Understand the causes and evaluation steps for Lung Cancer, including early warning signs, major risk factors, and life-saving diagnostic procedures.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Evaluation of Lung Cancer begins with understanding the triggers that damage lung cells. Exposure to toxins, especially tobacco smoke, is the primary cause. Evaluation is crucial because symptoms often do not appear until the disease is advanced.
The evaluation process involves a range of diagnostic steps, starting with screening for high-risk individuals. The goal is to find the cancer when it is small and localized. This multi-step approach is vital for achieving the best possible outcome for patients.
The most important step in early detection is recognizing the common warning signs. These signs can be easily mistaken for less serious ailments like a cold or the flu. If these symptoms persist, especially in high-risk individuals, immediate medical consultation is required.
Symptoms can vary slightly based on the type and location of the cancer. Knowing these differences helps doctors narrow down the possible diagnosis before imaging tests.
When the tumor is localized (confined to one area), symptoms often involve the airways. The tumor irritates the lining of the bronchi, leading to irritation and difficulty breathing.
If the cancer has spread (metastasized) outside the chest, new symptoms appear in other parts of the body. These may be the first warning signs of Lung Cancer in some patients.
Certain symptoms require immediate emergency care. These signs indicate a life-threatening complication or rapid tumor growth. If any of the following occur, seek urgent medical help.
These are factors that cannot be changed but contribute to an individual’s risk level. They help identify who is at high risk of Lung Cancer for targeted screening.
These are factors related to lifestyle and environment that can be changed to reduce risk. Taking action against these factors is the most effective Lung Cancer, Causes and Evaluation prevention strategy.
When lung cancer is suspected, evaluation begins with non-invasive tests. These initial steps are crucial for confirming the presence of an abnormality and guiding further invasive procedures.
If initial imaging identifies a suspicious nodule, advanced procedures are required for a definitive diagnosis and staging. These steps determine the exact Causes of the Lung Cancer and the best treatment plan.
Biopsy: The only way to confirm cancer. A tissue sample is taken, often using a needle inserted through the chest wall (CT-guided biopsy) or through the airways (bronchoscopy).
Bronchoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is passed down the throat into the airways to visualize the lungs and collect tissue samples.
Molecular Testing: Tissue is tested for specific genetic mutations (like EGFR, ALK, or PD-L1). This determines eligibility for highly effective targeted therapies or immunotherapy.
While the cancer itself is similar, there are subtle gender differences in Lung Cancer Symptoms. Women who have never smoked are more likely than men to develop adenocarcinoma, a type often found in the outer edges of the lung.
Women are also more likely to present with specific genetic mutations (like EGFR) that are targetable with oral medications. Otherwise, symptoms of coughing and shortness of breath are generally the same in both men and women.
The total risk assessment summary combines all factors, from smoking history, environmental exposure, and family genetics. This comprehensive view helps doctors determine the appropriate surveillance plan.
At LIV Hospital, we use established risk calculators to identify patients who qualify for annual LDCT screening. This targeted screening saves lives by catching tumors early when treatment is most effective.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Warning signs include a persistent cough, coughing up blood, unexplained chest pain, and unexplained weight loss or fatigue.
High-risk individuals include current or former heavy smokers, those with significant workplace exposure to toxins like asbestos, and those with a strong family history.
While core symptoms are similar, women who have never smoked are statistically more likely to develop adenocarcinoma, a type often linked to specific treatable genetic mutations.
The biggest factor is smoking tobacco. Other factors include exposure to radon gas in the home and occupational exposure to substances like asbestos.
Most cases are not purely hereditary. However, a family history suggests a higher genetic susceptibility to environmental damage from smoking or toxins.

The American Cancer Society says the 5-year survival rate for lung cancer is about 22%. But, this rate changes a lot based on the cancer’s
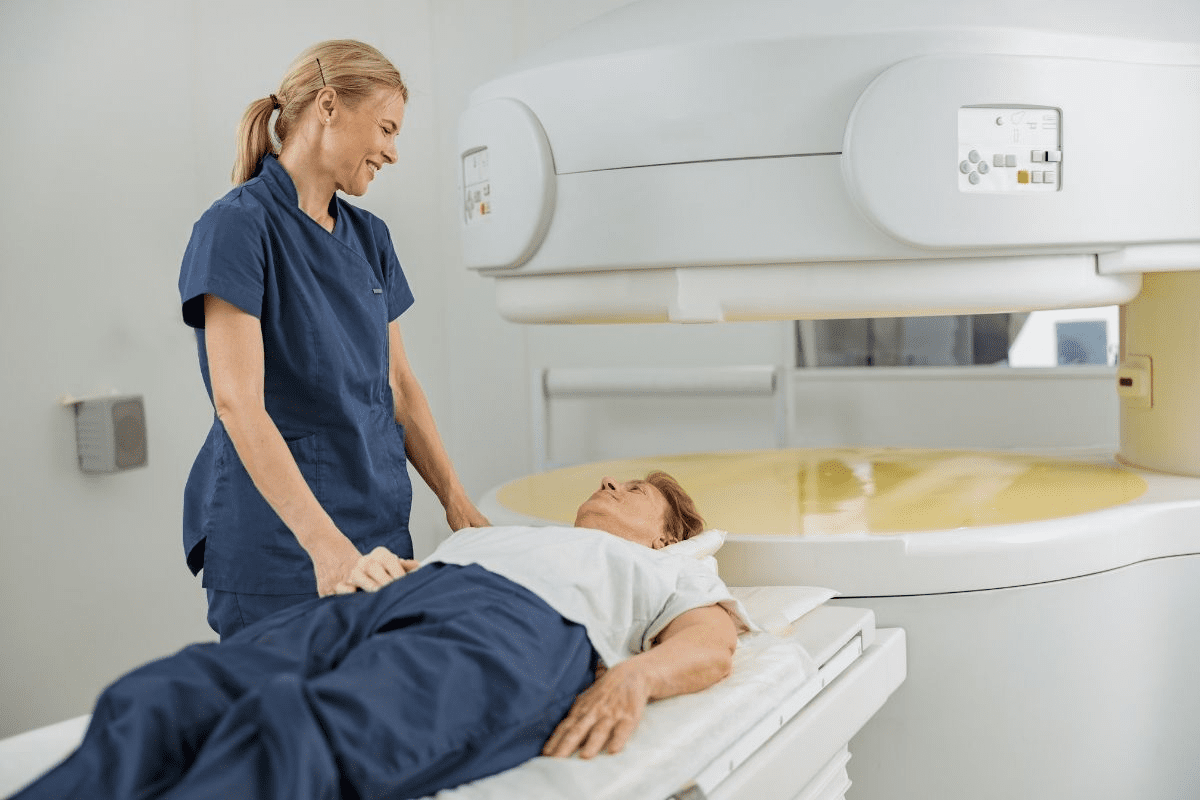
Medical technology keeps getting better, and the PET scan is a big step forward. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is key for checking lung health. PET
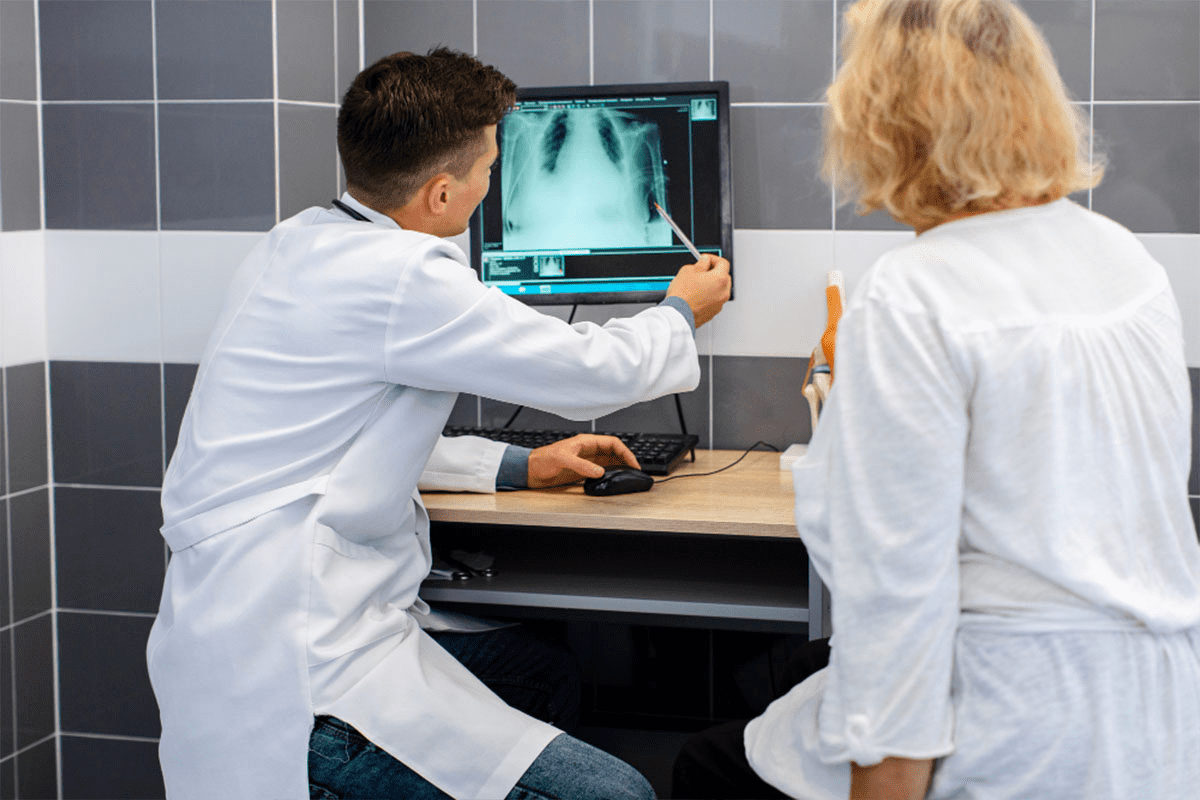
Lung cancer is a major cause of death worldwide. Early detection is key for effective treatment. The Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan of the lungs
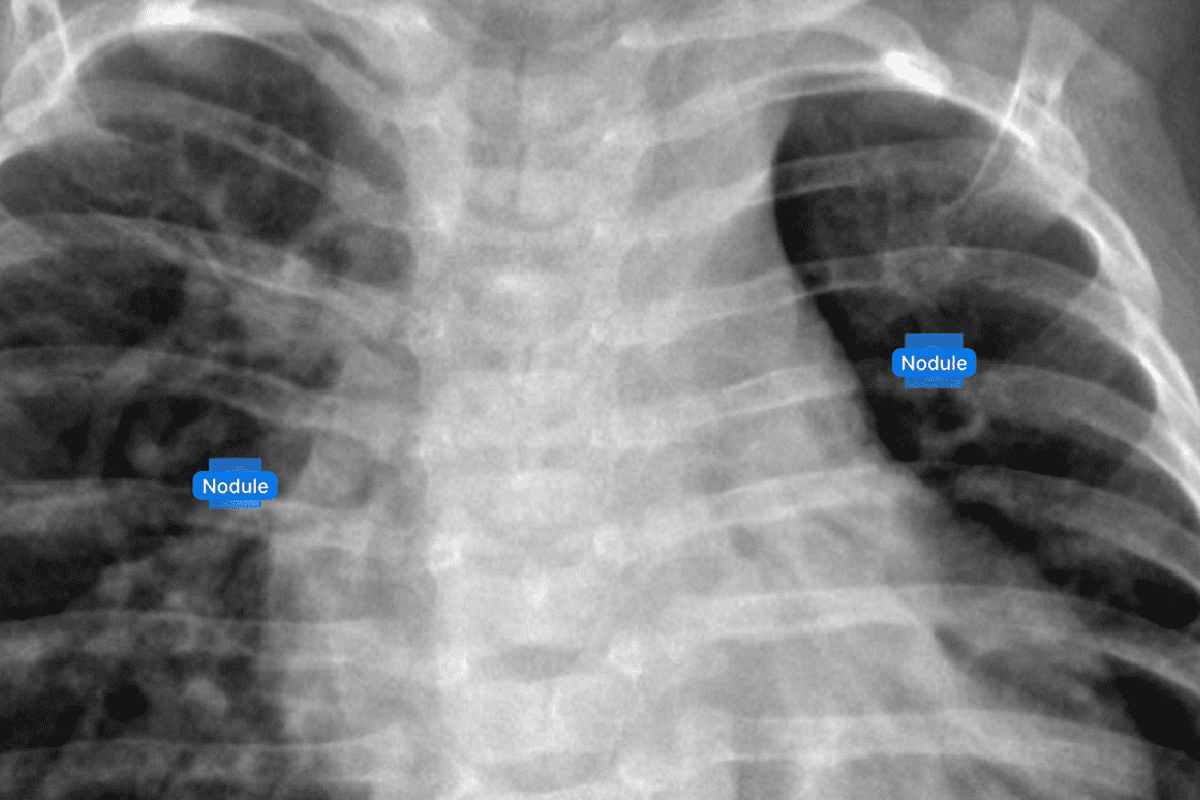
Lung cancer is a big health problem worldwide.PET scan lung nodule cancer detection it early is key to treating it well. A surprising fact is
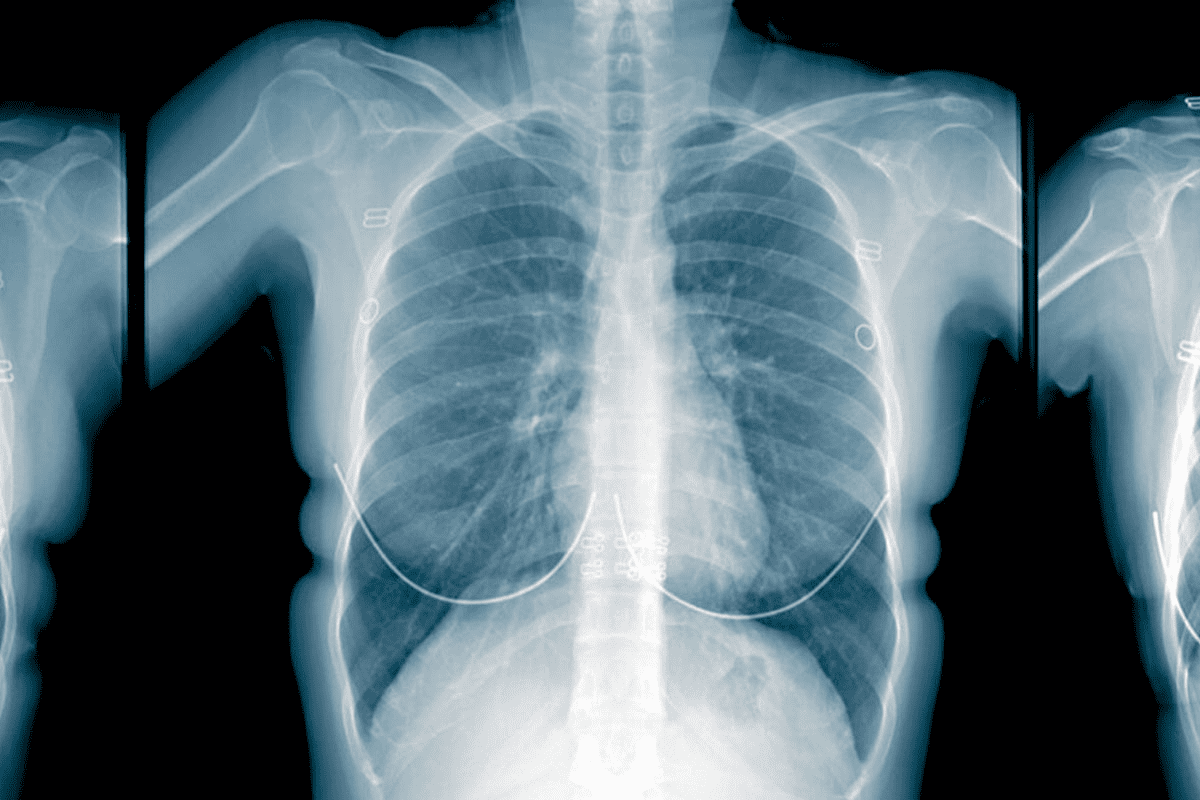
Lung cancer is a top cause of cancer deaths worldwide, and finding it early is key to improving survival chances. That’s why tools like PET
Cancer diagnosis has become more advanced. Yet, a shocking fact is that 1 in 2 people will get some form of cancer in their life.

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)