas of a person’s health. This includes symptoms that make daily life very hard.
Bone and Joint Complications
Bones and joints are often hurt by Sickle Cell Disease. This can cause chronic pain and make it hard to move. Joint pain and swelling are common, making things even tougher.
Chest Pain and Acute Chest Syndrome
Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) is very serious. It causes chest pain, fever, and breathing problems. ACS can be deadly and needs quick medical help.
Organ Damage from Repeated Crises
Repeated sickling can harm organs like the spleen, kidneys, and liver. Splenic sequestration can cause severe anemia and even death if not treated fast. This damage can lead to long-term health problems.
Impact on Daily Functioning and Quality of Life
Sickle Cell Disease symptoms greatly affect daily life. Patients struggle to do normal things, go to school or work, and enjoy social events.
“Living with Sickle Cell Disease is a constant battle, not just against pain, but against the myriad of complications that affect every aspect of life.”
Having a strong support system and good care is key. It helps patients deal with these challenges and improve their well-being.
Diagnosis and Monitoring of Sickle Cell Disease
Early detection is key in managing sickle cell disease. It starts with newborn screening. This disease affects how red blood cells are made, causing them to curve like a sickle. Doctors use tests and genetic analysis to find the sickle cell gene.
Newborn Screening Programs
Newborn screening is essential for catching sickle cell disease early. A simple blood test is done when the baby is 24 to 48 hours old. This test looks for abnormal hemoglobin, which might show sickle cell disease or the sickle cell trait. Finding it early helps manage the disease better, improving the child’s life.
Blood Tests and Genetic Analysis
After newborn screening, blood tests and genetic analysis are important. Blood tests check for hemoglobin S levels. Genetic testing finds the mutations that cause sickle cell disease. This info helps with family planning and managing the disease.
Using Mobile Health Technology for Monitoring
Mobile health technology, like Impact Mobile, helps monitor sickle cell disease. It lets patients track symptoms and medication. Doctors can then adjust treatment plans, helping patients get better faster.
“The integration of mobile health technology into the management of sickle cell disease represents a significant advancement in patient care, enabling more personalized and responsive treatment strategies.”
Using these tools, doctors can give better care to sickle cell disease patients. This improves their quality of life and health outcomes.
Current Pain Management Approaches for Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is complex, needing a mix of treatments for each patient. This approach helps manage pain effectively.
Managing pain well is key to a better life for those with sickle cell disease. We’ll look at different methods, like medicines and non-medical ways, and special care plans.
Pharmacological Pain Control Strategies
Medicines are a big part of treating sickle cell disease pain. Opioids are used for bad pain, but they must be watched closely because of addiction risks. Non-opioid analgesics, like NSAIDs, help with less severe pain. Also, hydroxyurea can cut down on pain episodes.
|
Medication Type |
Use in Sickle Cell Disease |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Opioids |
Severe pain crises |
Effective for acute pain relief |
|
NSAIDs |
Mild to moderate pain |
Reduces inflammation and pain |
|
Hydroxyurea |
Reducing pain crises frequency |
Decreases sickling episodes |
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management
There are also non-medical ways to handle sickle cell disease pain. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and relaxation therapy help patients deal with ongoing pain. Exercise, when safe, and using heat or cold packs also help.
Circle Medical and Other Specialized Care Models
Places like Circle Medical give full care to sickle cell disease patients. They team up doctors, pain experts, and mental health workers for a complete care plan. They also use apps to keep an eye on patients and adjust treatments as needed.
By mixing medicines, non-medical methods, and special care, doctors can give tailored pain care to sickle cell disease patients.
Living with the Most Painful Blood Disorder
Living with sickle cell disease is tough. It brings unpredictable pain and emotional ups and downs. People with this disease face physical pain and mental health issues too.
Mental Health Challenges of Chronic Pain
Pain crises can really mess with your mind. Anxiety and depression are common. These feelings come from the constant fear of pain.
Key mental health challenges include:
- Anxiety related to pain crises
- Depression stemming from chronic pain and lifestyle limitations
- Stress from managing a complex medical condition
Support Systems and Resources
Having a strong support system is key. This includes family, friends, and healthcare providers. Also, support groups and resources like counseling help a lot.
Effective support systems may involve:
- Regular check-ins with healthcare providers
- Participation in support groups for shared experiences and advice
- Family and friends who understand the condition and can offer emotional support
Navigating Daily Life with Unpredictable Pain
Managing daily life with sickle cell disease is a challenge. It’s about balancing pain management, staying healthy, and doing normal things. Being ready for pain crises is important.
Strategies for daily life include:
- Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Having a pain management plan in place
- Being aware of triggers that can initiate pain crises
Advances in Sickle Cell Research and Treatment
Sickle cell disease research has seen big leaps forward. This has led to new ways to treat the condition. Thanks to these advances, managing sickle cell disease is changing for the better.
Gene Therapy Breakthroughs
Gene therapy is a new hope for sickle cell disease. It aims to fix the genetic issue causing the disease. Early trials show promising results, with patients seeing big improvements.
Novel Pain Management Approaches
Dealing with pain is key in sickle cell disease care. New methods, like non-drug treatments and targeted therapies, are being tested. These aim to lessen pain crises, making life better for patients.
Promising Clinical Trials
Many clinical trials are underway for sickle cell disease. They’re looking at gene editing and new drugs. These trials could bring safer, more effective treatments in the future.
|
Treatment Approach |
Description |
Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Gene Therapy |
Corrects genetic mutation causing sickle cell disease |
Potential cure, reduced pain crises |
|
Novel Pain Management |
Non-pharmacological and targeted therapies |
Improved pain relief, enhanced quality of life |
|
Gene Editing Technologies |
Precise editing of genes to correct mutations |
Potential for long-term cure, minimal side effects |
Conclusion
Sickle cell disease is a complex condition marked by chronic pain. It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand it well. This disease affects how the body makes hemoglobin, leading to abnormal red blood cells.
These abnormal cells can cause blockages and other serious issues. A detailed look at sickle cell disease shows its big impact on daily life. It can lead to constant pain, more infections, and damage to organs.
Managing sickle cell disease requires a team effort. This includes using medicines and other methods to control pain. It also means regular check-ups and support for those affected.
In summary, sickle cell disease is a tough condition that needs more research and better treatments. By covering the main points of this disease, we stress the need for full care and ongoing support. We must keep looking for new ways to help patients with sickle cell disease.
FAQ
What is sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder. It affects how red blood cells make hemoglobin. This causes them to have an abnormal ‘sickle’ shape. It leads to health issues like pain, anemia, and infections.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell disease?
Symptoms include pain episodes, anemia, and infections. It can also cause bone and joint problems, chest pain, and damage to organs.
How is sickle cell disease diagnosed?
It’s diagnosed through newborn screening, blood tests, and genetic analysis. Mobile health technology, like Impact Mobile, is also used for monitoring.
What is a vaso-occlusive crisis?
A vaso-occlusive crisis happens when sickled red blood cells block blood vessels. This leads to tissue ischemia and pain. These episodes can vary in duration and intensity.
How is pain managed in sickle cell disease?
Pain management includes pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies. Specialized care models, like Circle Medical, are also used. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual’s needs.
What is the difference between having the sickle cell trait and sickle cell disease?
Having the sickle cell trait means carrying one abnormal gene. It doesn’t usually cause the full disease but can pass it to offspring. Sickle cell disease occurs when an individual has two abnormal genes, one from each parent.
What are the economic implications of sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease is costly for healthcare systems. Costs can exceed $1.7 million per patient over their lifetime.
Are there any new treatments or research for sickle cell disease?
Yes, there are ongoing research and new treatments. This includes gene therapy breakthroughs, novel pain management approaches, and promising clinical trials.
How does sickle cell disease affect daily life?
It can significantly impact daily functioning and quality of life. It causes unpredictable pain episodes, organ damage, and other complications. It requires a lot of care and support.
What is the significance of being homozygous for the sickle cell gene?
Being homozygous for the sickle cell gene means having two copies of the abnormal gene. This results in the full manifestation of sickle cell disease. It’s different from being a carrier with one normal and one abnormal gene.
How does gene flow affect the prevalence of sickle cell disease?
Gene flow can spread the genes associated with sickle cell disease to different populations. This can affect its prevalence.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024, May 15). Data and statistics on sickle cell disease. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/data.html CDC
- Medical News Today. (n.d.). Rare blood disorders. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/rare-blood-disorders
- DKMS UK. (n.d.). Blood cancer / types of blood disorder. https://www.dkms.org.uk/learn-more/blood-cancer/types-of-blood-disorder
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (n.d.). Sickle cell disease. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sickle-cell-disease
- Vejlstrup, A., et al. (2019). Release of active peptidylarginine deiminase into the circulation during cardiac surgery and its association with thrombosis. [Journal Name]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6549760/ PMC
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11427447/