Regenerative medicine has grown a lot, with stem cell therapy becoming a hopeful treatment for many diseases. Did you know over 2,000 patients in the U.S. have tried unproven stem cell therapy side effects for knee osteoarthritis, often without understanding the potential risks?
This therapy uses stem cells to fix or replace damaged tissues. It could help with back pain and spinal cord injuries. However, there are concerns about its safety and possible side effects.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cell therapy is a regenerative treatment that uses stem cells to repair damaged tissues.
- It is used to treat various conditions, including osteoarthritis and back pain.
- The therapy involves injecting stem cells into the affected area.
- Potential side effects and pain associated with stem cell injections are concerns for patients.
- Understanding how stem cell therapy works is key to knowing its benefits and risks.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy Basics

Stem cells can turn into many different cell types. This makes them key in regenerative medicine. They help fix or replace damaged tissues, aiding in healing and growth.
What Are Stem Cells and How Do They Work?
Stem cells are cells that can become many types of cells in our bodies. They go to injured or sick areas to fix them. This is at the heart of regenerative medicine, which uses our body’s healing powers.
Stem cells work by interacting with other cells. They can calm the immune system, lessen swelling, and help grow new tissues. They do this by sending out growth factors and cytokines that help heal.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Medical Treatments
There are many stem cell types used in medicine, each with its own uses:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: These come from embryos and can become any cell type. But, their use is debated and strictly controlled.
- Adult Stem Cells: These are in adult bodies and can’t change into as many cell types as embryonic stem cells. Yet, they’re often used in treatments.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): These are adult cells that can change into many cell types, like embryonic stem cells.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): A type of adult stem cell that can turn into bone, cartilage, and muscle cells.
The Science Behind Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine aims to fix or replace damaged tissues and organs. It uses stem cells, tissue engineering, and making artificial organs. It’s all about understanding how stem cells can become specific cells and fix damaged areas.
This field is growing fast, with new research every day. As we learn more, regenerative medicine could help with many diseases and injuries.
The Stem Cell Harvesting Process
Harvesting stem cells is key to regenerative medicine. It lets us use stem cells for healing. Stem cells come from places like bone marrow, fat, and blood. Each source has its own way of getting the cells.
Bone Marrow Extraction Methods
Getting stem cells from bone marrow is common. This method takes bone marrow from the hip or sternum while the patient is numb. The marrow is full of mesenchymal stem cells that can turn into different cell types.
The steps for bone marrow extraction are:
- Preparing the patient with local anesthesia
- Inserting a needle into the bone marrow cavity
- Aspirating the bone marrow into a syringe
- Processing the aspirate to isolate stem cells
Adipose (Fat) Tissue Collection
Fat tissue is also a good source of stem cells. To get stem cells from fat, doctors use liposuction, a small surgery. These stem cells are great for healing and are used in many treatments.
The steps for fat tissue collection are:
- Administering local anesthesia to the donor site
- Performing liposuction to extract fat tissue
- Processing the extracted tissue to isolate stem cells
Blood-Derived Stem Cell Collection
Stem cells from blood are collected through apheresis. This method draws blood, separates stem cells, and returns the rest. It’s less invasive than other methods.
The steps for blood-derived stem cell collection are:
- Drawing blood from the patient
- Separating stem cells using a specialized machine
- Returning the remaining blood components to the patient
Each method has its benefits and risks. The choice depends on the treatment, patient health, and doctor’s advice.
Pain Levels During Stem Cell Harvesting
Harvesting stem cells can be uncomfortable, depending on the method and the patient. Knowing the pain levels for each technique is key for those thinking about stem cell therapy.
Bone Marrow Aspiration Pain Experience
Bone marrow aspiration is a common way to get stem cells. It takes bone marrow from the pelvis or sternum. Even though it’s done under local anesthesia, some pain or discomfort can happen during and after.
The pain can differ a lot from person to person. Some feel pressure or a dull ache, while others might feel sharp pain. Afterward, pain meds help manage the discomfort.
Adipose Tissue Extraction Discomfort
Getting stem cells from fat tissue is another method. This is done under local anesthesia or mild sedation. The pain from this method is usually less than bone marrow aspiration.
Patients might see bruising, swelling, or soreness at the site, like after liposuction. These symptoms are short-lived and can be eased with pain meds and rest.
Is Donating Stem Cells Painful?
Donating stem cells, through bone marrow or blood, can be a bit painful. But, how much pain varies greatly among people.
| Harvesting Method | Typical Pain Level | Post-Procedure Discomfort |
| Bone Marrow Aspiration | Moderate to High | Yes, managed with pain medication |
| Adipose Tissue Extraction | Low to Moderate | Yes, bruising and soreness |
| Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Collection | Low | Minimal, some fatigue |
Talking to your healthcare provider about pain concerns before stem cell harvesting is vital. Knowing the risks and benefits of each method helps patients make better choices.
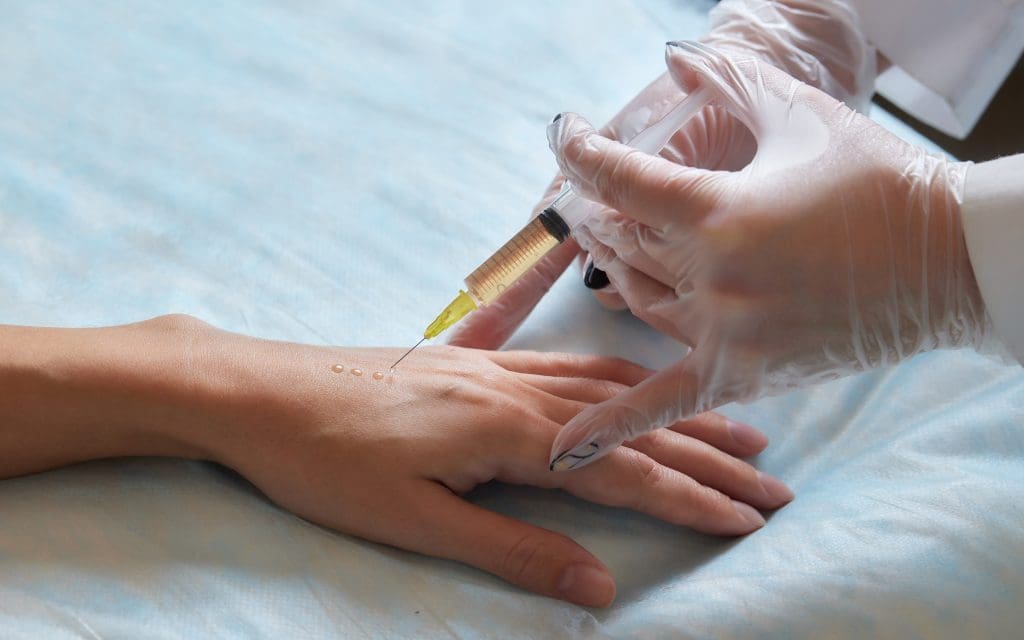
The Stem Cell Injection Procedure
It’s important to know about the stem cell injection procedure if you’re thinking about it. This treatment uses stem cells to help heal and grow new tissue.
Preparation Before Injection
Before the injection, several steps are taken to make sure it goes well. Preparation is key to reduce risks and get the best results.
- Patient evaluation: Checking the patient’s health and the condition being treated.
- Stem cell harvesting: Getting stem cells from the patient or a donor.
- Cell processing: Getting the stem cells ready for injection.
- Imaging: Using ultrasound or X-ray to guide the injection.
The Injection Process Step-by-Step
The stem cell injection process has several steps:
- Positioning: The patient is placed to make it easy to reach the injection site.
- Cleansing: The area is cleaned and ready for the injection.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used to lessen discomfort.
- Injection: The stem cells are injected into the targeted area.
- Post-injection care: The patient is watched for a short time after the procedure.
Use of Anesthesia and Pain Management
Pain management is a big part of the stem cell injection procedure. Local anesthesia is often used to numb the area, making the injection less painful. After the procedure, some soreness may occur, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
| Pain Management Method | Description | Effectiveness |
| Local Anesthesia | Numbing the injection site | High |
| Over-the-counter Pain Medications | Managing post-procedure soreness | Moderate |
Pain Levels During Stem Cell Injections
How much pain you feel during stem cell injections can change a lot. This depends on many things. Knowing these can help those thinking about stem cell therapy.
Factors Affecting Pain Perception
Many things can change how much pain you feel during stem cell injections. These include:
- Individual Pain Tolerance: Everyone feels pain differently.
- Injection Site: Where you get the injection can affect how much it hurts.
- Technique and Expertise of the Practitioner: The skill of the person giving the injection matters.
- Use of Anesthesia or Sedation: Anesthesia or sedation can make the pain less.
Typical Pain Ratings from Patients
People usually rate their pain during stem cell injections from 1 to 10. Most say it’s a 2 to 5, which means mild to moderate pain.
Is Stem Cell Treatment Painful Compared to Other Procedures?
It’s hard to say how stem cell injections compare to other treatments in terms of pain. But, they are often seen as less invasive and less painful than surgery.
Some important things to think about are:
- Stem cell therapy uses less invasive methods.
- Local anesthesia can help reduce pain.
- Recovery time is usually shorter than with surgery.
In summary, pain during stem cell injections can differ. But, knowing what affects pain and comparing it to other treatments can help patients make better choices.
Post-Injection Pain and Recovery
After stem cell therapy, patients often feel some discomfort. Knowing what to expect can help manage worries and improve recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Sensations
Right after the injections, patients might feel mild pain or discomfort at the site. This is usually because of the injection and the body’s reaction to the stem cells. Pain management like ice packs or pain relievers can help.
Days 1-7 After Treatment
In the first week, patients might feel different levels of pain or discomfort. This is when the body starts to react to the therapy. Some might feel:
- Mild soreness at the injection site
- Swelling or redness
- A general feeling of being unwell
These symptoms are usually short-lived and will get better as the body heals. It’s key to follow the post-procedure care instructions from healthcare professionals for a smooth recovery.
Worse Pain After Stem Cell Injection: When to Be Concerned
While some pain is normal, severe pain can be a warning sign. If patients feel:
- Severe pain that doesn’t respond to pain medication
- Increasing swelling or redness around the injection site
- Fever or chills
they should immediately contact their healthcare provider. These signs could mean an infection or other serious issues that need medical help.
Recovering from stem cell therapy takes time. By understanding the possible pain and knowing when to seek help, patients can feel more confident in their recovery.
Common Stem Cell Therapy Side Effects
It’s important to know the possible side effects of stem cell therapy. This is true for any medical treatment. Stem cell therapy can have side effects, from mild to severe.
Injection Site Reactions
Injection site reactions are common with stem cell therapy. These can be pain, swelling, redness, or bruising at the injection site. Most of the time, these reactions are mild and go away in a few days.
Common injection site reactions include:
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling or inflammation
- Redness or bruising
- Infection (rare)
Systemic Side Effects
Some people may feel systemic side effects after stem cell therapy. These effects are not just at the injection site but can affect the whole body. Symptoms can include fatigue, headache, or nausea.
Examples of systemic side effects:
- Fatigue or malaise
- Headache
- Nausea or dizziness
- Fever or chills
As noted by the researchers,
“The use of stem cell therapy has shown promising results in treating various conditions, but it’s essential to be aware of the possible systemic side effects.”
Rare but Serious Complications
While rare, serious complications can happen with stem cell therapy. These can include severe infections, allergic reactions, or tumor formation. It’s important for patients to be closely watched by their healthcare provider to lower the risk of these complications.
Rare but serious complications may include:
- Severe infections
- Allergic reactions
- Tumor formation
- Unintended growth or differentiation of stem cells
In conclusion, stem cell therapy is promising but knowing its side effects is key. Patients should talk to their healthcare provider about their risks and any worries they have.
Stem Cell Applications for Different Body Regions
Stem cells can treat many conditions, from back pain to arthritis. They are being studied for their ability to heal and repair damaged tissues. This is true for both musculoskeletal and degenerative conditions.
Stem Cell Injections for Back Pain
Back pain can really affect your life. Stem cell injections are a new hope for those who haven’t found relief elsewhere. They aim to fix damaged tissues and lower inflammation.
- They might help reduce pain and improve how well you can move.
- Because they come from your own body, there’s less chance of them being rejected.
Stem Cell Injections for Shoulder Conditions
Shoulder problems, like tendonitis and rotator cuff injuries, are hard to fix. Stem cell therapy is being looked at to help heal and ease pain in the shoulder.
- Stem cells are injected into the problem area.
- People might see better function and less pain.
Stem Cell Therapy for Joints and Arthritis
Arthritis and other joint issues can cause a lot of pain and limit your movement. Stem cell therapy is being studied as a way to fix joint tissues and ease symptoms.
Key considerations include:
- Stem cells might be able to fix damaged cartilage.
- They could also lower inflammation and make joints work better.
Even though stem cell therapy looks promising, it’s important to talk to a doctor. They can help figure out the best treatment for your specific problem.
Stem Cell Therapy for Specific Conditions
Stem cell therapy is a new way to treat diseases. It’s getting a lot of attention for its ability to handle complex conditions. These conditions were hard to treat before.
Stem Cell Treatment for Cancer
Stem cell therapy for cancer is being studied a lot. Stem cells can fix or replace damaged tissues caused by cancer. They can also help after treatments like chemotherapy.
Researchers think stem cells might even target cancer cells. They could also carry treatments to fight cancer.
Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury and Nerve Regeneration
Stem cell therapy might help with spinal cord injuries. Stem cells can turn into different cell types. This makes them good for fixing damaged nerve tissue.
Studies show stem cell transplants can improve motor function in animals. Now, human trials are checking if it works for us too.
Stem Cell Applications for Cerebral Palsy and Neurological Disorders
Stem cell therapy is also being looked at for cerebral palsy and other neurological disorders. The goal is to fix or replace damaged brain cells. This could help with motor skills and thinking.
Early studies suggest stem cell therapy might help some patients. But, more research is needed to know for sure.
As research goes on, we’re learning more about stem cell therapy. It could be a game-changer for many diseases. Ongoing studies will help us understand its benefits and limits better.
Effectiveness and Duration of Results
Knowing how long stem cell therapy lasts is key for patients. Stem cell injections are used to treat many conditions. Their success depends on several things.
How Long Do Stem Cell Injections Last?
The benefits of stem cell injections vary. They depend on the condition, the stem cells’ quality, and the patient’s health. Studies show the effects can last from months to years.
Factors influencing the duration of stem cell injection benefits include:
- The severity of the condition being treated
- The number of stem cells injected
- The overall health of the patient
- Post-procedure care and rehabilitation
Before and After Stem Cell Therapy: What to Expect
Before stem cell therapy, patients get checked to see if they’re a good fit. This includes looking at their medical history, doing a physical exam, and running tests.
After the treatment, some side effects might happen. These can be pain or swelling at the injection site. They usually go away in a few days. It can take weeks to see the full effects of the therapy.
Factors Affecting Treatment Success
Many things can affect how well stem cell therapy works. This includes the type of stem cells, how they’re delivered, and the patient’s lifestyle and health.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Success |
| Stem Cell Type | The source and type of stem cells used | High-quality stem cells improve outcomes |
| Delivery Method | The technique used to administer stem cells | Precise delivery enhances efficacy |
| Patient Health | The overall health and condition of the patient | Better health status correlates with improved results |
By knowing these factors and what to expect, patients can make better choices about their treatment.
Comparing Stem Cell Therapy Pain to Alternative Treatments
When looking into stem cell therapy, a big question is: how does the pain compare to other treatments? This includes surgeries, medications, and physical therapy. Knowing these differences helps patients make better choices for their health.
Surgical Alternatives and Their Pain Profiles
Surgeries are often more invasive than stem cell therapy. Procedures like joint replacements or spinal fusions need a lot of recovery time. They can also cause a lot of pain after surgery.
On the other hand, stem cell injections are less invasive. They might cause less pain and lead to quicker recovery times.
| Treatment | Invasiveness | Recovery Time | Pain Level |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Minimally Invasive | Short | Mild to Moderate |
| Surgical Alternatives | Invasive | Long | Moderate to Severe |
Medication-Based Treatments vs. Stem Cell Therapy
Medications like corticosteroids and pain relievers can help for a while. But they might have side effects and not fix the real problem. Stem cell therapy tries to heal and might offer relief for longer with fewer side effects.
Key differences include:
- Duration of Relief: Stem cell therapy might last longer than medication.
- Side Effects: Stem cell therapy usually has fewer side effects than taking medication for a long time.
Physical Therapy and Other Conservative Approaches
Physical therapy and other non-surgical methods can work well for some issues. But they might not help as much with severe or degenerative problems. Using stem cell therapy with these methods could make them more effective.
By comparing stem cell therapy to other treatments, patients can make better choices. It’s important to talk to doctors to find the best treatment for each person’s needs.
Conclusion: Is Stem Cell Therapy Worth the Discomfort?
Stem cell therapy is seen as a hopeful treatment for many health issues. It can help those with chronic pain and degenerative diseases. Even though it might cause some discomfort, the benefits are worth it.
The pain from stem cell injections can vary. It depends on where the injection is given and how sensitive you are to pain. Most people find the pain during and after the treatment to be manageable.
Thinking about stem cell therapy means looking at both the good and the bad. For many, the chance to feel less pain and move better is enough. Always talk to a doctor to see if this treatment is good for you.
Knowing what stem cell therapy involves helps patients make smart choices. This way, they can take charge of their health and feel better.
FAQ
Can stem cell therapy be used to treat neurological disorders?
Yes, it’s being researched for conditions like cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. The results are promising, but more research is needed.
What is the difference between mesenchymal stem cell therapy and other types of stem cell therapy?
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy uses a specific stem cell type. These cells can become bone, cartilage, and muscle cells. Other therapies might use different stem cells, like hematopoietic stem cells.
How are stem cells administered?
They’re given through injections, either directly to the affected area or into a vein. The method depends on the condition and the type of stem cells.
Is donating stem cells painful?
Donating stem cells can be a bit uncomfortable, mainly during the harvesting. But, the pain is usually manageable. Donors get local anesthesia or other pain relief options.
Can stem cell therapy cure cancer?
It’s being studied as a cancer treatment, but it’s not a cure. It might be used with other treatments to help heal and grow new cells.
Is stem cell therapy effective for back pain?
It shows promise for back pain, like degenerative disc disease. But, results can differ. It depends on the person and their condition.
How long do stem cell injections last?
Results from stem cell injections vary. It depends on the person, the condition, and how severe it is. Some see relief for months or years, while others might need more treatments.
What are the possible side effects of stem cell therapy?
Side effects can include pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site. Some might feel tired or have headaches. Rare but serious problems can also happen.
How are stem cells harvested?
Stem cells come from places like bone marrow, fat tissue, and blood. Getting them involves a small surgery, like bone marrow aspiration or liposuction. It’s done under local anesthesia.
Is stem cell therapy painful?
Pain from stem cell therapy can differ for each person. It depends on the procedure and the area treated. Some might feel pain, while others won’t.
What is stem cell therapy and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy is a way to fix or replace damaged cells and tissues. It uses stem cells, which can turn into different cell types. This helps in healing and growing new cells.