Acute pyelonephritis is a serious bacterial infection that affects the kidneys and renal pelvis. Understanding this condition is key for early recognition and effective treatment. We will look into its definition, how common it is, and what causes it.
This infection usually starts as a UTI in the bladder and moves up to the kidney. Escherichia coli is the main cause in about 80-90% of cases. For more on diagnosis and treatment, check out the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Key Takeaways
- Acute pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of the kidneys and renal pelvis.
- Escherichia coli is the most common causative organism.
- The condition typically arises as an ascending UTI.
- Understanding the pathophysiology is key for effective treatment.
- Early recognition is key to preventing complications.
Understanding Acute Pyelonephritis: Definition and Epidemiology
Acute pyelonephritis is a kidney infection that can be serious if not treated right. It’s important to know what it is, how it’s classified, and who is at risk.
Definition and Classification of Kidney Infections
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the renal pelvis. It’s a type of urinary tract infection that affects the kidneys. It can be acute or chronic, with acute being sudden.
Classification helps doctors choose the right treatment. It depends on how severe the infection is, any underlying health issues, and if it’s complicated or not.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Acute pyelonephritis is more common in women. This is because women have a shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to reach the kidneys. Other risk factors include urinary tract blockages, diabetes, and weakened immune systems.
Knowing the risk factors is key to preventing acute pyelonephritis. By identifying those at high risk, we can act early and prevent severe infections.
Symptoms include flank pain, fever, and nausea. Pyelonephritis flank pain is a major sign. Diagnostic criteria include symptoms, lab tests, and sometimes imaging.
Pyelonephritis Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations
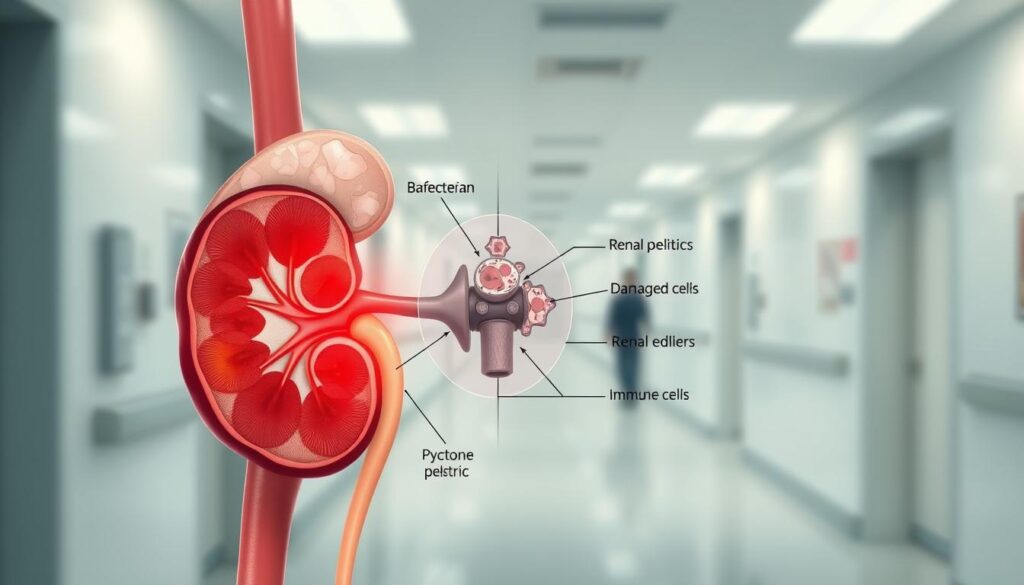
Acute pyelonephritis is a complex condition. It involves the host and the pathogen working together. We will look at how bacteria move from the lower urinary tract to the kidneys, causing infection and inflammation.
Mechanisms of Infection and Bacterial Spread
The main way pyelonephritis happens is when bacteria move up from the lower urinary tract to the kidneys. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the most common cause, found in 80-90% of cases. The bacteria start in the periurethral area and move up through the urethra into the bladder, known as ascending infection.
Then, the bacteria reach the kidneys through the ureters. Several things help them make this journey, including:
- Urinary tract obstruction
- Vesicoureteral reflux
- Abnormalities in the urinary tract anatomy
E. coli and Bacterial Virulence Factors
E. coli strains that cause pyelonephritis have special traits. These traits help them stick to and invade the urinary tract cells. The key factors include:
- P-fimbriae, which help them stick to uroepithelial cells
- Hemolysin, which damages host cells
- Capsular antigens, which protect them from the host’s immune system
Inflammatory Response and Tissue Damage
When bacteria get into the renal parenchyma, it triggers a strong inflammatory response. This response brings in immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages. They release substances that cause inflammation and can damage tissues, leading to scarring and possibly affecting kidney function.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
The symptoms of acute pyelonephritis can vary but often include:
- Fever and chills
- Flank pain or tenderness
- Dysuria and urinary frequency
- Nausea and vomiting
It’s important to recognize and treat these symptoms quickly. This helps prevent complications and reduces the risk of long-term kidney damage.
Conclusion: Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Diagnosing pyelonephritis requires a mix of clinical checks, lab tests, and imaging. Urine analysis (UA) results are key in spotting the infection and shaping treatment plans.
Effective treatment for pyelonephritis often includes antibiotics. For acute cases, doctors pick antibiotics based on the infection’s severity and the germ causing it, usually Escherichia coli. In complicated cases, treatment might be more intense, including hospital stays and stronger antibiotics.
It’s vital to know the difference between chronic and acute pyelonephritis. Acute is a sudden infection, while chronic is a long-term or recurring issue that can harm the kidneys.
We stress the need for quick and correct diagnosis to guide treatment and avoid complications. By grasping the disease’s causes and symptoms, healthcare teams can offer better care and better results for patients.
FAQ
What is acute pyelonephritis?
Acute pyelonephritis is a urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects the renal pelvis and parenchyma. It’s usually caused by bacteria.
What are the risk factors for developing acute pyelonephritis?
Risk factors include being female, having urinary tract issues, using catheters, having diabetes, and a history of UTIs.
How does Escherichia coli cause pyelonephritis?
Escherichia coli is the main cause of pyelonephritis. It uses special factors to stick to and invade the urinary tract. This allows it to reach the kidneys.
What are the symptoms of acute pyelonephritis?
Symptoms include flank pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and painful urination. The severity can vary.
How is acute pyelonephritis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical signs, lab tests like urinalysis and urine culture, and imaging like ultrasound or CT scans.
What is the treatment for acute pyelonephritis?
Treatment includes antibiotics. The type and length of treatment depend on the infection’s severity and the bacteria causing it.
What is the difference between acute and chronic pyelonephritis?
Acute pyelonephritis is a sudden infection. Chronic pyelonephritis is ongoing or recurring, leading to kidney damage over time.
Can pyelonephritis be prevented?
Yes, prevention involves keeping the urinary tract healthy, managing health conditions, and using antibiotics wisely.
What is complicated pyelonephritis?
Complicated pyelonephritis occurs in people with urinary tract issues or other health problems.
How does pyelonephritis affect the kidneys?
Pyelonephritis can cause kidney inflammation and scarring. This can lead to long-term damage or reduced kidney function.