Last Updated on October 21, 2025 by
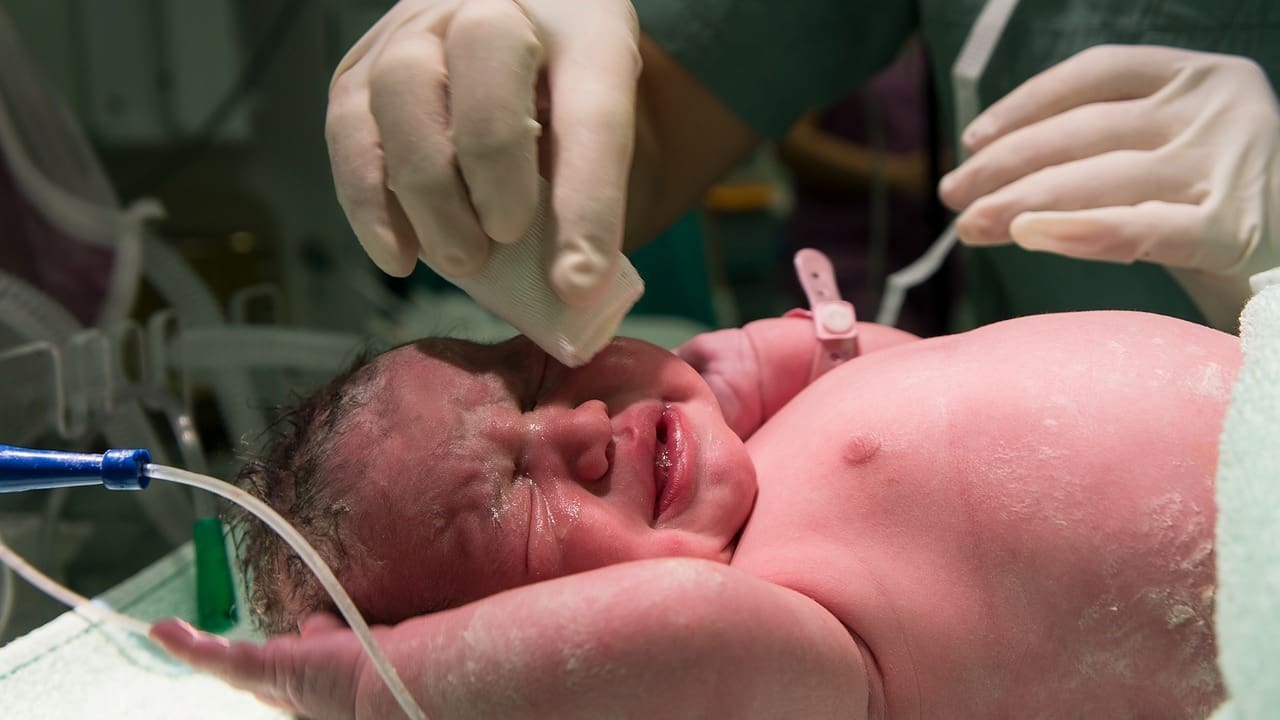
Medical technology has made cord blood transplants much more successful. This has given hope to patients all over the world. In the U.S., over 246,500 cord blood units have been registered. This has led to more than 7,550 unrelated blood stem cell transplants every year.
The global cord blood banking industry is now worth over $6.8 billion. Almost 5 million units are stored worldwide.
At Liv Hospital, we understand how important cord blood transplants are. Our focus on patients sets new standards in healthcare. We offer full support to those looking for advanced medical treatments.
Umbilical cord blood was once seen as waste. Now, it’s valued for its healing powers. It’s packed with stem cells that can turn into many blood cell types. This makes it a key tool for treating serious diseases like leukemia and immune disorders.
Cord blood stem cells are primitive cells that can become different blood cell types. They’re vital for fixing the blood system after a transplant. Their power to regenerate and repair damaged tissues opens new ways to treat diseases.
Getting cord blood is safe, painless, and easy. It’s done by clamping the umbilical cord and taking the blood into a special bag. The blood is then tested, processed, and frozen for future use.
| Process | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Cord Blood Collection | Safe and non-invasive extraction after birth | Ensures availability of stem cells |
| Testing and Processing | Laboratory analysis and preparation | Determines viability and quality |
| Cryopreservation | Freezing for long-term storage | Preserves stem cells for future use |
Understanding cord blood stem cells and how they’re collected and stored shows their value in medicine. It’s a life-saving option for those needing umbilical cord blood transplant treatments.
The journey of umbilical cord blood transplants is filled with medical breakthroughs. The first successful stem cell transplant happened in 1958. This marked the start of a new chapter in transplant medicine.
Cord blood became a key source of stem cells in the late 1980s. This was the beginning of a new era in treating diseases.
The use of cord blood for transplants started with its discovery as a stem cell source. The first cord blood transplant was done in 1988. This opened doors for more research and advancements.
Important steps included setting up cord blood banks. Also, standardizing how to collect and store it.
Now, cord blood transplants help treat serious diseases like leukemia and lymphoma. They also help with genetic disorders. The ability to save cord blood for later use is a big plus for families.
has improved patient outcomes. This is a big win for those needing these transplants.
Research keeps going, opening up new ways to use cord blood. This could lead to new treatments for many health issues.
The global cord blood banking industry has hit a big milestone, going over $6.8 billion in value. This huge growth shows how much people now value cord blood stem cells for medical treatments.
The industry’s growth isn’t just about money; it’s also about more cord blood units being stored. Almost 5 million units are stored worldwide now. This shows a big increase in people wanting to save cord blood for future medical needs.
Several economic factors are pushing this growth. More people are learning about the power of cord blood stem cells in treating diseases. This has led to more parents choosing to bank their cord blood. Also, better medical tech and higher cord blood transplant success rates have helped the industry grow.
A leading expert in the field said, “The progress in cord blood banking and transplants has opened new ways to treat serious diseases.” This view is shared by the increasing need for cord blood banking services worldwide.
These factors together help the industry grow strong. It’s now a key player in the global healthcare scene.
The U.S. has a huge collection of cord blood units, with over 246,500 units ready for use. This large number comes from both public and private cord blood banks across the country.
In the U.S., cord blood banking is mainly split into public and private options. Public banks collect donations for anyone needing a transplant. On the other hand, private banks keep the blood for the donating family’s use. Public banking helps increase the registry’s diversity, while private banking offers a personal stem cell source for families who can afford it.
Even with so many units, finding a match can be hard. The registry mainly has donations from people of European descent. This makes it tough for those from minority groups to find a suitable match.
The cost of banking cord blood varies a lot. Public banking is free, but private banking can be pricey, with both initial and yearly fees. Insurance coverage also varies, sometimes covering some or all costs. Families thinking about cord blood banking need to consider these costs and the possible benefits.
Every year, over 7,550 unrelated blood stem cell transplants happen worldwide. This shows how these treatments are becoming more common for serious diseases.
These transplants are used for many health issues. Here’s how they’re spread out:
| Disease Category | Percentage of Total Transplants |
|---|---|
| Blood Cancers | 55% |
| Blood Disorders | 25% |
| Immune System Disorders | 15% |
| Metabolic Disorders | 5% |
The success of these transplants changes with each condition. Studies show that success rates have gone up. Some conditions see better results than others.
“The advancement in transplant technology and donor matching has significantly improved patient outcomes.”
Finding the right donor is key for these transplants. It’s important to know the eligibility criteria for bone marrow transplants. Waiting times have gotten shorter thanks to better matching technology.
Knowing about the success and use of these transplants helps both patients and doctors. It aids in making better treatment choices.
Umbilical cord blood transplants are a key treatment for many serious diseases. The success of these transplants depends on the disease being treated.
Cord blood transplants work well for some types of leukemia and lymphoma. For acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the survival rate can be 40% to 60%. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) also sees success rates around 30% to 50%.
Cord blood transplants are also promising for immune disorders like severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Success rates for these conditions can reach 80% to 90%, depending on the disorder and the patient’s health.
For rare genetic diseases, cord blood transplants might be a lifesaver. While there’s less data, some studies show success rates of 50% to 70%.
| Disease Type | Success Rate Range |
|---|---|
| Leukemia (ALL) | 40% – 60% |
| Leukemia (AML) | 30% – 50% |
| Immune Disorders (SCID) | 80% – 90% |
| Rare Genetic Diseases | 50% – 70% |
These success rates highlight the value of umbilical cord blood transplants for many serious conditions. As research grows, we can look forward to even better results.
Cord blood transplants are safer because they have a lower risk of immune incompatibility. This makes them a good choice for those needing a stem cell transplant. It’s key to the transplant’s success and helps avoid complications.
Cord blood stem cells are different from bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cells. They are immunologically naïve, meaning they are less likely to cause a strong immune reaction. This reduces the risk of problems.
The naivety of cord blood stem cells means there’s a lower chance of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). GVHD is when the donor’s immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues. This makes cord blood transplants safer for those at high risk of GVHD.
The immunological naivety of cord blood stem cells is a big plus. These cells haven’t seen antigens before, so they’re less likely to cause an immune reaction. This makes cord blood transplants safer for treating many diseases.
In summary, the lower risk of immune incompatibility with cord blood transplants is a big reason they’re becoming more popular. Knowing the benefits of cord blood stem cells helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment.
Cord blood stem cells can treat over 80 diseases, giving hope to patients everywhere. This is a big plus of umbilical cord blood transplant compared to other stem cell therapies. These cells can turn into many types, helping with a wide range of health issues.
Cord blood stem cells are often used for blood disorders and cancers. This includes leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. They can fix the blood system, making them great for these diseases. Studies show cord blood stem cell treatments work well for blood cancers.
Immune system problems, like SCID, can also be treated with cord blood stem cells. These cells replace bad immune cells with good ones. This helps kids with these conditions a lot.
Cord blood stem cells are also used for metabolic and storage disorders. This includes Hurler syndrome and Krabbe disease. They replace missing enzymes or cells, easing symptoms.
As research grows, more diseases will be treatable with cord blood stem cells. This is good news for patients and doctors. The success stories show how important cord blood stem cell transplant is in medicine today.
Recent studies have shown great promise in using cord blood transplants for kids with neurological disorders. This is a big deal because it gives hope to children with these conditions.
We’re seeing a big change in treating neurological disorders in kids. This is thanks to new technology in cord blood transplants. These transplants could greatly improve the lives of kids with severe neurological conditions.
Cerebral palsy is a condition where cord blood transplants are showing a lot of promise. Studies show that cord blood stem cells can help improve motor function and cognitive abilities in kids with cerebral palsy. These stem cells might help repair damaged brain tissues.
Research on using cord blood transplants for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is also showing good results. Early clinical trials suggest that cord blood therapy can improve social and communication skills in kids with ASD. These early findings are very encouraging.
Researchers are also looking into using cord blood transplants for other neurological disorders.
“The versatility of cord blood stem cells makes them an exciting area of research for a wide range of neurological conditions,”
As we learn more about cord blood transplants, it’s clear they hold a lot of promise. They could greatly improve outcomes for kids with neurological disorders. The future of cord blood therapy looks very promising, with ongoing research and trials leading to new treatments.
Families often wonder if they’ll need a stem cell transplant before their child turns 20. This question is key when deciding to bank their child’s cord blood. Studies show the chance of needing a transplant by age 20 is 0.06%.
The chance of needing a stem cell transplant depends on many things. This includes genetics and the environment. Even though the overall chance is 0.06%, each person’s situation can be different.
Some factors can make it more likely you’ll need a stem cell transplant. These include:
Knowing these risk factors can help families decide about cord blood banking.
When thinking about cord blood banking, families should consider the benefits and costs. They should understand their child’s risk factors and the use of cord blood stem cells in the future.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Probability |
|---|---|
| Family History | Increases likelihood |
| Genetic Predispositions | May significantly increase likelihood |
| No Known Risk Factors | 0.06% probability |
By knowing these factors and the statistical likelihood, families can make informed decisions about cord blood banking. This ensures it’s the right choice for them.
Cord blood transplantation is on the verge of a new era. New technologies are leading the way. The field of regenerative medicine is growing, opening up new uses for cord blood.
New methods are being developed to make cord blood transplants better. For example, scientists are working on ways to grow more cord blood cells ex vivo. This could lead to more successful transplants.
Cord blood stem cells are being studied for treating many conditions. They might help with neurological disorders like cerebral palsy. Early results are encouraging.
Many clinical trials are testing cord blood transplants in different situations. A summary of these studies is in the table below:
| Condition | Trial Status | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Cerebral Palsy | Ongoing | Improved motor function |
| Autism Spectrum Disorder | Recruiting | Enhanced cognitive development |
| Leukemia | Active | Increased survival rates |
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see big changes in cord blood transplantation. This will bring new hope to patients all over the world.
We’ve looked into umbilical cord blood transplants and their role in today’s medicine. The cord blood transplant success rate is key to their effectiveness. We’ve discussed seven important points, like the size of the cord blood banking industry and its uses.
The future looks bright for umbilical cord blood transplant procedures. Research and new technologies are making them more promising. As we move forward in regenerative medicine, cord blood transplants will likely play a bigger role. This could bring new hope to many patients.
Knowing these facts helps people make better choices about cord blood banking and transplants. It’s vital to keep researching and investing in this field. This way, we can unlock the full power of umbilical cord blood transplants.
The success rate of umbilical cord blood transplants varies. It depends on the disease, patient factors, and the cord blood unit’s quality. Studies show cord blood transplants can be as effective as bone marrow transplants in some cases.
Cord blood transplants have lower risks of immune problems and graft-versus-host disease than bone marrow transplants. While success rates vary, cord blood is a good alternative when bone marrow donors are scarce.
Cord blood stem cell therapy treats over 80 diseases. This includes blood disorders, cancers, immune system issues, and metabolic disorders. Cord blood stem cells are versatile and valuable for many medical uses.
Over 246,500 cord blood units are registered in the U.S. This provides a big resource for transplant patients. The number of units is growing as more people learn about cord blood banking.
The chance of needing a stem cell transplant by age 20 is about 0.06%. But, certain factors can increase this risk. It’s important for families to think about cord blood banking.
Cord blood stem cells are less likely to cause immune problems. This makes them a good choice for transplants, even when a matched donor is not available.
Yes, recent studies show promise for treating pediatric neurological disorders with cord blood transplants. Research is ongoing to explore more uses in regenerative medicine.
The cord blood banking industry has grown to over .8 billion. It’s expanding as more families see the benefits of cord blood banking for future medical needs.
Public cord blood banking donates blood for anyone in need. Private banking stores it for the family’s use. Families should choose based on their needs and circumstances.
Challenges include ensuring a diverse registry, improving access, and managing costs. Overcoming these challenges is key to fully utilizing cord blood transplants.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!