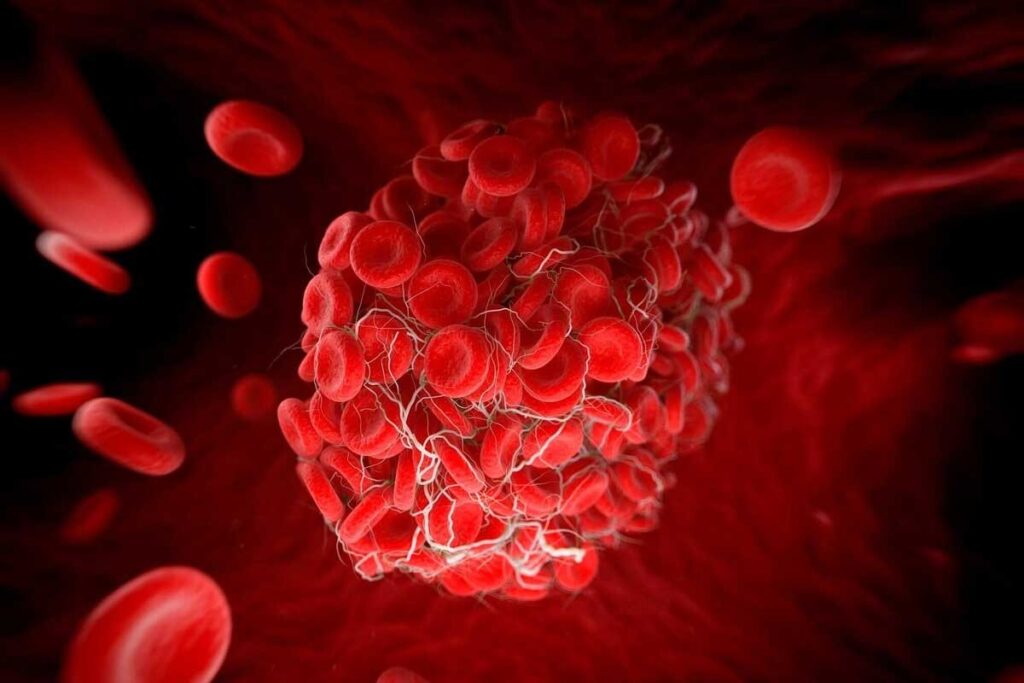
Thrombi, also known as blood clots, are solid masses that block blood flow in the vascular system. At Liv Hospital, we understand the risks associated with thrombus formation. This can lead to serious health issues. Thrombosis, or blood clotting inside a blood vessel, can harm the circulatory system. If you’re wondering what is thrombi, it refers to these harmful clots that can obstruct normal blood flow and cause complications.
It’s important to understand thrombi to see their health impact. Our team at Liv Hospital is here to help. We provide care and advice for those at risk of thrombus-related problems.
Thrombi, or blood clots, form inside blood vessels. Their importance is huge. A thrombus is a clot in the vascular system. It’s made of platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
A thrombus is a blood clot in a blood vessel. The word thrombi means more than one clot. Making a thrombus involves platelets sticking together, fibrin being deposited, and red and white blood cells gathering.
Blood clots help stop bleeding when a blood vessel is hurt. But, if they form where they shouldn’t, they can cause big problems. A thrombus has key parts:
Knowing how thrombi work in health and sickness is key. They’re good for stopping bleeding, but bad if they block important blood paths.
It’s important to understand the terms related to blood clots. This includes thrombus, thrombi, and thrombosis. We’ll look at how to use these terms correctly and address common mistakes.
A thrombus is a blood clot in a blood vessel. The plural form, thrombi, means more than one clot. Thrombosis is when a thrombus forms.
Knowing these terms helps doctors and patients talk clearly about blood clot issues.
People often misspell thrombus as trombus, throbus, thrumbus, or thromubs. These errors can cause confusion in medical records and studies. Using the right words is key to correct diagnosis and treatment.
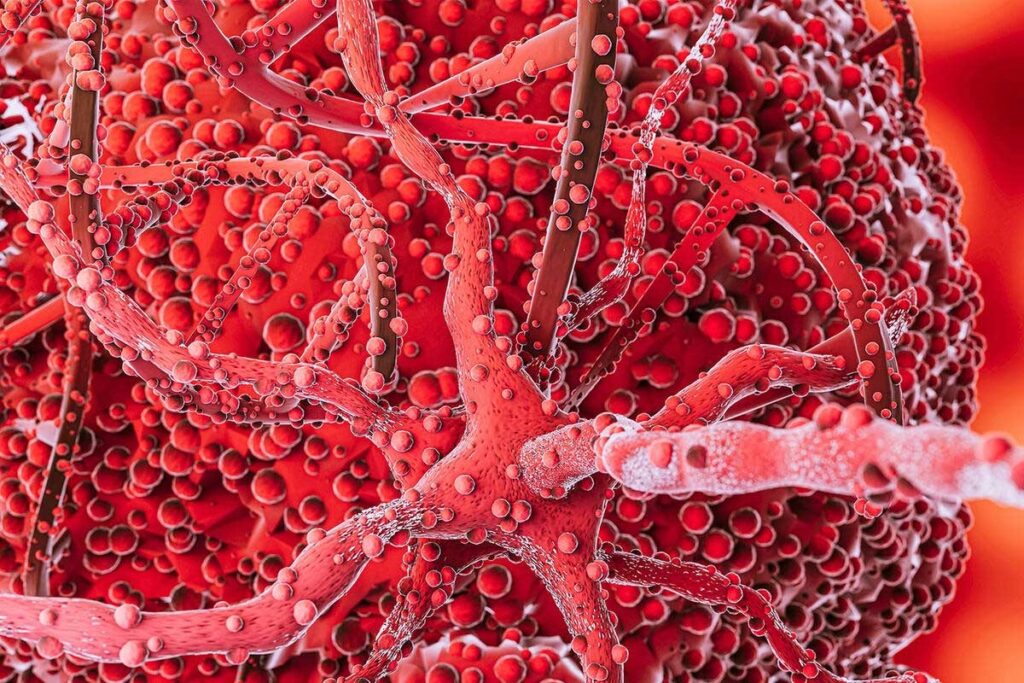
Blood clots, or thrombi, are complex structures made of many elements. These elements are vital for our body’s functions. They form through a detailed process involving cells and proteins.
A thrombus mainly has platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, and white blood cells. Platelets start the clotting process. Fibrin is the framework that keeps the clot together. Red blood cells get trapped, and white blood cells show an inflammatory response.
As a renowned hematologist, notes:
“The composition of a thrombus can vary significantly depending on its location within the body and the underlying cause of its formation.”
Seeing a blood clot’s structure helps us understand it better. A diagram shows how platelets, fibrin, and blood cells are arranged in the clot.
| Component | Function |
| Platelets | Initiate clotting and aggregate to form the initial plug |
| Fibrin | Provides the structural framework, stabilizing the clot |
| Red Blood Cells | Trapped within the clot, contributing to its size and stability |
| White Blood Cells | Indicates an inflammatory response and may be involved in clot resolution |
Knowing about blood clots’ composition and structure is key. It helps us understand their role in health and disease. By seeing how these components work together, we can grasp the complex clotting process.
Blood clotting is a key response to injury. But it can cause serious health problems if it happens when it shouldn’t. We’ll look at how blood clots form, both as a protective action and as a harmful process.
When a blood vessel gets hurt, the body quickly forms a clot to stop too much bleeding. This starts with platelet activation, where platelets stick to the injury and clump together. At the same time, the coagulation cascade kicks in, making fibrin that holds the clot in place.
This clotting is key to stopping bleeding and starting healing. But it can also cause dangerous clots if conditions are right.
Pathological thrombosis happens when a clot forms in a healthy vessel without injury. It can be caused by abnormal blood flow, hypercoagulability, or endothelial dysfunction. These clots can block blood flow, causing tissue damage and serious problems like stroke or heart attack.
Knowing how thrombosis works is key to understanding the dangers of blood clots. It also shows why we need to take steps to prevent them.
Thrombi are not all the same. They differ in their makeup, where they form, and how they affect blood vessels. Knowing these differences is key to diagnosing and treating thrombosis well.
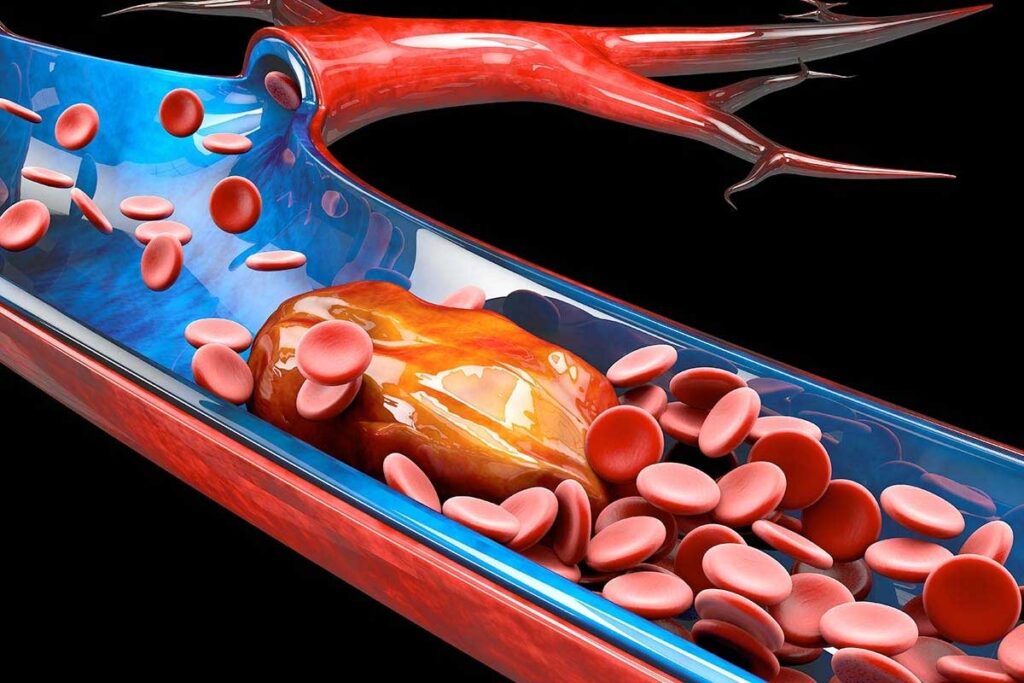
An occlusive thrombus blocks a blood vessel completely. It stops blood from flowing to the tissue or organ it supplies. This can cause serious problems, like tissue damage and organ failure.
Mural thrombi stick to the vessel wall but don’t block it fully. They might not cause immediate severe symptoms. But, they can lead to health issues like partial blockage and a higher risk of embolism.
Thrombi can also be grouped by where they form and what they’re made of. For example, arterial thrombi often block the blood vessel completely. They are linked to sudden heart attacks. We’ll look into these classifications to see their impact on health.
The makeup and effect of thrombi on blood vessels are vital. They help decide the best treatment plan.
Thrombus formation can happen in many parts of the body. Each location has its own risks. Knowing these spots is key to diagnosing and treating thrombi-related conditions well.
Arterial thrombi form in arteries. They can cause serious problems like stroke and heart attack. These clots often happen because of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up and damages the artery walls.
Venous thrombi form in veins. They are often linked to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT can be very dangerous if the clot breaks loose and goes to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Cardiac thrombi form in the heart chambers. They usually happen because of atrial fibrillation or after a heart attack. These clots can break loose and affect other organs.
It’s important to understand the risks of thrombi in different places. This helps us give the right care and prevention plans. The image below shows the vascular system and where thrombi can form.
Knowing the risk factors for thrombosis is key to preventing it. Many factors can lead to thrombus formation. Identifying these can help manage and lower the risk.
Genetics plays a big role in thrombosis. Some genetic conditions can make blood clot more easily. For example, the Factor V Leiden mutation raises the risk of venous thrombosis.
| Genetic Condition | Effect on Clotting |
| Factor V Leiden | Increases the risk of venous thrombosis |
| Antithrombin deficiency | Reduces the ability to regulate clot formation |
Lifestyle and environment also play a big part in thrombosis risk. Smoking damages blood vessels and raises the risk of clots. Long periods of sitting, like on flights or in bed, also increase the risk of blood clots.
“Immobility is a significant risk factor for venous thromboembolism, highlighting the importance of regular movement during prolonged travel or bed rest.”
Some medical conditions raise the risk of thrombosis. Cancer, heart disease, and obesity are examples. Knowing these risks helps in the early detection and management of thrombosis.
Understanding the risk factors for thrombus development helps in prevention and early intervention. This can reduce the incidence of thrombosis and its complications.
The signs of thrombosis can be hard to spot at first. But knowing what to look for is key to catching it early. Thrombi show up differently, depending on if they’re in arteries or veins.
Arterial thrombi cause severe and sudden symptoms. These include intense pain, pale skin, no pulse, coldness, and numbness. These happen because the blood flow in the arteries is suddenly blocked.
Venous thrombosis shows up with swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected limb. The symptoms come on more slowly than with arterial thrombi.
If you have severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or sudden severe pain in a limb, get help right away. These could be signs of a serious condition.
| Symptom | Arterial Thrombi | Venous Thrombosis |
| Pain | Severe, sudden | Gradual, swelling-related |
| Swelling | Minimal | Common |
| Pulse | Pulselessness | Normal or slightly affected |
Thrombosis can lead to serious conditions like pulmonary embolism. Blood clots in the body’s vessels can harm many organs. We’ll look at how thrombi affect the brain, heart, and lungs.
Thrombosis can cause a stroke by blocking brain vessels. This can damage brain tissue and lead to disability or death. Quick medical help is key to reducing stroke damage.
Thrombi in the coronary arteries can cause a heart attack. A blocked artery can harm or kill heart muscle. This can weaken the heart and raise the risk of more heart problems.
Pulmonary embolism happens when a clot blocks a lung artery. It’s a serious condition that can be deadly if not treated quickly. Other dangerous issues include deep vein thrombosis and clots in vital areas.
| Condition | Description | Consequences |
| Stroke | Obstruction of a cerebral vessel by a thrombus | Brain damage, disability, or death |
| Heart Attack | Blockage of a coronary artery by a thrombus | Damage or death of heart tissue |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Blockage of a pulmonary artery by a thrombus | Respiratory distress, potentially fatal |
The link between blood acid levels and clotting is complex but vital. Clotting is a delicate process that can be affected by blood acidity levels.
Blood lactic acid is key to showing how active our metabolism is. It builds up when we exercise hard and our body can’t get enough oxygen. Lactic acid levels can rise in conditions of strenuous exercise, shock, or sepsis, affecting the body’s acid-base balance.
The body’s acid-base balance is carefully controlled. Changes can deeply affect how we clot blood. Too much acidity can make blood clot more easily, raising the risk of blood clots.
| Acid-Base State | Effect on Coagulation |
| Acidosis | Increased risk of thrombosis due to enhanced coagulability |
| Alkalosis | Potential for decreased coagulability, though less commonly associated with thrombotic events |
| Normal Balance | Optimal coagulation function, with a balanced risk of bleeding and clotting |
Keeping the acid-base balance right is key for good clotting. We need to understand how metabolism, acid-base balance, and clotting work together. This helps us manage blood clotting problems better.
Thrombosis is a big problem worldwide, affecting heart health everywhere. It shows how big its impact is, not just on people but also on healthcare and economies.
Thrombosis is a major reason for sickness and death globally. It plays a big role in heart diseases. Studies show it’s linked to a lot of heart-related deaths.
Research shows a strong connection between thrombotic events and heart deaths.
Thrombi-related conditions cost a lot in healthcare and money. They lead to big hospital bills, treatment costs, and long-term care expenses. Here’s a detailed look at these costs:
| Category | Cost (USD) | Percentage of Total Healthcare Expenditure |
| Hospitalization | 10 billion | 30% |
| Treatment | 5 billion | 15% |
| Long-term Care | 8 billion | 25% |
Good public health strategies are key to fighting thrombosis. We need to spread the word about risk factors, encourage prevention, and make sure people get the right treatment fast. With a strong public health plan, we can lessen the impact on heart health.
Understanding thrombi is key to reducing their health impact. Knowing the risks helps people take steps to avoid thrombosis. This is important for everyone’s health.
It’s vital to recognize thrombi symptoms early. This means getting medical help quickly. We should all focus on preventing thrombosis by living healthily, managing health issues, and knowing our genetic risks.
Preventing thrombosis is a big job that needs everyone’s help. We must spread the word about thrombi risks and health effects. This way, we can help people protect their heart health.
Our main goal is to lower the number of thrombosis cases and their effects. Together, we can make a big difference in the lives of those with thrombi-related conditions.
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms inside a blood vessel. It’s made of platelets, fibrin, and blood cells.
A thrombus is one blood clot. Thrombi are many blood clots.
Thrombosis is when blood clots form in the blood vessels. It’s a natural response to injury or can be a disease.
Thrombi can form in arteries, veins, and the heart. Each place has its own risks and problems.
Risk factors include genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions. These increase the chance of blood clots.
Symptoms depend on where the clot is. They can include signs of artery or vein problems. These need quick medical help.
Acid-base balance can change how blood clots. For example, lactic acidosis can affect clot formation.
Thrombi can cause serious problems. These include stroke, heart attack, and pulmonary embolism. These are life-threatening.
Managing thrombosis involves public health efforts. This includes awareness, prevention, and treatment to lower risks.
Thrombosis is a major cause of illness worldwide. It puts a big burden on healthcare and the economy.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us