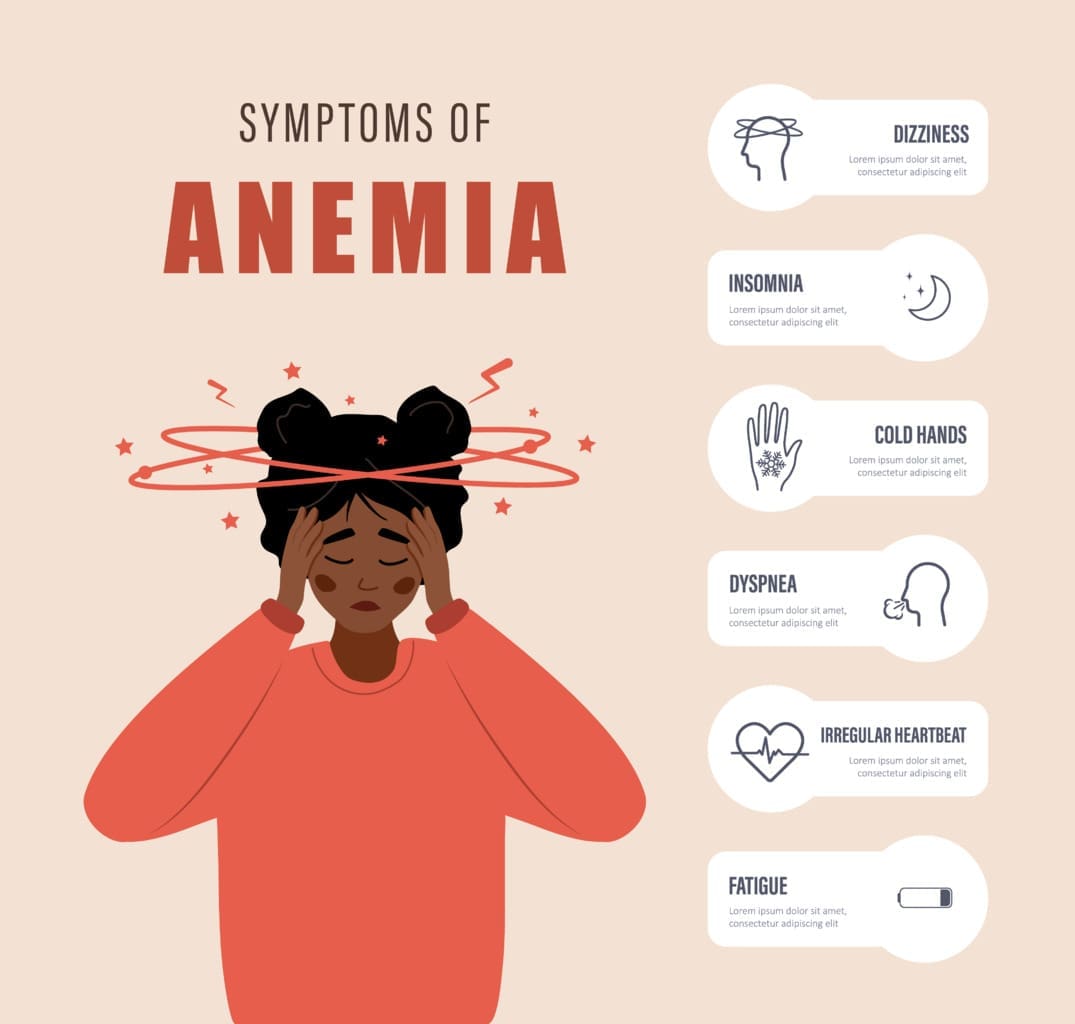
At Liv Hospital, we know how worrying it is to feel tired all the time and have low red blood cells. These signs might mean something serious, like cancer. Anemia is a big problem for cancer patients, making their life harder and affecting their treatment.
Anemia can make you feel very tired, weak, dizzy, and pale. The American Cancer Society says anemia is a big deal for cancer patients. It’s important to know the main anemia cancer symptoms and get help when you need it.
Key Takeaways
- Anemia is a common condition in cancer patients, impacting their quality of life.
- Recognizing key anemia cancer symptoms is important for early detection.
- Symptoms like persistent fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and paleness should not be ignored.
- Seeking medical attention is vital if you experience these symptoms.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing complete care and support for international patients.
Understanding the Connection Between Anemia and Cancer
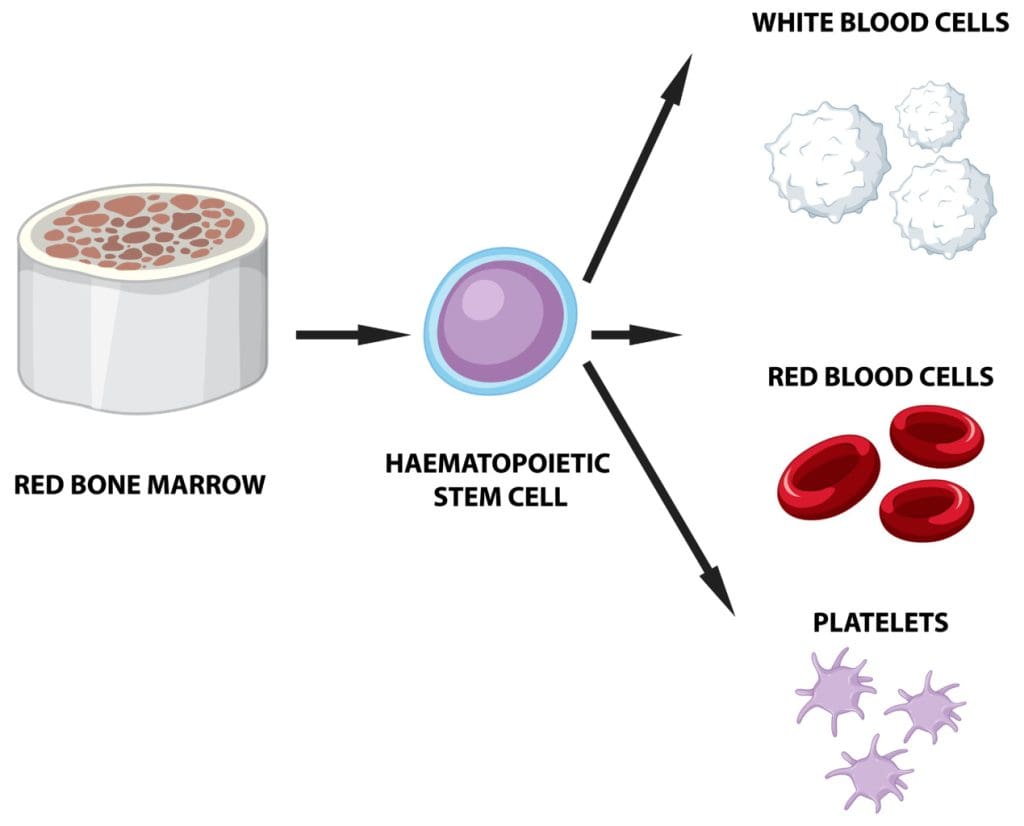
Anemia in cancer patients is a big deal. It’s when there aren’t enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This can really hurt a patient’s life and how well they can be treated.
What is Anemia and How Does it Relate to Cancer?
Anemia means your body has too few red blood cells or they don’t carry enough hemoglobin. This makes it hard for your body to get enough oxygen. Cancer can cause anemia by messing with the bone marrow, causing more blood loss, or making inflammation that lowers red blood cell production.
For example, some cancers like leukemia directly harm the bone marrow. Other cancers, like those in the gut, can cause a lot of blood loss, leading to anemia.
The Prevalence of Anemia in Cancer Patients
Anemia is common in cancer patients. It really affects their life quality and how well they can be treated. How common anemia is depends on the cancer type, its stage, and the treatments used.
| Type of Cancer | Prevalence of Anemia |
|---|---|
| Blood Cancers (Leukemia, Lymphoma) | High |
| Gastrointestinal Cancers | Moderate to High |
| Other Cancers | Variable |
Knowing how common and why anemia is in cancer patients is key. It helps manage the condition better and improves patient results.
Recognizing Key Anemia Cancer Symptoms

It’s important to spot anemia symptoms in cancer patients early. This can help improve their treatment and care. Anemia often shows as fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and paleness in those with cancer. Knowing these signs is key to getting them the right medical help.
Physical Manifestations: Fatigue, Weakness, and Paleness
Fatigue is a common sign of anemia in cancer patients. It makes everyday tasks hard. It’s often paired with weakness and a lack of energy. Also, anemia can make someone look pale because of fewer red blood cells.
Colon cancer can also lead to anemia. This can cause dizziness and shortness of breath. These symptoms can really hurt a cancer patient’s quality of life.
Cognitive and Circulatory Symptoms
Anemia in cancer patients can also affect the mind. It can make it hard to focus and remember things. Circulatory symptoms include rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath, even when resting. This is because the body doesn’t get enough oxygen with fewer red blood cells.
It’s important to remember that anemia is common in cancer patients. But it can also mean there’s cancer. For example, low iron levels might point to colon cancer. So, if you keep feeling anemic, see your doctor.
Understanding anemia symptoms in cancer patients helps us care for them better. Early treatment can greatly improve their life during cancer treatment.
How Cancer Causes Anemia: The Biological Mechanisms
It’s important to know how cancer leads to anemia. This is because cancer affects the body in many ways. It can harm the production and life of red blood cells.
Bone Marrow Disruption in Cancer
Cancer can harm the bone marrow, where red blood cells are made. Metastatic cancer cells can get into the bone marrow and mess with its work. This can lower the number of red blood cells made, causing anemia.
Some cancers, like leukemia and lymphoma, start in the bone marrow. They can stop blood cells from being made. We’ll look at this more later.
Increased Blood Loss in Certain Cancers
Some cancers make you lose more blood, leading to anemia. For example, colorectal cancer can bleed in the digestive tract. Cervical or uterine cancer can cause vaginal bleeding.
- Cancers that cause internal bleeding
- Tumors that lead to chronic blood loss
- Cancer treatments that affect blood clotting
These situations mean you lose more red blood cells than your body can make. This leads to anemia.
Inflammation and Reduced Red Blood Cell Production
Cancer can also make your body inflamed. This inflammation can lower how many red blood cells are made. Inflammatory cytokines can stop the hormone that helps make red blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Chronic inflammation reduces erythropoietin production
- Inflammatory cytokines affect iron metabolism
- Reduced red blood cell lifespan due to inflammation
This shows how cancer, inflammation, and anemia are all connected. It’s why treating cancer-related anemia needs a full approach.
Types of Cancer Most Commonly Associated with Anemia
Knowing which cancers often lead to anemia is key to early treatment. Anemia is when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. It can really affect a cancer patient’s life. Some cancers are more likely to cause anemia because of how they work.
Blood Cancers: Leukemia, Lymphoma, and Multiple Myeloma
Blood cancers like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma often cause anemia. Leukemia can crowd out healthy blood cells, leading to anemia. Lymphoma affects the immune system and can also cause anemia by filling up the bone marrow. Multiple myeloma affects plasma cells and can stop the bone marrow from working right.
Gastrointestinal Cancers and Chronic Bleeding
Gastrointestinal cancers, like colon cancer, can lead to anemia because of ongoing bleeding. This bleeding can be either visible or hidden. Studies show that colon cancer is a big reason for iron deficiency anemia because of blood loss in the gut.
Other Cancers That May Present with Anemia
Other cancers can also cause anemia. This includes cancers that spread to the bone marrow and mess with blood cell production. Anemia in these cancers can mean the disease is advanced or the bone marrow is heavily involved.
| Cancer Type | Mechanism Leading to Anemia | Prevalence of Anemia |
|---|---|---|
| Leukemia | Bone marrow infiltration | High |
| Colon Cancer | Chronic bleeding | Common |
| Multiple Myeloma | Suppression of normal bone marrow | Frequent |
Some cancers are more likely to cause anemia, making it important for doctors to watch for it. Catching and treating anemia early can really help patients do better.
The Relationship Between Low Iron Levels and Cancer Risk
Low iron levels can be a sign of cancer. It’s important to know how iron deficiency is linked to cancer. This helps in early detection and treatment.
Iron Deficiency Anemia as a Potent Warning Sign
Iron deficiency anemia means the body doesn’t have enough iron. This is because it can’t make enough hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
This condition can point to problems like colon cancer. Chronic bleeding in the colon can cause iron deficiency.
Research shows iron deficiency anemia can signal some cancers early. For example, it can be a sign of colon cancer or other cancers in the gut.
How Cancer Treatments Can Affect Iron Levels
Cancer treatments can lower iron levels. Surgeries that remove parts of the gut can affect iron absorption. This can lead to deficiency over time.
Chemotherapy and radiation can also harm the gut lining. This can reduce iron absorption. It’s key to watch iron levels in cancer patients to avoid anemia.
Understanding the link between low iron and cancer helps us spot at-risk patients. We can then offer the right care. This includes treating cancer and managing iron deficiency anemia to improve outcomes.
Interpreting Blood Test Results: When to Be Concerned
It’s important to understand your blood test results to catch health problems early. Blood tests can show a lot about your health, like signs of anemia and its link to cancer. We’ll help you understand your blood test results, focusing on key signs and what they might mean for your health.
Understanding RBC and Hemoglobin Counts
Red Blood Cell (RBC) count and hemoglobin levels are key in blood tests. RBC count shows how many red blood cells you have. Hemoglobin is a protein in these cells that carries oxygen. Low counts can mean anemia, which might be linked to cancer.
Normal ranges for these tests vary slightly between laboratories but generally:
- RBC count: approximately 4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter for men and 3.90-5.03 million cells per microliter for women.
- Hemoglobin: about 13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter for men and 12-16 grams per deciliter for women.
What Low Blood Counts Might Indicate
Low RBC or hemoglobin counts can mean health issues, like anemia. Anemia can be a sign or side effect of cancer or its treatments. Studies show that abnormal blood test results, including low counts, can point to cancer or other health problems. Always talk to your healthcare provider to understand your test results.
| Condition | RBC Count | Hemoglobin Level |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 4.32-5.72 million/μL (men) | 13.5-17.5 g/dL (men) |
| Normal | 3.90-5.03 million/μL (women) | 12-16 g/dL (women) |
| Anemia | Below normal range | Below normal range |
Other Blood Markers That May Suggest Cancer
Other blood markers can also show cancer. These include tumor markers, substances made by cancer or in response to it. While not sure on their own, they help when looked at with other tests and symptoms.
Working closely with your healthcare provider is key to understanding your blood test results. If you’re worried about your results or have symptoms, get medical advice right away.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Anemia Symptoms
Don’t ignore persistent anemia symptoms. Knowing when to see a doctor is key for your health. Anemia might signal a serious issue that needs medical care. We’ll talk about red flags for seeking help and how to tell if anemia is linked to cancer.
Red Flags That Should Not Be Ignored
Certain anemia symptoms need immediate medical attention. These include:
- Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath or dizziness
- Chest pain or rapid heartbeat
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, see a healthcare professional right away. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Distinguishing Between Cancer-Related and Other Types of Anemia
Not all anemia is cancer-related. But, some signs might point to a higher risk. These include:
- Family history of cancer
- Age, as the risk of many cancers increases with age
- Previous cancer diagnosis or treatment
- Unexplained changes in blood counts
Talk to your healthcare provider about your risk factors and anemia symptoms. They can figure out the cause and suggest the right tests or treatments.
Remember, anemia can be a sign of cancer, but it often points to other treatable conditions. Getting medical help will help find the cause and guide the right treatment.
Treatment Approaches for Cancer-Related Anemia
Treating anemia in cancer patients is a complex task. It involves managing both the anemia and the cancer itself. This approach is key to improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Medical Interventions for Anemia in Cancer Patients
Medical treatments for anemia in cancer patients aim to boost red blood cell count and ease symptoms. Iron supplementation is often used to treat iron deficiency, a common cause of anemia. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) also help by stimulating red blood cell production. Sometimes, blood transfusions are needed to quickly increase red blood cell count and relieve severe anemia symptoms.
A complete treatment plan may also include addressing the cancer itself. This can involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the cancer type and stage. Treating the cancer can also help alleviate anemia symptoms.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Supplementation | Oral or intravenous iron to address deficiency | Increases red blood cell production, alleviates fatigue |
| Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs) | Medications that stimulate red blood cell production | Reduces need for blood transfusions, improves anemia symptoms |
| Blood Transfusions | Transfusion of red blood cells to quickly increase count | Rapidly improves anemia symptoms, enhances quality of life |
Liv Hospital’s Multidisciplinary Approach to Cancer Care
At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch, ethical care for international patients. Our team of oncologists, hematologists, nutritionists, and supportive care specialists work together. They create personalized treatment plans for cancer patients with anemia.
Our approach includes thorough diagnostic evaluations to find the causes of anemia and cancer. We use the latest treatments, including advanced iron supplementation, ESAs, and blood transfusions. Our supportive care team also provides nutritional counseling and symptom management to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
We aim to improve patient outcomes by integrating cancer treatment with anemia management. Our commitment to delivering world-class healthcare ensures our patients receive the best care possible.
Conclusion: Managing Concerns About Anemia and Cancer
It’s key to understand how anemia and cancer are linked. We’ve seen how anemia can signal cancer, often due to bleeding or bone marrow issues. This knowledge is vital for catching cancer early and treating it well.
Spotting anemia’s signs like tiredness, weakness, and pale skin can lead to cancer diagnosis sooner. While anemia might not always mean cancer, some cancers do cause it. This makes it important to watch for these symptoms.
Knowing about anemia and cancer symptoms is critical. Anemia can be a side effect of cancer. If you keep feeling tired or weak, see a doctor. They can find out why you’re feeling this way.
By tackling anemia and cancer concerns, people can improve their health. Doctors can also give better care. Liv Hospital shows how treating anemia in cancer patients is possible with the right approach.
Does low red blood cells mean cancer?
Low red blood cells, or anemia, can hint at cancer. But, it’s not the only reason. We must look deeper to find the real cause.
Can anemia be a sign of cancer?
Yes, anemia can point to cancer. Some cancers, like blood cancers and those in the gut, can lead to anemia.
Can cancer cause anemia?
Yes, cancer can lead to anemia. It does this by affecting the bone marrow, causing more blood loss, and through inflammation.
What types of cancer are most commonly associated with anemia?
Blood cancers, like leukemia and lymphoma, and some gut cancers are often linked to anemia.
Is low iron a symptom of cancer?
Low iron levels might signal certain cancers, like those in the gut.
Can low iron be a sign of cancer?
Yes, low iron can be a cancer warning sign. Look out for fatigue, weakness, and paleness too.
How do I interpret blood test results for anemia?
We check RBC and hemoglobin counts for anemia. Low counts mean anemia. Then, we look for the cause.
When should I seek medical attention for anemia symptoms?
See a doctor if you feel tired, weak, or pale. Don’t ignore persistent or severe symptoms.
What is the treatment for cancer-related anemia?
Treatments include iron supplements, blood transfusions, and tackling the cancer itself.
Is anemia a symptom of blood cancer?
Yes, anemia is common in blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
Can a low blood count mean cancer?
A low blood count might suggest cancer. But, it’s not the only reason. We must find the real cause.
Is anaemia a sign of cancer?
Yes, anaemia can be a cancer sign. Look for fatigue, weakness, and paleness too.
Is iron deficiency a sign of cancer?
Iron deficiency anemia might warn of certain cancers, like those in the gut.
References
- Healthline. (n.d.). Anemia and cancer: What you need to know. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/cancer/anemia-cancer
- WebMD. (n.d.). Cancer and anemia. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/cancer/cancer-and-anemia
- MD Anderson Cancer Center. (n.d.). Anemia and cancer: physical and emotional effects. Retrieved from https://www.mdanderson.org/patients-family/diagnosis-treatment/emotional-physical-effects/anemia-cancer.html
- Patient Power. (n.d.). What cancer types cause low hemoglobin? Retrieved from https://www.patientpower.info/navigating-cancer/what-cancer-types-cause-low-hemoglobin
- UPMC Hillman Cancer Center. (n.d.). Anemia in patients. Retrieved from https://hillman.upmc.com/patients/community-support/education/miscellaneous/anemia-in-patients




































