Dermatology focuses on the health of the skin, hair, and nails. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of acne, eczema, skin cancer, and cosmetic procedures.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
Dermatology is the branch of medicine focused on diagnosing, treating, and preventing problems with the skin, hair, nails, and mucous membranes. The skin is our largest and most visible organ, protecting us from germs, injuries, and harmful substances in the environment. Dermatology stands out because it includes medical, surgical, and cosmetic care. Dermatologists help with many conditions, from common ones like acne, eczema, and warts to serious illnesses such as melanoma and autoimmune skin diseases. Skin problems can also be early signs of other health issues, like lupus or liver disease. The main aim is to keep the skin healthy and looking its best.
Skin disorders come in many forms and can range from mild to severe. Some are short-term, like hives or infections, while others are long-lasting, such as psoriasis or rosacea. Some involve changes in skin structure, like moles or cysts. These conditions often include inflammation, infection, or unusual cell growth.

Information about facilities: Highlight the advanced technological infrastructure. Mention the Digital Dermoscopy unit for mapping moles and detecting skin cancer early. Describe the Phototherapy units (PUVA/NB-UVB) for treating chronic conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo. Emphasize the Laser Center, equipped with specific wavelengths for vascular lesions, pigmentation, and scar revision.
Here’s an interesting fact: your skin is always renewing itself. Every minute, you lose about 30,000 to 40,000 dead skin cells. In just 28 days, you have a brand new outer layer of skin, which is important for healing and protection.

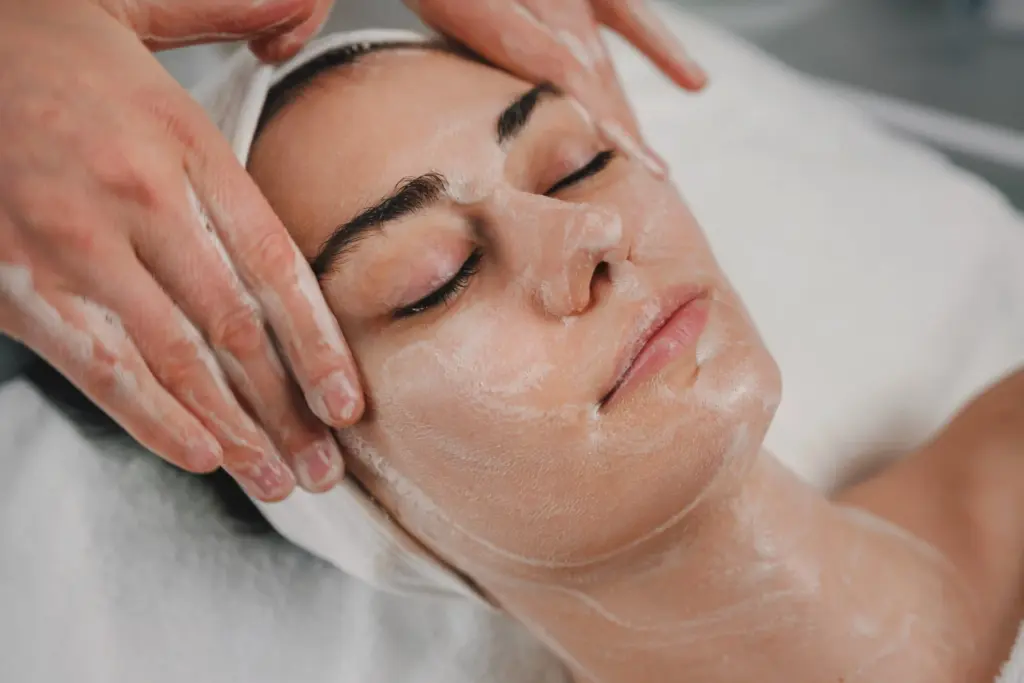
Skin conditions can affect both your body and your mind. Physically, they may cause itching, pain, or make you more likely to get infections. Because skin problems are often visible, they can also lead to social stigma, anxiety, and lower self-confidence. Severe cases, like bad acne or psoriasis, can have a big impact on mental health and social life.
Who is at risk: Identify risk factors. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause of skin aging and cancer. Genetics plays a huge role in eczema and psoriasis. Allergens (fragrances, metals) and environmental pollutants trigger reactions. Stress is known to exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions.
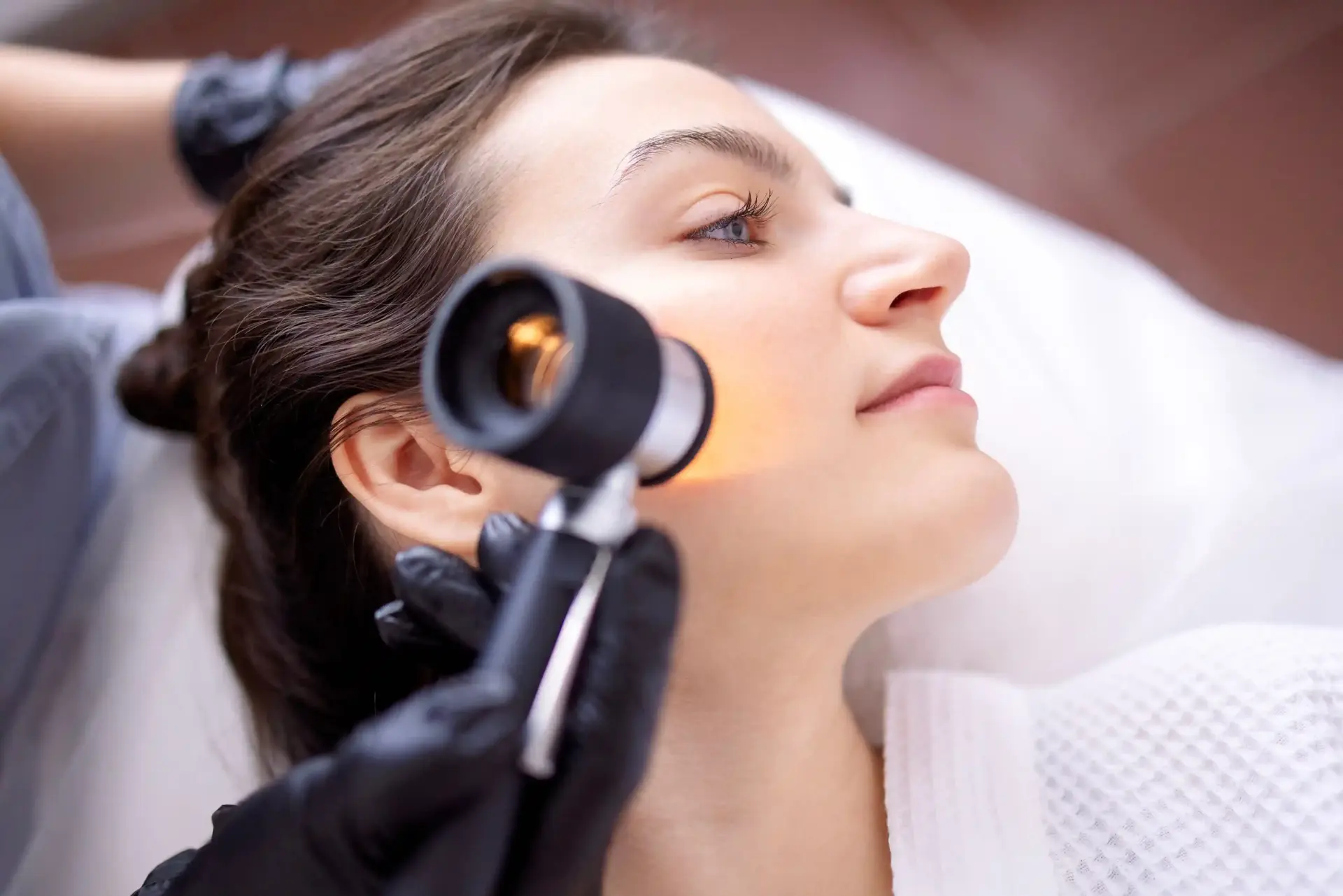
Diagnosing skin conditions starts with a careful look at your skin. Doctors often use a tool called a dermoscope, which is a special magnifier with light, to see details that aren’t visible to the naked eye. Sometimes, a small sample of skin (a biopsy) is taken to check for cancer or complex rashes. Patch testing can help find out if you are allergic to certain substances.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
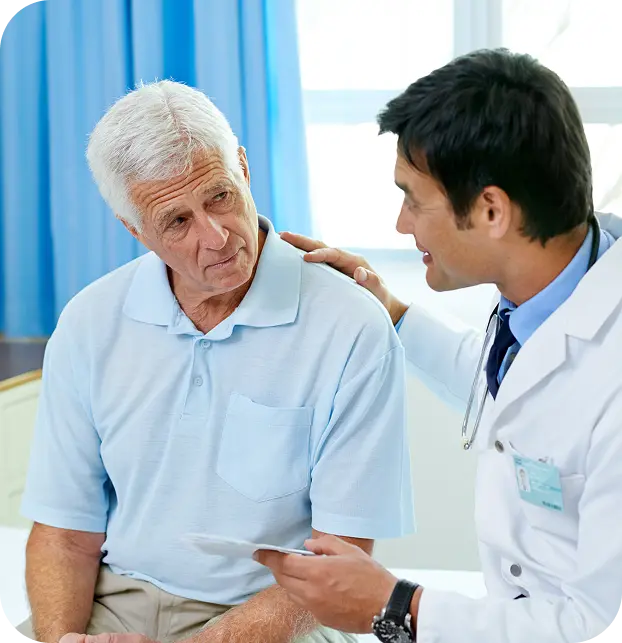

A dermatologist is a specially trained doctor who looks beyond what’s on the surface. They can tell the difference between a harmless mole and a dangerous melanoma. They also figure out if a rash needs antibiotics for an infection or steroids for an autoimmune problem.
Treatment for skin conditions is tailored to each person. It can include creams or ointments applied to the skin, or medicines taken by mouth, like antibiotics or retinoids. For long-term inflammatory diseases, newer treatments called biologic injections target certain parts of the immune system to help clear the skin.
Journey details: Outline the patient’s path. For surgical procedures (such as cyst removal or cancer excision), the procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting. For cosmetic concerns, plans may involve a series of laser sessions. Monitoring is key to balancing treatment efficacy with safety in chronic conditions.
Complex skin problems often need a team approach. Dermatologists work closely with other specialists, like rheumatologists for psoriatic arthritis, oncologists for advanced melanoma, and plastic surgeons for reconstruction after removing large tumors. This teamwork helps make sure you get complete care for both medical and surgical needs.
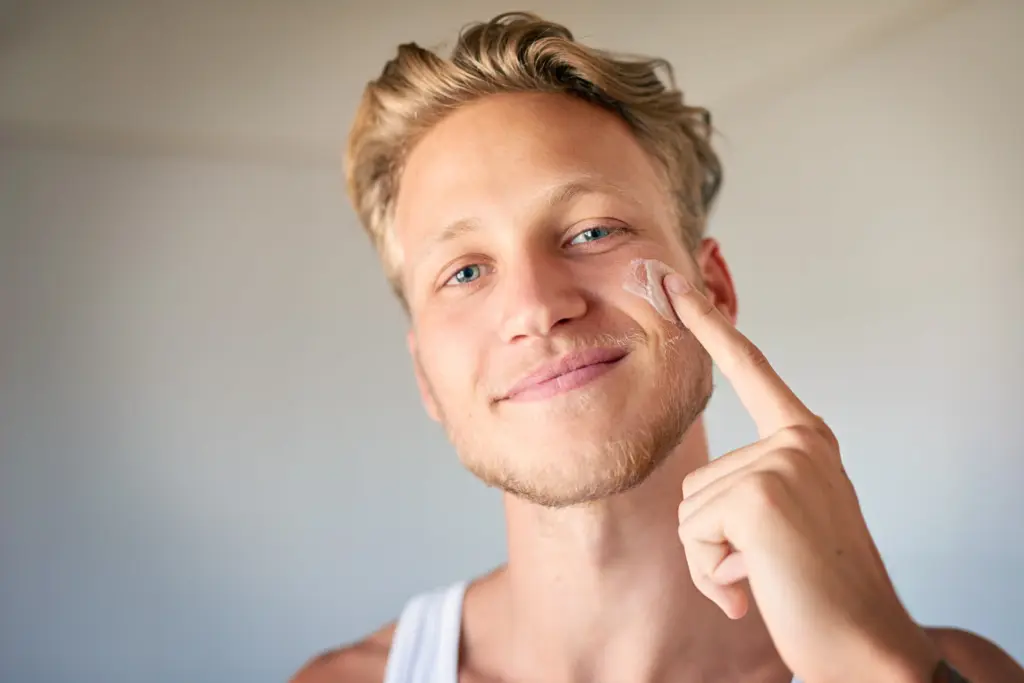

Before starting treatment, it’s important to be prepared. If you’re having laser therapy, you need to avoid the sun before and after to prevent burns. For acne treatments like Isotretinoin, your doctor will closely monitor your liver and cholesterol levels. Remember, skin healing takes time, and it may be weeks before you see results.
Good skin care is built on a few key habits. Using sunscreen is the best way to prevent aging and skin cancer. Regularly checking your skin helps you spot changes in moles early. Keeping your skin moisturized and following gentle routines can protect your skin barrier and help prevent problems like eczema or irritation.
In an era where non-medical personnel often perform skin procedures, Liv Hospital stands for medical safety and expertise.
Our clinic is equipped with the latest FDA-approved laser and energy devices.
We understand that the skin reflects internal health.
At Liv Hospital, we combine the science of medicine with the art of aesthetics to help you feel comfortable and confident in your own skin.
A dermatologist must complete medical school, followed by a one-year internship and a specialized three-year residency program focused exclusively on the skin, hair, and nails, culminating in board certification exams.
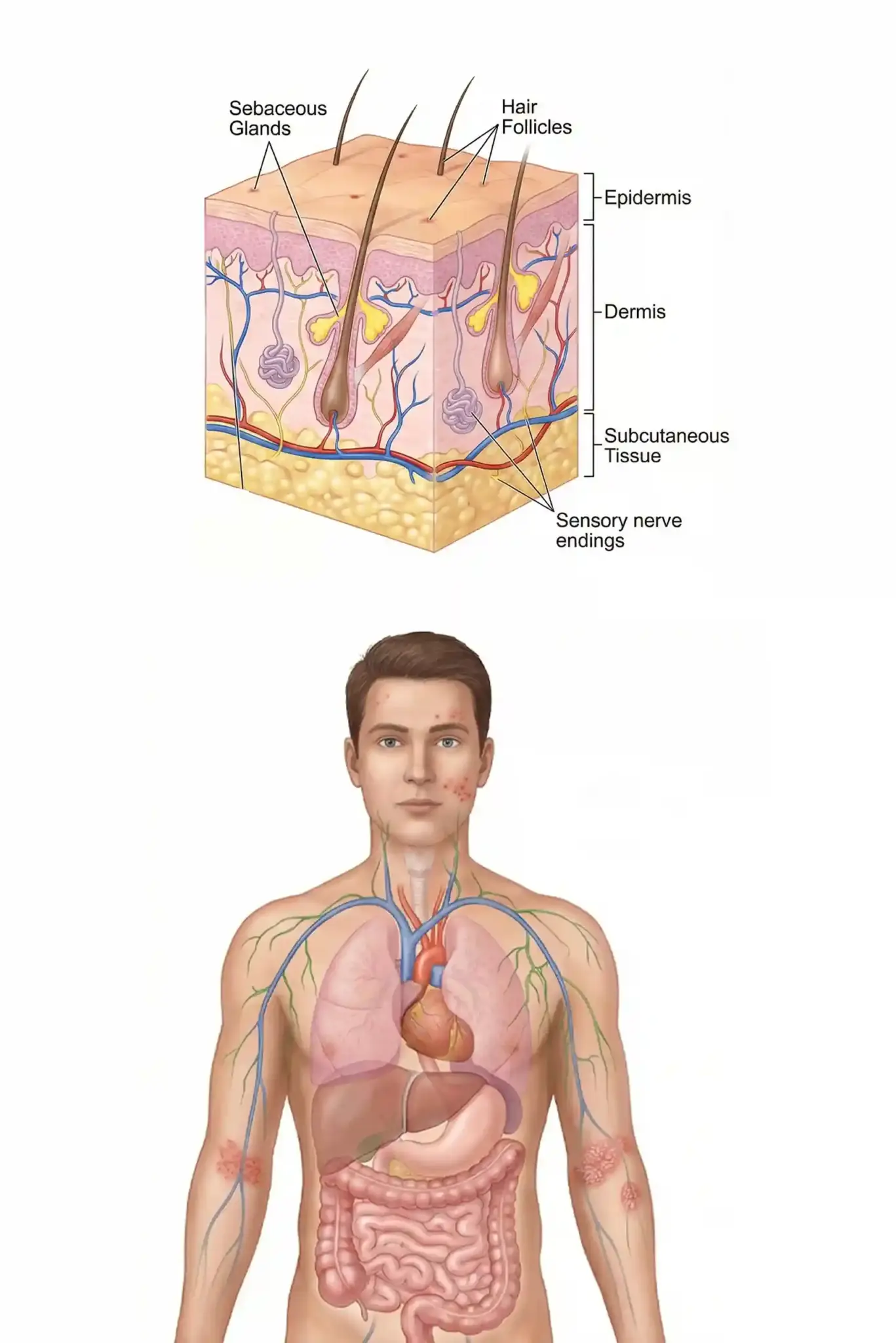
While the skin is the primary focus, they also treat conditions affecting the hair, nails, and mucous membranes (mouth, nose, eyelids), as all these tissues are biologically related.
The skin is considered an organ because it is composed of multiple tissues that work together to perform specific, vital functions, such as protection, temperature regulation, and sensation, just like the heart or liver.
The skin consists of three main layers: the epidermis (outermost), the dermis (middle structural layer), and the hypodermis (deepest fat layer), which connects to the muscles and bones below.
Yes, dermatologists are trained in dermatologic surgery to remove skin cancers, moles, and cysts, and to perform cosmetic procedures; some undergo further fellowship training for complex surgeries such as Mohs micrographic surgery.


how long does it take for a scab to heal Nearly 5 million people in the United States get surgical excisions every year. After such

ultraviolet radiation lamp Phototherapy, or light therapy, uses specific light wavelengths. It’s often used for jaundice in newborns and some skin issues. Studies show it’s

Over 1 in 5 Canadians will get cancer, says the Canadian Cancer Society. This shows how key accurate diagnosis is. But can a surgeon reliably
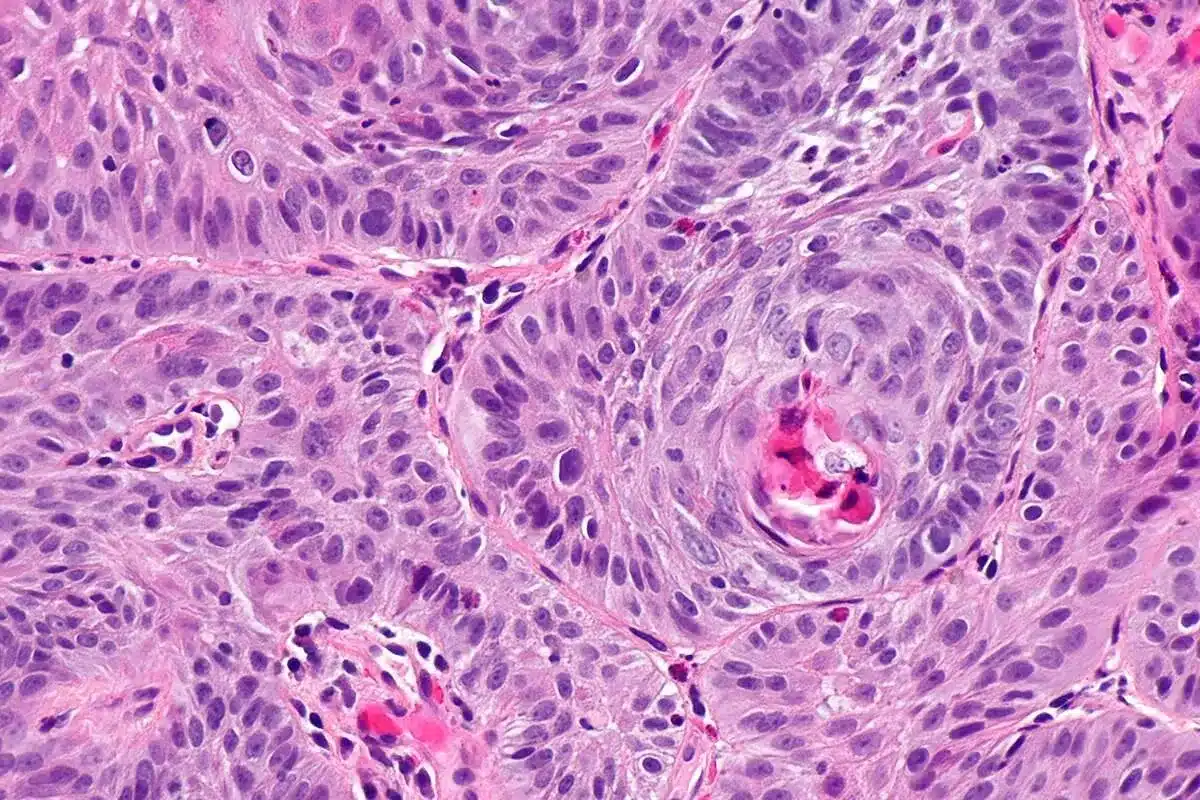
Squamous cell carcinoma is a common skin cancer found in thousands globally each year. It’s a big worry, as one in five Americans will get
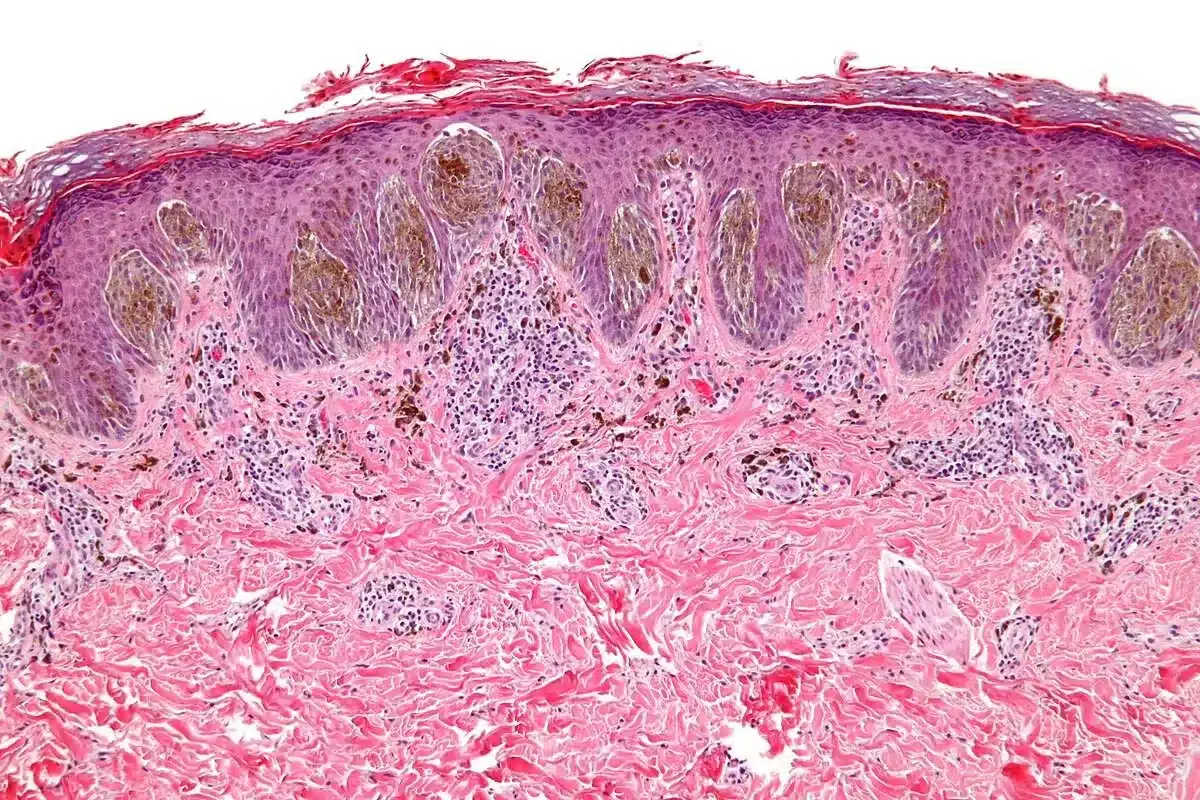
Melanoma is a dangerous form of skin cancer. If caught early, it has a very good treatment outcome. The American Academy of Dermatology says the
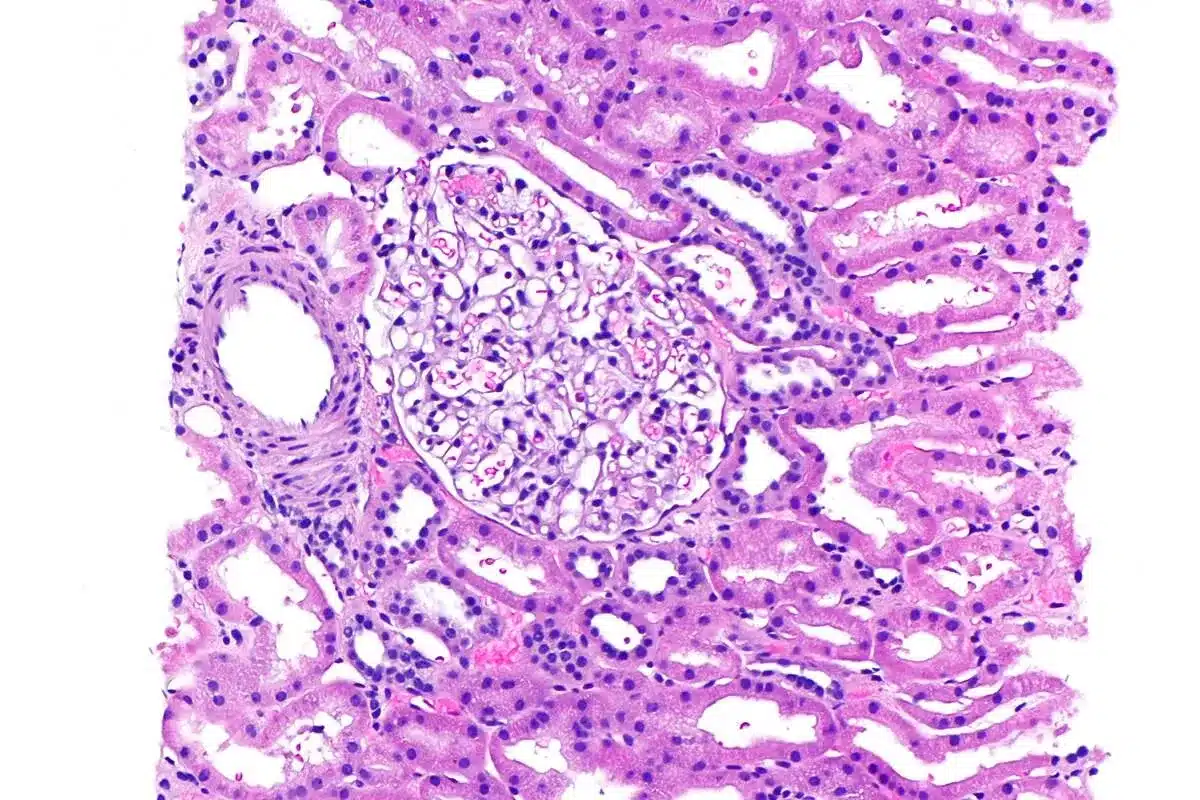
Nearly 1.8 million new cancer cases are diagnosed every year in the United States. Biopsies are key in finding these cases. A biopsy means taking

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)