Reading a chest radiograph correctly is key to diagnosing pneumonia and finding the right treatment. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need for accurate chest X-ray interpretation. This is because it greatly affects how well a patient does.Guide to interpreting a chest radiograph of pneumonia, focusing on identifying infiltrates and consolidation patterns.
Pneumonia is a big health issue, causing a lot of sickness and death. Spotting it early and starting antibiotics quickly can make a big difference. We use chest radiography to see if pneumonia is there and how bad it is. This helps us decide how to treat it and check if treatment is working.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate interpretation of chest radiographs is essential for pneumonia diagnosis.
- Chest radiography helps determine the extent and location of pneumonia.
- Early recognition and treatment of pneumonia improve patient outcomes.
- Liv Hospital follows international medical standards for pneumonia diagnosis and treatment.
- Precise chest X-ray interpretation guides treatment decisions and assesses treatment response.
The Critical Role of Chest Radiography in Pneumonia Diagnosis
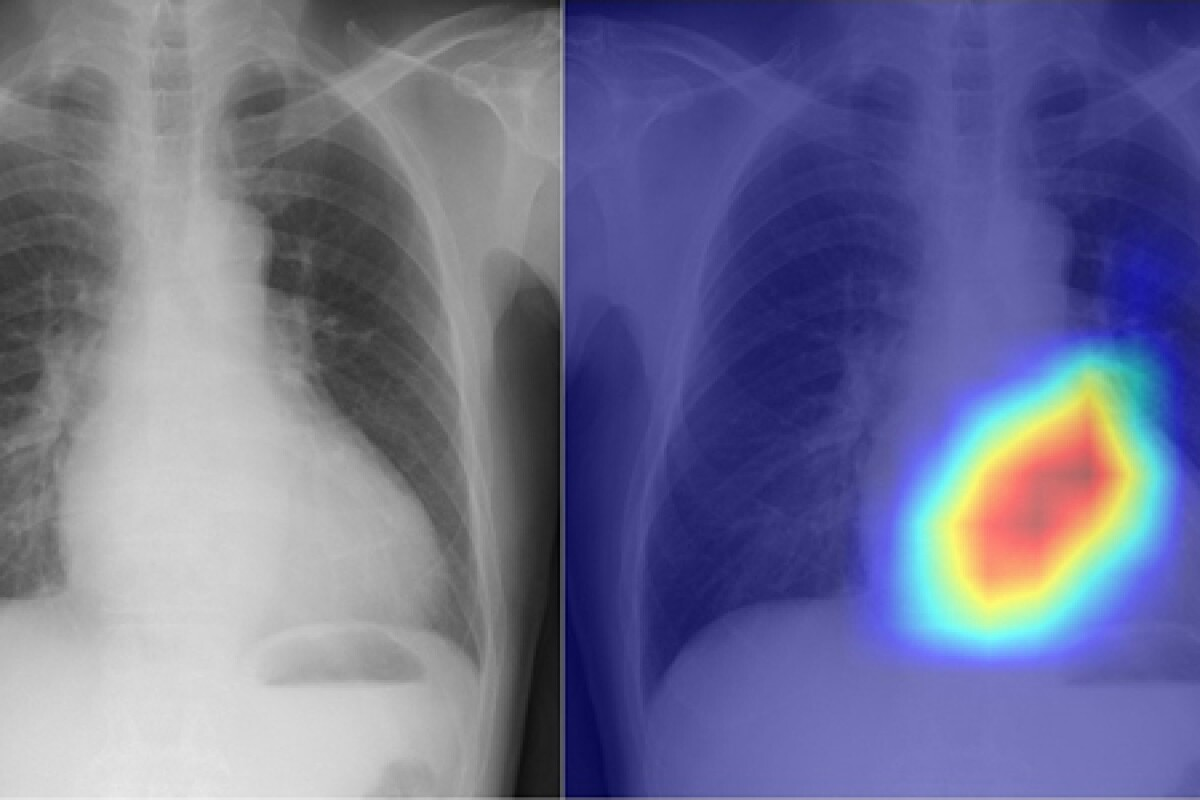
Chest radiography is key in diagnosing and managing pneumonia. It helps spot pneumonia and gauge its severity. Early chest X-rays can greatly improve patient care.
Impact on Morbidity and Mortality Rates
Chest X-rays play a big role in fighting pneumonia. They help doctors catch pneumonia early. This leads to better treatment and lower death rates.
When to Order a Chest X-ray for Suspected Pneumonia
Deciding when to get a chest X-ray for pneumonia depends on several factors. We look at how bad the symptoms are, the patient’s age, and their health. For example, older or sick patients need chest X-rays sooner.
|
Clinical Scenario |
Recommendation |
|---|---|
|
Severe symptoms (e.g., high fever, difficulty breathing) |
Immediate chest X-ray |
|
Mild symptoms in high-risk patients (e.g., elderly, immunocompromised) |
Consider early chest X-ray |
|
Mild symptoms in low-risk patients |
Clinical observation; X-ray if symptoms worsen |
Essential Anatomy and Radiographic Terminology
To understand chest radiographs well, knowing the basics is key. You need to know the normal lung look, important landmarks, and the mediastinum. This knowledge helps spot problems like pneumonia.
Normal Lung Fields and Anatomical Landmarks
The lung areas on a chest X-ray show different shades, with lungs being darker because they’re full of air. Important landmarks include the costophrenic angles and the cardiac silhouette, or heart outline.
- The right lung is bigger than the left.
- The diaphragm is higher on the right because of the liver.
- The trachea is a midline structure that splits into the right and left main bronchi.
Mediastinal Structures and Silhouettes
The mediastinum, the chest’s middle part, houses the heart, trachea, esophagus, and big blood vessels. The heart’s outer shape is visible on an X-ray. Knowing where the heart’s parts are helps spot changes that might mean something’s wrong.
Important mediastinal silhouettes include:
- The aortic arch.
- The pulmonary artery.
- The cardiac silhouette, which can show if the heart is too big.
Understanding Radiographic Densities
Density on an X-ray shows how dark or light something is, which tells us about its type. Air is black (least dense), bone is white (most dense), and soft tissues like the heart and muscles are gray.
Knowing these densities helps:
- Spot lung problems like pneumonia.
- See pleural effusions, which look like darker areas.
Learning the essential anatomy and radiographic terms helps doctors better diagnose and treat conditions like pneumonia.
Systematic Approach to Reading a Chest Radiograph of Pneumonia
To accurately diagnose pneumonia, healthcare professionals must follow a systematic approach when reading chest radiographs. This method ensures all important information is considered. It helps avoid missing critical details.
We suggest using the ABCDE method for chest X-ray interpretation. This systematic approach covers all key aspects of the radiograph.
The ABCDE Method for Chest X-ray Interpretation
The ABCDE method is a mnemonic that stands for Airway, Bones, Cardiac silhouette, Diaphragm, and Extrathoracic structures. This method ensures a thorough evaluation of the chest radiograph.
- Airway: Assess the trachea and main bronchi for any abnormalities, such as displacement or obstruction.
- Bones: Evaluate the bony structures for fractures, lesions, or other abnormalities.
- Cardiac silhouette: Examine the heart size and contour for signs of cardiomegaly or other cardiac abnormalities.
- Diaphragm: Inspect the diaphragm for elevation, flattening, or other irregularities.
- Extrathoracic structures: Review the soft tissues and other extrathoracic structures for abnormalities.
Technical Quality Assessment
Assessing the technical quality of the chest radiograph is key. Factors like patient positioning, inspiration level, and penetration greatly affect image interpretation. A well-exposed radiograph with proper patient positioning is vital for accurate diagnosis.
Comparison with Previous Imaging
Comparing the current chest radiograph with previous studies offers valuable insights. It shows how pneumonia has progressed or resolved. This comparison helps identify changes, like increasing consolidation or complications.
By adopting a systematic approach to chest radiograph interpretation, healthcare professionals can improve diagnostic accuracy. This leads to better care for patients with pneumonia.
Recognizing Classic Radiographic Patterns of Pneumonia
Pneumonia shows different radiographic patterns, each with unique features. These patterns help doctors diagnose and understand pneumonia’s severity.
Lobar Consolidation: Appearance and Distribution
Lobar consolidation means one or more lung lobes are filled with fluid and cells. This is often seen in pneumococcal pneumonia. The affected area looks consolidated and white on X-rays.
Bronchopneumonia Pattern: Multifocal Opacities
Bronchopneumonia shows scattered, patchy opacities in multiple lobes. It’s common in Staphylococcus aureus or gram-negative infections. These patches often surround bronchi, showing how the infection spreads.
Interstitial Patterns: Reticular and Reticulonodular Changes
Interstitial pneumonia affects the lung’s spaces, leading to reticular or reticulonodular patterns. These are typical in viral or Mycoplasma infections. The reticular pattern looks like a network, while the reticulonodular pattern includes small nodules.
Atypical Presentations and Mimics
Not all pneumonia looks typical on X-rays. Some cases may have unusual features or look like other conditions. For example, some infections can cause cavities or pneumatoceles, making diagnosis harder. Knowing these atypical presentations is key for correct diagnosis.
Understanding these classic radiographic patterns helps doctors better diagnose and manage pneumonia.
Identifying Organism-Specific Radiographic Findings
It’s key to know the radiographic signs of pneumonia to diagnose it right. The type of germ causing the pneumonia affects how it looks on X-rays. Spotting these signs helps doctors target the right treatment.
Bacterial Pneumonia Characteristics
Bacterial pneumonia shows up as consolidation on chest X-rays. Lobar consolidation is a big sign, where a whole lobe gets affected. You can see air bronchograms in the solid area.
The most common germs, like Streptococcus pneumoniae, cause solid areas in one or more lobes. Other germs, like Klebsiella pneumoniae, can lead to severe infections with cavities.
|
Bacterial Pathogen |
Typical Radiographic Findings |
|---|---|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Lobar consolidation, often with air bronchograms |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
Severe consolidation, possible cavitation |
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
Bronchopneumonia pattern, often bilateral |
Viral Pneumonia Patterns
Viral pneumonias show different signs on X-rays than bacterial ones. You might see reticulonodular opacities or patchy areas of consolidation. These can spread out or appear in many spots.
Influenza and RSV are common viral causes, showing up as bilateral interstitial infiltrates. Some viruses, like varicella-zoster, can cause severe pneumonia, mainly in those with weakened immune systems.
Fungal and Opportunistic Infections
Fungal and opportunistic infections are big concerns for those with weakened immune systems. Cavitary lesions and nodules are common signs. Aspergillus species can form aspergillomas in cavities.
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) is a big worry in HIV/AIDS patients. It shows up as bilateral, symmetric, fine reticular or ground-glass opacities.
Spotting these specific signs is key for diagnosing and treating pneumonia.
Detecting Complications on Chest Radiographs
Complications from pneumonia can be spotted on chest radiographs. This shows how key it is to carefully look at these images. We’ll look at how to see issues like pleural effusion, empyema, pneumothorax, and lung abscess on these images.
Pleural Effusion: Blunting of Costophrenic Angles
Pleural effusion is a common issue after pneumonia. It’s when fluid builds up in the pleural space. On a chest radiograph, this looks like blunting of the costophrenic angles on both front and side views. Finding a pleural effusion means the infection might be serious and could need drainage.
Empyema: Loculated Fluid Collections
Empyema happens when pus builds up in the pleural space, often from pneumonia. On an X-ray, empyema shows as loculated fluid collections. These can be very serious and need the right treatment, like antibiotics and drainage.
Pneumothorax: Recognition and Sizing
Pneumothorax is when air gets into the pleural space, a complication of pneumonia. On a chest radiograph, it’s seen by the absence of lung markings beyond the collapsed lung’s edge. Knowing how big the pneumothorax is is important. Big ones might need a chest tube.
Lung Abscess: Cavity Formation with Air-Fluid Levels
A lung abscess is a serious issue from pneumonia, with a cavity in the lung. On an X-ray, a lung abscess shows as cavity formation with air-fluid levels. It needs quick treatment, usually antibiotics and sometimes draining the abscess.
Evaluating Treatment Response Through Serial Imaging
Monitoring treatment response through serial imaging is key for managing pneumonia. Serial chest radiographs help us see how well a patient is doing. They also help us catch any complications early.
Expected Timeline of Radiographic Improvement
The timeline for radiographic improvement in pneumonia patients varies a lot. We usually see initial improvements in 2-4 weeks after starting treatment. But, it can take several months for all radiographic abnormalities to clear up.
Factors influencing the rate of improvement include:
- The severity of the initial pneumonia
- The patient’s overall health and immune status
- The effectiveness of the chosen treatment regimen
- The presence of any underlying lung disease
Persistent or Progressive Radiographic Abnormalities
Seeing persistent or progressive radiographic abnormalities can mean a complication or treatment failure. Possible causes include:
- Development of a secondary infection or superinfection
- Inadequate or inappropriate antibiotic therapy
- Underlying immunocompromised state
- Presence of a non-infectious mimicker of pneumonia
In such cases, we need to reassess the patient’s clinical status. We might consider further diagnostic testing or adjust the treatment plan.
Long-term Radiographic Sequelae
Some patients may have long-term radiographic sequelae after pneumonia. These can include:
- Residual scarring or fibrosis
- Persistent atelectasis or volume loss
- Bronchiectasis or other structural lung changes
These changes can affect the patient’s lung function and overall health long-term. So, follow-up imaging and clinical assessment are vital for managing these patients.
Common Interpretation Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Diagnosing pneumonia with chest radiography needs careful attention to avoid mistakes. Interpreting chest X-rays can be tricky due to several factors. These factors can lead to wrong diagnoses if not handled correctly.
Anatomical Overlaps and Superimpositions
One big challenge in reading chest X-rays is dealing with anatomical overlaps. These can look like or hide real health issues, like pneumonia.
For example, the diaphragm can look like lung consolidation if it overlaps. To avoid mistakes, look for signs like air bronchograms or silhouetting of structures.
Patient Positioning Effects
Patient position during X-rays can greatly affect the reading. A rotated chest X-ray can make one lung look more opaque than the other. This can lead to wrong diagnoses.
It’s very important to ensure the patient is positioned correctly. Checking the spinous processes alignment can help confirm proper positioning.
Dealing with Portable Radiography Limitations
Portable X-rays, used in ICU, have their own challenges. These include variable patient position and exposure settings. These can make images hard to read.
Knowing the limits of portable X-rays is key. For example, underexposed images can hide small details.
|
Limitation |
Impact on Diagnosis |
Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Underexposure |
Difficulty detecting subtle abnormalities |
Adjust exposure factors; consider repeat radiograph if necessary |
|
Variable patient positioning |
Potential for misinterpreting anatomical structures |
Use positioning aids; verify patient alignment |
Interobserver Variability Challenges
Interobserver variability is a big challenge in reading chest X-rays. Different readers may see the same image differently, based on their experience.
To tackle this, using standard protocols and ongoing education helps. Getting a second opinion from a more experienced radiologist can also be helpful in tricky cases.
By knowing these common pitfalls and how to avoid them, healthcare professionals can make more accurate diagnoses. This leads to better care for patients.
Conclusion
Reading chest X-rays correctly is key to diagnosing and treating pneumonia. By using a systematic approach, we can get better at diagnosing and care for our patients.
This article covered how important chest X-rays are in diagnosing pneumonia. We talked about the basics of reading X-rays and the patterns seen in pneumonia. We also looked at how different germs and complications show up on X-rays.
A cough that hurts and feels like it’s burning can be a sign of pneumonia. Knowing how to help with chest congestion and cough is important. By understanding X-rays, we can find the cause of pneumonia and treat it effectively.
In short, knowing how to read chest X-rays is a must for healthcare workers dealing with pneumonia. By improving at this, we can help our patients more and lower the risk of pneumonia-related problems.
FAQ
What is the role of chest radiography in diagnosing pneumonia?
Chest radiography is key in diagnosing pneumonia. It helps find pneumonia, see how far it has spread, and check if treatment is working.
How does chest radiography impact patient outcomes in pneumonia?
Chest radiography helps start treatment quickly. This is important for better patient outcomes in pneumonia.
What are the typical radiographic patterns seen in pneumonia?
Pneumonia shows up on X-rays as white spots in the lungs. These spots can be patchy, spread out, or in one area.
How do different types of pneumonia-causing organisms affect radiographic findings?
Bacterial pneumonias show white spots in the lungs. Viral infections might look like a net or patchy white areas.
What complications of pneumonia can be visualized on chest radiographs?
Chest X-rays can spot complications like fluid in the lungs, abscesses, and air in the chest. These can affect how well a patient does.
How is treatment response monitored through serial chest radiographs?
Chest X-rays track how well treatment is working. They help doctors know if they need to change the treatment plan.
What are some common challenges in interpreting chest radiographs for pneumonia?
Reading chest X-rays can be tricky. Issues like overlapping images, bad positioning, and different opinions can make it hard. But, knowing these challenges helps.
How can healthcare professionals improve their diagnostic skills in reading chest radiographs for pneumonia?
To get better at reading chest X-rays, follow a step-by-step approach. Know the common mistakes and what pneumonia looks like. This will help improve your skills.
What is the significance of understanding radiographic densities in chest radiography?
Knowing about radiographic densities is key. It helps doctors tell normal from abnormal on chest X-rays.
How does the ABCDE method aid in chest X-ray interpretation?
The ABCDE method is a helpful guide. It ensures a thorough check of the chest X-ray.
What are the radiographic characteristics of a tight chest after a cold?
A tight chest after a cold might mean pneumonia is not fully gone. X-rays might show white spots or fluid in the lungs.
How can chest congestion with headache be evaluated on a chest radiograph?
Chest X-rays can spot congestion and headache causes. They look for white spots or fluid in the lungs.
What helps alleviate chest congestion and cough associated with a cold?
To ease congestion and cough, doctors might use medicines. These can include expectorants, bronchodilators, and antibiotics if needed.
How can severe cough and chest congestion be managed?
Severe cough and congestion need a mix of treatments. This includes medicines to stop coughing and help breathe, and rest and fluids.
What is the difference between acute bronchitis and a chest cold?
Acute bronchitis is inflammation of the airways, causing cough and sputum. A chest cold is a broader term for respiratory symptoms.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5922324/