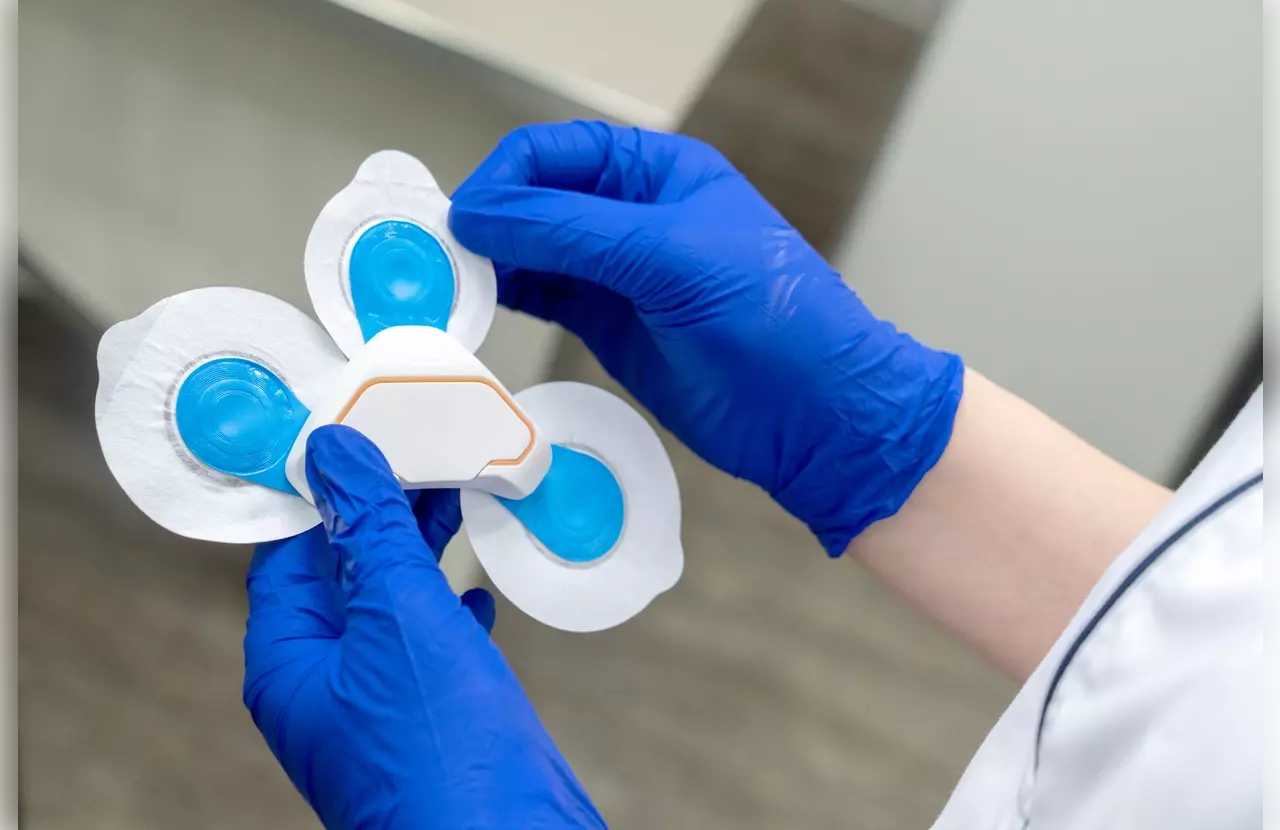
Medical technology is advancing fast with stem cell patches. These devices help repair tissues and reduce swelling. They are made from biocompatible materials like extracellular matrix, biodegradable polymers, or hydrogels. These materials help cells stick together and deliver treatments.
Some patches also have bioactive nanocrystals or growth factor coatings to work better. As research grows, stem cell patches are being tested for many uses. These include healing wounds, fixing heart damage, and treating nerve problems.
Key Takeaways
- Stem cell patches are made from biocompatible materials like extracellular matrix and biodegradable polymers.
- These patches provide a scaffold for cell adhesion and therapeutic delivery.
- Experimental patches use bioactive nanocrystals or growth factor coatings to enhance functionality.
- Applications include wound healing, cardiac regeneration, and treating neuropathy.
- Current research is focused on exploring the benefits and limits of stem cell patches.
The Science of Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
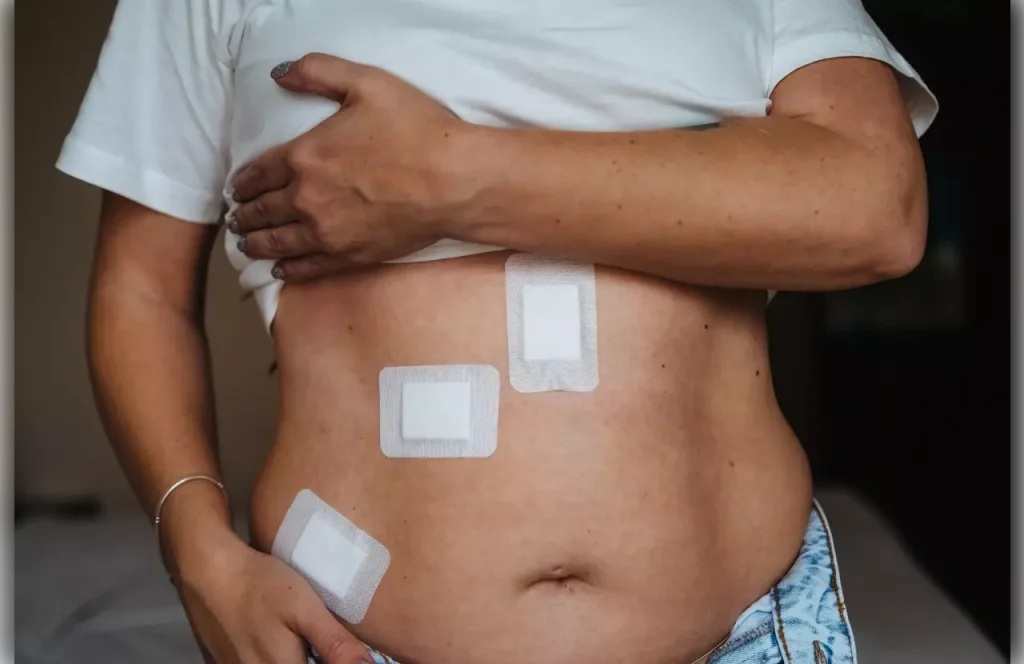
Regenerative medicine, powered by stem cells, is changing how we heal and repair tissues. We’re seeing a big change in medical treatments, with stem cells at the heart of it.
What Makes Stem Cells Unique
Stem cells can turn into different cell types. This makes them key for fixing damaged tissues and growing new ones. They can help fix heart damage and treat brain disorders.
Some stem cell patches use special nanocrystals or growth factors instead of cells. This shows how flexible stem cell tech can be.
The Evolution of Stem Cell Delivery Methods
How we deliver stem cells has changed a lot. We used to just inject them, but now we have patches. These patches release growth factors or help cells grow.
Stem cell patches are great because they’re easy to use and keep releasing medicine. They can help with problems like cracked fingertips, caused by the environment or health issues like eczema or diabetes.
| Delivery Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Injection | Stem cells are injected directly into the target area | Immediate delivery, targeted treatment |
| Stem Cell Patches | Patches release growth factors or provide a scaffold for cell growth | Non-invasive, sustained release of therapeutic agents |
| Light Therapy Patches | Deliver low-energy light to stimulate cellular activity | Non-invasive, promotes cellular healing |
What Are Stem Cell Patches Made Of: Core Components and Materials
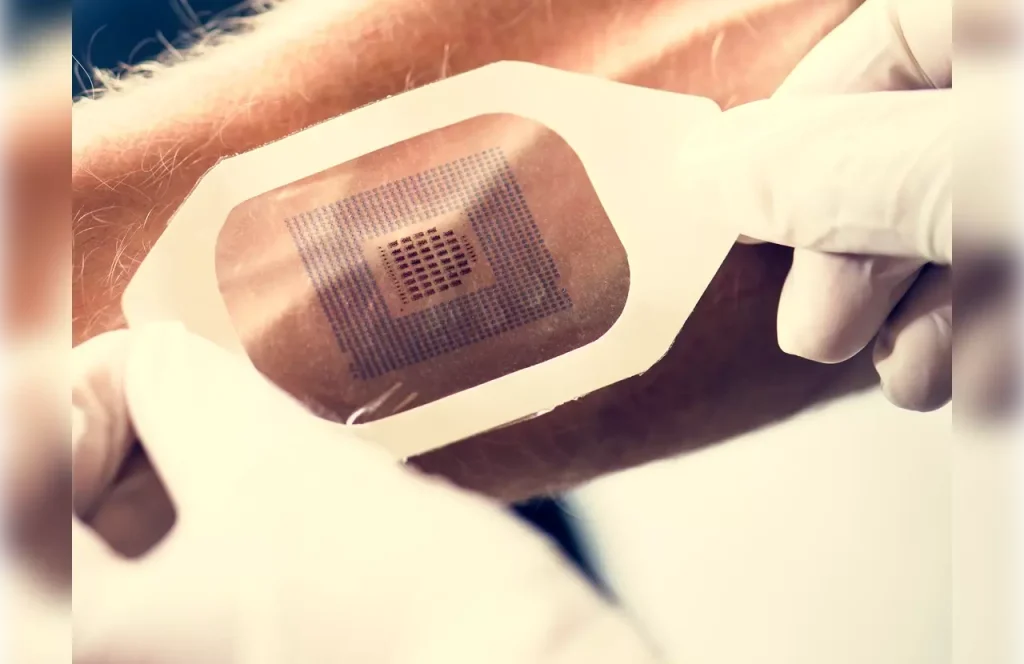
Stem cell patches are made from materials that help cells grow and heal. These materials are key to the patches’ success in delivering stem cells to the body.
Biocompatible Scaffolds and Matrices
Biocompatible scaffolds and matrices are at the heart of stem cell patches. They act like the body’s natural support system, helping cells stick, grow, and change. These can be made from extracellular matrix components like collagen or biodegradable polymers such as poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). The right material depends on the patch’s purpose and how fast it should break down.
Hydrogels and Their Role in Stem Cell Patches
Hydrogels are a key part of some stem cell patches. They hold a lot of water, creating a wet environment that helps healing and growth. Hydrogels can be made to break down at specific rates and have the right strength. They’re great for keeping cells and bioactive molecules safe.
Non-Cellular Components: Amino Acids, Sugars, and Salts
Stem cell patches also include non-cellular parts like amino acids, sugars, and salts. These help cells by providing nutrients, keeping the right balance of water, and supporting the patch’s structure. For example, amino acids help build proteins, and sugars give cells energy. It’s important that these components are safe, as some, like diethylene glycol (DEG), can be harmful.
We choose our materials carefully to make sure they work well and are safe. The mix of biocompatible scaffolds, hydrogels, and other components helps achieve the goals of stem cell patch therapy.
Types of Stem Cell Patches Available Today
Stem cell technology is growing fast, leading to many types of stem cell patches. These patches meet different needs in therapy. They show how regenerative medicine is getting better and wider in use.
Cell-Loaded vs. Cell-Free Patches
Stem cell patches fall into two main groups: cell-loaded and cell-free. Cell-loaded patches have live stem cells that are applied to the area needing repair. On the other hand, cell-free patches use materials like growth factors to start cell activity without adding cells.
Key differences between cell-loaded and cell-free patches:
- Cell-loaded patches have live stem cells.
- Cell-free patches use materials to start cell activity.
- Cell-loaded patches might repair tissues more directly.
- Cell-free patches are more stable and last longer.
Stem Cell Activation Patches
Stem cell activation patches boost the body’s stem cell work. They have compounds that wake up and move stem cells to repair tissues. Some use bioactive nanocrystals or growth factors to work.
Stem Cell Reactivation Patches
Stem cell reactivation patches wake up dormant stem cells. They help the body fix itself better. This can help with conditions like psoriasis, where skin cells grow too fast.
PEX Patches: Technology and Materials
PEX patches use special technology and materials. Their exact makeup can change, but they often use new biomaterials for healing. Knowing how PEX patches work is key to seeing their benefits.
Key features of PEX patches:
- They use advanced biomaterials.
- They might help heal tissues better.
- They work in ways that might be different from other patches.
The Technology Behind Stem Cell Phototherapy Patches
Stem cell phototherapy patches use light therapy to boost stem cell activity. They send specific light wavelengths to the body. This helps repair and grow tissues.
Influence of Light Therapy on Cellular Activity
Light therapy helps cells heal better. It makes stem cells grow and change into different types. This is key for fixing damaged tissues.
Light therapy works by turning on growth and repair signals in cells. This can make tissues heal faster. It also helps in many medical treatments.
Key Effects of Light Therapy on Stem Cells:
- Increased cellular proliferation
- Enhanced differentiation of stem cells
- Stimulation of natural healing processes
Design and Components of Stem Cell Light Therapy Patches
Stem cell light therapy patches have special parts. They have LEDs or other light sources, safe materials, and sometimes nanocrystals. These help the therapy work better.
The design makes sure the light reaches the right spot safely. This boosts the therapy’s benefits and cuts down on side effects.
Role of Bioactive Nanocrystals
Bioactive nanocrystals are added to some patches. They make the light therapy stronger. This can lead to better tissue repair and growth.
Using nanocrystals is a new way to make stem cell phototherapy more effective. It opens up new ways to treat medical issues.
How Do Stem Cell Patches Work: Delivery and Activation Mechanisms
Stem cell patches are a new way in regenerative medicine. They deliver treatments without surgery, helping the body heal itself. These patches work with the body’s natural healing to fix and grow tissues.
Transdermal Delivery Systems
Stem cell patches use a special skin delivery system. This system lets the treatments go straight to where they’re needed. It skips the digestive system, keeping the treatments strong and effective.
Growth Factor Release and Signaling Pathways
These patches release growth factors. These factors are key for telling cells what to do. They help cells grow, change, and multiply, supporting healing and growth.
Stimulation of Endogenous Stem Cells
Another important thing is waking up the body’s own stem cells. By doing this, the patches help the body heal itself better. This can help with many health issues.
Tissue Integration and Regeneration Processes
The main goal of stem cell patches is to help tissues heal and grow. They do this by sending treatments and waking up stem cells. This leads to new tissue and better health.
| Mechanism | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Transdermal Delivery | Efficient transfer of therapeutic agents through the skin | Improved bioavailability, reduced degradation |
| Growth Factor Release | Stimulation of cellular signaling pathways | Enhanced cellular activity, tissue repair |
| Endogenous Stem Cell Stimulation | Activation of body’s natural stem cells | Promotes natural healing, tissue regeneration |
| Tissue Integration | Formation of new tissue structures | Restoration of tissue function, healing |
Knowing how stem cell patches work is key to seeing their benefits. As research grows, we’ll see more progress in this field.
Medical Applications of Stem Cell Patches
Researchers are looking into many uses for stem cell patches. They’re studying how these patches can help with wound healing and fixing damaged hearts. These patches might also treat other medical issues.
Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration
Stem cell patches could help heal wounds and grow new skin. They might make it easier for people with long-lasting wounds or serious skin damage to get better.
Vitamins E and C are important for skin health. Stem cell patches might help by making more cells.
Stem Cell Patches for Neuropathy Treatment
Stem cell patches might also treat neuropathy. They could help grow new nerves and reduce swelling. This could help people with nerve pain.
Other Emerging Clinical Applications
Stem cell patches are also being looked at for other uses. These include:
- Tissue engineering
- Orthopedic repair
- Anti-aging treatments
| Application | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Wound Healing | Enhanced tissue regeneration, improved wound closure |
| Cardiac Repair | Regeneration of damaged heart tissue, improved heart function |
| Neuropathy Treatment | Nerve regeneration, reduced neuropathic symptoms |
As research keeps going, we’ll see more uses for stem cell patches. This could bring new treatments to patients all over the world.
Claimed Benefits of Stem Cell Patch Therapy
Stem cell patch therapy is gaining attention for its possible benefits. It’s important to look at both the good and the bad sides. These patches are marketed to help with tissue repair, reduce inflammation, manage pain, and offer a non-invasive treatment.
Enhanced Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Stem cell patches are said to help repair and grow new tissue. They are believed to boost the body’s healing process. This could lead to better healing of wounds, damage, and degenerative conditions.
Inflammation Reduction
They are also claimed to reduce inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a big problem in many diseases. Stem cell patches might help control the immune system, lowering inflammation.
Pain Management and Symptom Relief
Stem cell patch therapy is also for pain relief and symptom management. The patches release growth factors and other molecules. These might help ease pain and improve symptoms in different conditions.
Convenience and Non-Invasive Nature
Stem cell patches are easy to use and don’t hurt. They are applied on the skin, unlike some other treatments that need injections or surgery. This makes them more available to many people.
Even though they promise to repair tissue and reduce inflammation, there’s not much solid evidence. Some medicines can dry out the skin, making it harder for patches to work well.
“The field of stem cell therapy is rapidly evolving, but it’s essential to tell the difference between promising research and proven treatments.”
| Claimed Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Tissue Repair | Promotes natural healing, potentially improving wound healing and tissue damage outcomes |
| Inflammation Reduction | Modulates immune response, potentially reducing chronic inflammation |
| Pain Management | Releases growth factors to alleviate pain and improve symptoms |
| Convenience | Non-invasive, topical application making it accessible to a broader range of patients |
Scientific Evidence: Do Stem Cell Patches Really Work?
Stem cell patches show promise in medicine, but the science is not settled. It’s important to look at both the good and the bad of these products.
Review of Clinical Studies and Research
Many studies have looked at stem cell patches, with mixed results. Some have shown great promise, like in treating chronic wounds. For example, a study found that these patches helped heal diabetic foot ulcers.
Recent studies have found:
- They help repair and grow new tissue
- They can improve heart function in some patients
- They might help with nerve damage
But, we need more solid evidence to fully trust these patches.
Limitations of Current Research
While the research is encouraging, there are big gaps. Many studies have small groups and vary in quality. The World Health Organization also points out a need for better rules in the stem cell patch market.
Some major issues include:
- There’s no standard for making these patches
- Reports of side effects are not always clear
- We don’t have enough long-term data
Distinguishing Between Marketing Claims and Scientific Facts
It’s key to separate marketing hype from real science with stem cell patches. Some products make big claims that aren’t backed up. Always look for research from trusted sources.
When checking claims, remember:
- Seek out studies in respected journals
- Be cautious of products with too-good-to-be-true promises
- Talk to doctors before trying new treatments
By being smart consumers, we can see what stem cell patches really offer and make smart choices.
Potential Risks and Considerations When Using Stem Cell Patches
Stem cell patches have their own set of risks and considerations. It’s important to look at both the good and bad sides of these products. This way, we can make informed decisions.
Safety Concerns and Reported Side Effects
Stem cell patches are usually safe, but side effects can happen. These can be mild, like skin irritation, or serious. It’s key to think about the risks, like allergic reactions or bad interactions with other treatments.
Commonly reported side effects include:
- Skin irritation or redness
- Itching or rash at the application site
- Allergic reactions to patch materials
Regulatory Status and FDA Oversight
The rules for stem cell patches vary. Some are watched by the FDA, while others are not. Knowing the rules helps ensure these products are safe and work well. We’ll look at the current rules and what they mean for users.
| Regulatory Classification | Description | FDA Oversight |
|---|---|---|
| Class II Medical Device | Patches that are considered moderate risk | Yes, requires pre-market notification |
| Biologic | Patches containing biological materials | Yes, requires pre-market approval |
| Dietary Supplement | Patches marketed as dietary supplements | Limited, unless making specific health claims |
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
The price of stem cell patches can change a lot. It depends on the maker, the type, and how it’s used. Insurance coverage also varies. We’ll talk about what affects the cost and insurance.
Factors affecting the cost of stem cell patches include:
- Manufacturing process and materials
- Research and development investments
- Clinical evidence supporting efficacy
Choosing Reputable Products and Providers
It’s important to pick good products and providers. Look into the maker’s reputation, check the evidence, and know the rules. We’ll give tips on how to choose wisely.
Tips for choosing reputable products:
- Look for products with clinical evidence supporting their claims
- Research the manufacturer’s reputation and history
- Understand the product’s regulatory classification
Conclusion: The Future of Stem Cell Patch Technology
Research is moving forward, and stem cell patch technology is getting better. New materials and technology are helping these patches become more useful. They could soon be a big part of fixing damaged tissues.
We think these patches will help treat many health problems. They might help fix damaged tissues, lower swelling, and ease pain. Their non-invasive nature makes them appealing to those looking for new treatments.
As we learn more about stem cells, these patches will become even more important. With more research and money going into this area, we’re excited. We believe stem cell patches will change how we fix damaged tissues, bringing hope to people everywhere.
What are stem cell patches made of?
Stem cell patches are made from materials like extracellular matrix, biodegradable polymers, or hydrogels. They might also have nanocrystals or growth factor coatings to boost their healing power.
How do stem cell patches work?
These patches release growth factors that help cells talk to each other. They also help the body’s own stem cells fix and grow tissues.
What are stem cell activation patches?
These patches aim to boost the body’s natural stem cell activity. They use bioactive materials to get cells working better.
What is the difference between cell-loaded and cell-free stem cell patches?
Cell-loaded patches have living cells, while cell-free ones use materials to start cell activity. Both can help with healing, depending on the condition.
Are stem cell patches effective for neuropathy treatment?
Some patches are being studied for neuropathy treatment. Early results look good, but more research is needed.
What is stem cell phototherapy?
It’s a light therapy that uses light to help cells and tissues heal. Patches for this therapy send specific light wavelengths to the body.
Do stem cell patches really work?
Their success depends on the condition, patch type, and individual health. Some studies show promise, but more research is needed.
What are the benefits of using stem cell patches?
They’re said to improve tissue repair, reduce inflammation, manage pain, and are easy to use because they’re non-invasive.
Are there any risks associated with using stem cell patches?
Yes, like any treatment, they can have risks and side effects. It’s important to know the regulatory status, choose reputable products, and consider cost and insurance.
How do I choose a reputable stem cell patch product?
Look for products that have been tested well, are made by trusted companies, and have clear instructions.
Are stem cell patches FDA-approved?
FDA rules on these patches vary. Some may be cleared for marketing, while others are considered investigational.
Can stem cell patches be used for wound healing?
Yes, they’re being studied for wound healing and skin regeneration. They might help create a good environment for cell growth and repair.
What is the role of bioactive nanocrystals in stem cell patches?
Bioactive nanocrystals in patches can enhance their healing effects. They can also influence cell activity and tissue repair.
References
- Nature Communications. s41467‘024‘48980‘0. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-48980-0
- PMC / NCBI. PMC3566655 (journal article). Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3566655/
- PMC / NCBI. PMC9749239 (journal article). Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9749239/


