Mesenchymal, in medical terms, refers to cells arising from the mesenchyme”the embryonic connective tissue that plays a crucial role in forming a variety of tissues like bone, cartilage, and fat. Mesenchymal mean relates to the origin and characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are multipotent and pivotal in regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into multiple cell types and modulate the immune response. Understanding what mesenchymal means helps grasp the versatile functions of MSCs in healing and tissue repair.
MSCs are also called mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells. These names show their wide range of roles in the body. They are key in fixing tissues and controlling the immune system.
Key Takeaways
- Mesenchymal stem cells are known by multiple names, including mesenchymal stromal cells and medicinal signaling cells.
- The various names reflect the diverse roles and functions of MSCs in the body.
- MSCs play a critical role in tissue repair and immune system modulation.
Definition of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Characteristics
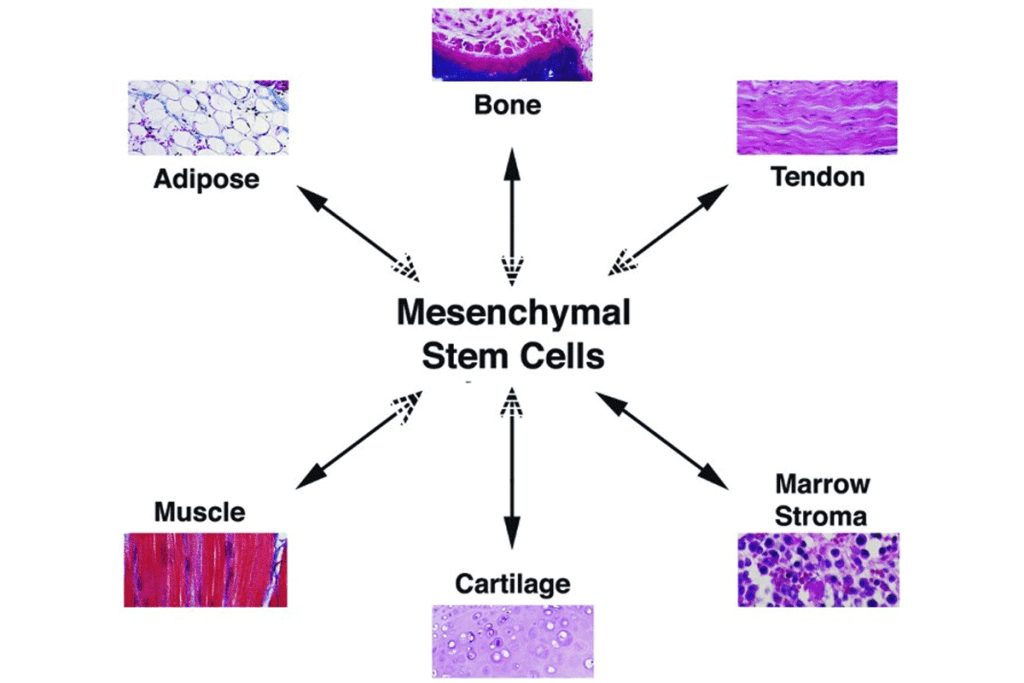
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are key in fixing and growing new tissues. MSCs are multipotent stem cells that can turn into different cell types. This skill is essential for fixing damaged tissues.
MSCs are defined by their ability to change into various cells and help the blood-making system. They also have immunosuppressive properties. This means they can calm down the immune system, helping to heal tissues.
Mesenchyme tissue is where MSCs come from. It’s a type of tissue that starts from the embryonic mesoderm. It’s important for growing and fixing tissues and organs. Knowing about mesenchyme tissue helps us see how MSCs can help in regenerative medicine.
- Multipotency: MSCs can turn into many cell types.
- Immunosuppressive properties: MSCs can calm the immune system.
- Tissue repair: MSCs help fix and grow new tissues.
Mesenchyme is a loose connective tissue that helps in tissue growth and healing. MSCs’ ability to change into different cells and calm the immune system makes them a focus in regenerative medicine.
The Origin and Discovery of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells, or MSCs, were first found in bone marrow. Later, they were discovered in other tissues too. Their discovery opened up new ways to understand how they help in healing and regrowing tissues.
At first, MSCs were taken from bone marrow. They could turn into different cell types like bone, cartilage, and fat cells. This made them very interesting for medical use. Now, MSCs are found in fat, dental pulp, and umbilical cord, among others.
Knowing MSCs are in many tissues has helped us see their role in health and sickness. It’s important to manage them well to use their healing powers. This means knowing how to get them, study them, and use them in medicine.
| Tissue Source | Year of Discovery | Key Characteristics |
| Bone Marrow | 1960s | Multipotent, ability to differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes |
| Adipose Tissue | 2000s | Easy to isolate, high proliferation rate |
| Dental Pulp | 2000s | Highly accessible, high chance of turning into nerve cells |
| Umbilical Cord | 2000s | Helps control the immune system, good for use between different people |
The table shows how MSCs were found in different places and what makes them special. Knowing these things is key to using MSCs for healing and growing new tissues.
What Does “Mesenchymal Mean”? Etymology and Scientific Context
The term “mesenchymal” comes from the concept of mesenchyme, a key tissue in development. To grasp its meaning, we must look into its etymology and scientific background.
The word “mesenchymal” is linked to “mesenchyme,” a cell network that turns into different connective tissue cells. These include bone, cartilage, and fat cells. The term “mesenchyme” itself is from Greek, with “mesos” meaning middle and “enchyma” meaning infusion or pouring in.
Common Misspellings: “Mesemchymal” and Other Variants
When talking about “mesenchymal,” misspellings like “mesemchymal” are common. These errors can confuse and make search results less accurate.
- “Mesemchymal” is a common misspelling that results from a typographical error.
- Other variants might include “mesanchymal” or “mesenchimal,” which are not recognized terms in the scientific community.
Breaking Down the Term “Mesenchymal”
To really understand “mesenchymal,” let’s break it down. This helps us see its role in science.
- The prefix “mes-” shows a link to the mesoderm, a germ layer in embryos that forms connective tissue.
- The root “enchymal” points to mesenchyme, highlighting its role in creating various connective tissues.
Knowing the etymology and meaning of “mesenchymal” helps us dive into the world of mesenchymal stem cells.
What is Mesenchyme Tissue and Its Relationship to MSCs
mesenchyme tissue
Mesenchyme is a key type of tissue in the early stages of development. It plays a big role in creating different types of connective tissues.
Mesenchyme comes from the mesoderm, one of the three main layers in an embryo. This layer is responsible for making bone, cartilage, and fat tissues.
Developmental Origins of Mesenchyme
The origins of mesenchyme are linked to the mesoderm. In early development, the mesoderm splits into different cells. These cells then form various connective tissues.
Mesenchyme is Known as What Type of Tissue?
Mesenchyme is called a type of embryonic connective tissue. It can turn into different cells like osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes.
| Tissue Type | Characteristics | Derived Cell Types |
| Mesenchyme | Embryonic, undifferentiated | Osteoblasts, chondrocytes, adipocytes |
| Connective Tissue | Supports other tissues | Fibroblasts, osteocytes, chondrocytes |
Functions of Mesenchyme in the Body
Mesenchyme’s main job is to create connective tissues. These tissues offer structural support, help with repair and regeneration, and aid in the immune response.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are connected to mesenchyme. They come from the same early stages and can turn into different cell types, just like mesenchyme.
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: The Most Common Alternative Name
The way we talk about mesenchymal stem cells has changed. Now, “mesenchymal stromal cells” is a common name. This change shows we understand these cells better.
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are found in places like bone marrow, fat, and umbilical cord tissue. They’re getting a lot of attention because of their possible uses in helping people.
Reasons for the Terminology Shift from “Stem” to “Stromal”
The name change from “stem” to “stromal” for MSCs comes from a better understanding of their role. “Stem” suggests they can turn into different cell types. But “stromal” means they help tissues work and stay healthy.
Several things led to this name change:
- Increased understanding of MSC function: Studies have shown MSCs help tissues stay healthy through signals, not just by changing into other cells.
- Recognition of MSC heterogeneity: Knowing MSCs are different from each other has made us rethink their name.
- International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) guidelines: The ISCT suggests calling them “mesenchymal stromal cells” to better describe them.
Caplan, a leader in MSC research, says “stromal” is a better term. It shows how our view of MSCs is changing and why we need clear names.
Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs): A Terminology Evolution
multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells
Research on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has led to a change in how we call them. Now, we say “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells.” This change shows we understand more about their abilities. It also shows how complex MSCs are and their role in our bodies.
The term “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells” highlights their ability to become different types of cells. This is important in mes management. It changes how we see and use these cells in medicine and research.
This change in names also shows we now know MSCs can do more. The table below shows the main differences between the old and new names.
| Terminology | Characteristics |
| Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) | Originally thought to be stem cells with limited differentiation |
| Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells | Now known for their ability to become many cell types and help repair tissues |
The move to “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells” shows we understand these cells better. This is good for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
In summary, calling them “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells” is a big step in mes management and MSC research. It gives a clearer picture of what they can do and their possibilities.
Medicinal Signaling Cells: A Proposed Modern Term
The term “medicinal signaling cells” is now used instead of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). It shows their healing power. This change is because it focuses on how these cells help fix tissues through signals.
Arnold Caplan, a leading MSC researcher, is behind this name change. To understand why, we need to look at Caplan’s views and the reasons for this shift.
Caplan’s Rationale for Renaming MSCs
Arnold Caplan is known as the “father of mesenchymal stem cells.” He believes the name “mesenchymal stem cells” is misleading. Caplan says MSCs don’t just act like stem cells. They mainly help by sending signals that aid healing and control the immune system.
Caplan’s research shows MSCs are more than stem cells. They are cells that send healing signals. Studies back this up, showing MSCs can treat many diseases and injuries. They do this by signaling to other cells, not by turning into specific cell types.
The term “medicinal signaling cells” captures this understanding. It highlights their role in sending healing signals, not just their stem cell traits. This change is more than just a name. It shows a deeper understanding of MSCs and their healing powers.
| Key Features | Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) | Medicinal Signaling Cells |
| Primary Function | Differentiation into various cell types | Paracrine signaling and immune modulation |
| Therapeutic Potentia | Repair and replacement of damaged tissues | Promotion of healing through signaling mechanisms |
| Nomenclature Emphasis | Stem cell properties | Medicinal signaling capabilities |
The table above shows the main differences between MSCs and medicinal signaling cells. By renaming MSCs, researchers want to stress their healing abilities and how they work.
Tissue-Specific Names for Mesenchymal Stem Cells
mesenchymal stem cells tissue-specific names
Tissue-specific names for MSCs give us insight into their origins and uses. These cells are named after the tissue they come from. This shows their wide range of sources and medical uses.
Bone Marrow-Derived MSCs
Bone marrow-derived MSCs are widely studied. They come from bone marrow and can turn into different cell types. This includes osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. They are used to treat bone and cartilage problems.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Adipose-derived stem cells come from fat tissue. They are easy to get and can turn into many cell types. These cells are being looked at for regenerative medicine, like repairing tissues and for beauty treatments.
Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Dental pulp stem cells come from tooth pulp. They can turn into different cell types, like odontoblasts and osteoblasts. They are being studied for dental repair and regenerative treatments.
Umbilical Cord-Derived MSCs
Umbilical cord-derived MSCs come from the umbilical cord after birth. They are valuable because they are easy to get and can help the immune system. They are being tested for treating diseases related to inflammation and immune issues.
The different names for MSCs show their complexity and versatility. Knowing about their sources and characteristics is key for improving their use in medicine. This is important for mes management in healthcare.
MES Management: Clinical Applications and Handling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Managing mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) well is key for their success in medicine. MSCs are promising for fixing damaged tissues and boosting the immune system. They can turn into different cell types.
MSCs are used in many ways, like treating diseases and fixing damaged tissues. As scientists learn more, MSCs are being used more in treatments and studies.
Laboratory Protocols for MSC Isolation and Culture
To get MSCs ready for use, special steps are followed. These steps help keep the cells healthy and strong. Here’s what happens:
- First, cells are taken from a patient or donor.
- Then, MSCs are separated using special techniques.
- Next, they are grown in a special mix that helps them grow.
- After that, the MSCs are checked to make sure they are what they should be.
Quality Control in Clinical Applications
Quality control is very important for MSC treatments. It makes sure the cells are safe and work well. Here are some important parts:
| Parameter | Description | Importance |
| Cell Identity | Checking if cells are MSCs | It’s important they are MSCs |
| Viability | Checking if cells are alive after freezing | It’s key for them to work well |
| Potency | Testing how well MSCs work | It shows how good they are for treatment |
By following strict steps and quality checks, MSCs can be used in new ways. This opens up new possibilities for fixing damaged tissues and boosting the immune system.
Conclusion: Navigating the Terminology of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
The world of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) is filled with complex terms. These terms change and are often used in different ways. It’s key to grasp the details of MSC language to make research and treatments clear.
Mesenchyme is a special tissue that helps MSCs grow and work. It’s a network of cells from early development. This tissue turns into different types of cells, including MSCs.
It’s easy to get confused with terms like “mesemchymal.” But, using the right words is important to avoid mistakes. MSCs are also called mesenchymal stromal cells and medicinal signaling cells. This shows how our understanding of them is growing.
As we learn more about MSCs, knowing the right terms helps everyone talk clearly. This includes researchers, doctors, and patients. By understanding MSC names, we can explore their full possibilities.
FAQ
What does “mesenchymal” mean?
“Mesenchymal” refers to cells or tissue from the mesoderm, a key layer in embryos. These cells can turn into different types, like connective tissue cells.
What is mesenchyme tissue?
Mesenchyme tissue is loose and not fully formed. It’s found in the body and helps in tissue growth and repair.
What is the difference between mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stromal cells?
MSCs and mesenchymal stromal cells are often confused. MSCs can change into many cell types. Stromal cells are a wider group, not always stem cells.
What are some common misspellings of “mesenchymal”?
People often misspell “mesenchymal” as “mesemchymal.” This mistake comes from the term’s complexity and its less-known nature.
What is the significance of mesenchymal stem cells in clinical applications?
MSCs are being studied for many uses, like fixing damaged tissues and controlling the immune system. They might help with diseases like osteoarthritis and autoimmune disorders.
How are mesenchymal stem cells isolated and cultured in the laboratory?
MSCs are taken from tissues like bone marrow and fat. They’re isolated using special methods and then grown in labs with specific media.
What is the importance of quality control in the clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells?
Quality control is key for MSCs in medicine. It makes sure the cells are safe and work well. This includes checking for purity and proper storage.
What are some tissue-specific names for mesenchymal stem cells?
MSCs from different tissues have their own names. For example, bone marrow MSCs, fat-derived stem cells, and those from umbilical cords.
What is the rationale behind renaming MSCs to “medicinal signaling cells”?
“Medicinal signaling cells” is suggested as a new name for MSCs. It highlights their ability to send signals that help in healing.
What is MES management in the context of mesenchymal stem cells?
MES management deals with how MSCs are handled and used in medicine. It includes how they’re grown in labs and checked for quality.
References
- Caplan, A. I. (2017). Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Time to Change the Name! Stem Cells Translational Medicine, 6(6), 1445-1451. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.17-0051



































