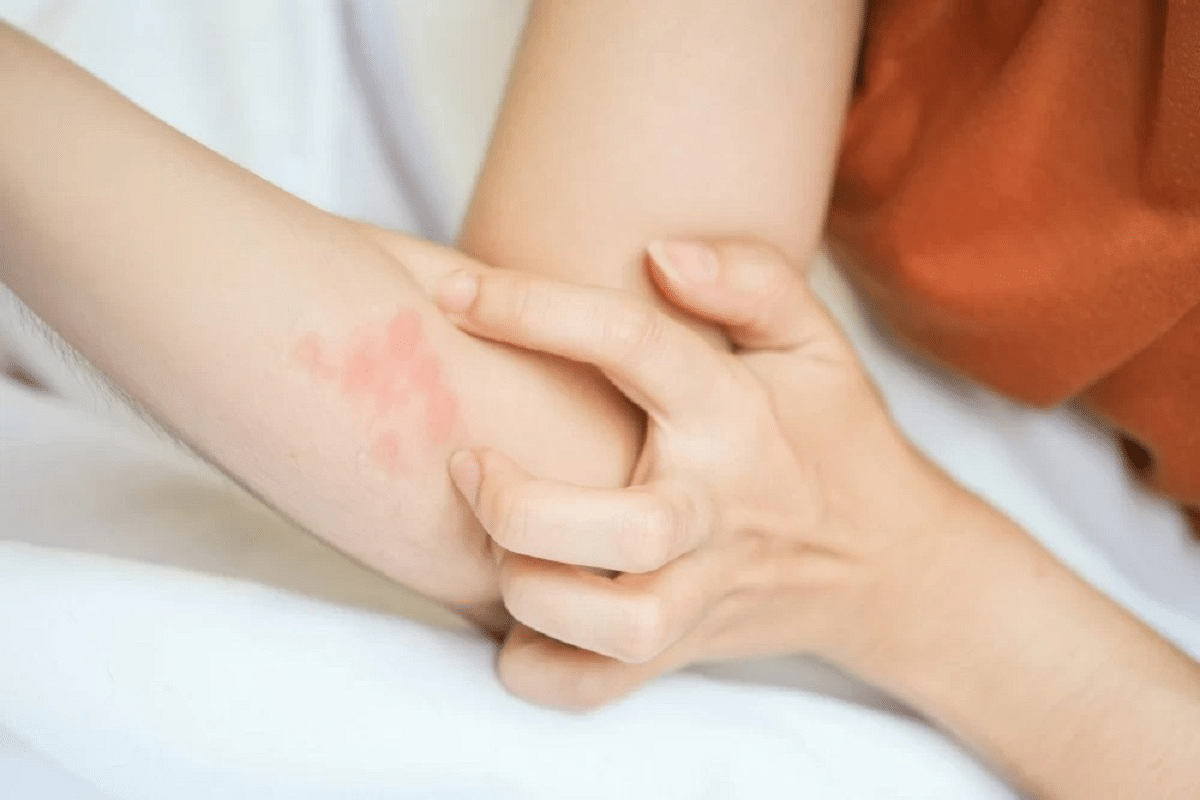
Imagine your body’s natural response to heat or exercise suddenly turning against you. It triggers intense itching and painful hives that appear within minutes. Cholinergic urticaria, also known as heat hives or exercise-induced urticaria, is a physical condition that affects many. Yet, it remains widely misunderstood. Defining chronological urticaria (Cholinergic Urticaria), explaining its unique triggers and how it differs from common chronic hives.
It is characterized by small, itchy papular wheals. These typically develop within 2 to 10 minutes and resolve within 30 to 60 minutes after the trigger is removed. We will explore how this condition differs from other types of urticaria and its impact on quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Cholinergic urticaria is triggered by an elevation in body temperature.
- It is characterized by small, itchy wheals that appear within minutes.
- The condition is often associated with sweating or heat exposure.
- Symptoms typically resolve within 30 to 60 minutes after the trigger is removed.
- Understanding cholinergic urticaria is key for effective management.
Understanding Cholinergic Urticaria

Cholinergic urticaria happens when your body temperature goes up. This leads to the formation of wheals and hives. It’s a chronic condition that can be hard to diagnose and manage.
Definition and Basic Characteristics
Cholinergic urticaria causes small, itchy hives or wheals when your body temperature rises. This can happen from exercising, taking hot showers, or feeling stressed. It’s called “cholinergic” because it involves acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter linked to sweating and other functions.
Prevalence and Demographics
About 5.1% to 11% of people with chronic urticaria have cholinergic urticaria. It’s more common in those with allergies. It usually starts in people aged 10-30 years, with more men than women getting it.
|
Demographic Characteristics |
Prevalence Details |
|---|---|
|
Age Group |
Typically affects individuals aged 10-30 years |
|
Gender Distribution |
Males are more frequently affected than females |
|
Prevalence in Chronic Urticaria Patients |
Affects approximately 5.1% to 11% of patients |
The Science Behind Cholinergic Urticaria
[Add image here]
Cholinergic urticaria is a complex condition. It involves both neurological and immunological responses. We will dive into its detailed pathophysiology.
Pathophysiology
The condition starts with the release of histamine from mast cells. This leads to wheals and hives. It’s triggered by a rise in body temperature, from exercise, hot showers, or stress.
We’ll look at how different body responses lead to cholinergic urticaria. It causes small, itchy wheals on the skin, with a burning feeling.
|
Pathophysiological Mechanism |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Histamine Release |
Mast cells release histamine when body temperature goes up, causing wheals. |
|
Acetylcholine Stimulation |
Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, stimulates sweat glands and may affect histamine release. |
|
Sweat Hypersensitivity |
Some people are very sensitive to their sweat, which can lead to cholinergic urticaria. |
Role of Acetylcholine and Histamine
Acetylcholine controls sweat glands. In cholinergic urticaria, it may cause histamine release, worsening symptoms.
Histamine is key in allergic reactions. It makes blood vessels expand, causing urticaria symptoms. Knowing how acetylcholine and histamine work together is key to finding treatments.
Sweat Hypersensitivity Theory
The sweat hypersensitivity theory suggests some people with cholinergic urticaria are very sensitive to their sweat. This sensitivity may start an immune response, causing symptoms.
Studies on this theory have shown possible treatments. These include reducing sweat or making patients less sensitive to it.
Triggers and Causes
Knowing what triggers cholinergic urticaria is key for managing symptoms. This condition is linked to a rise in body temperature. Various factors can cause this increase.
Heat and Temperature Elevation
Heat and rising body temperature are major triggers. When the body heats up, symptoms of cholinergic urticaria appear. This can happen from being in a hot place or having a fever.
Exercise-Induced Episodes
Exercise is another big trigger. It raises body temperature, causing symptoms. How hard and long you exercise affects how bad the reaction is.
Emotional Stress as a Trigger
Stress is also a trigger for cholinergic urticaria. It can make body temperature go up and release histamine. This leads to symptoms.
Hot Showers and Baths
Hot showers or baths quickly raise body temperature. This can trigger cholinergic urticaria in some people. The sudden temperature change is a big factor.
|
Trigger |
Description |
Effect on Body Temperature |
|---|---|---|
|
Heat and Temperature Elevation |
Environmental or internal heat increase |
Rises |
|
Exercise |
Physical activity |
Increases |
|
Emotional Stress |
Stress response |
Can increase |
|
Hot Showers/Baths |
Sudden temperature change |
Rises rapidly |
Understanding these triggers helps people with cholinergic urticaria manage their condition better. Avoiding or reducing these triggers can lessen how often and how severe episodes are.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
It’s important to know the symptoms of cholinergic urticaria to diagnose and treat it well. We’ll look at the main signs and how they change over time. This will give you a full picture of the condition.
Characteristic Wheals and Hives
Cholinergic urticaria shows up as small, itchy bumps called wheals. These bumps start within 2 to 10 minutes after a trigger and go away in 30 to 60 minutes. They can show up anywhere on the body and are often red around the edges.
Progression of Symptoms
The symptoms of cholinergic urticaria can change a lot from person to person. Some people might only notice a few mild bumps, while others might have many severe ones. Triggers can include heat, exercise, and stress.
Severity Spectrum
The severity of cholinergic urticaria can vary a lot. Mild cases might have just a few bumps that go away fast. But severe cases can have lots of bumps and other symptoms like headaches and dizziness.
|
Severity Level |
Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Mild |
Few wheals, minimal itching, resolves within 30 minutes |
|
Moderate |
Multiple wheals, moderate itching, resolves within 1 hour |
|
Severe |
Widespread wheals, intense itching, may be accompanied by systemic symptoms |
Knowing how cholinergic urticaria shows itself is key to helping people with it. By understanding its signs and how they change, we can find better ways to manage it. This can greatly improve the lives of those affected.
How Cholinergic Urticaria Differs from Other Urticaria Types
Cholinergic urticaria is unique among other urticaria types. It has its own triggers and features. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Comparison with Cold Urticaria
Cold urticaria happens when you’re exposed to cold, causing hives. Cholinergic urticaria, on the other hand, is triggered by rising body temperature. This can be from exercise, hot showers, or stress. Experts say the triggers are different, making accurate diagnosis important.
Differences from Dermatographism
Dermatographism makes your skin react to pressure, leading to hives. It’s not caused by temperature or stress like cholinergic urticaria. Instead, it’s from physical pressure or scratching.
Distinction from Aquagenic Urticaria
Aquagenic urticaria is rare and happens when you touch water, causing hives. Cholinergic urticaria is not caused by water but by rising body temperature. Knowing this helps in choosing the right treatment.
Contrast with Solar Urticaria
Solar urticaria makes your skin react to sunlight, causing hives. It’s different from cholinergic urticaria, which is caused by body temperature increase. Finding the exact cause is vital for effective treatment.
In summary, cholinergic urticaria is unique among urticaria types. Its specific triggers and features make it stand out. Getting the right diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
Diagnosis Methods
We diagnose cholinergic urticaria through a mix of clinical assessment, provocation tests, and differential diagnosis. This detailed approach helps doctors accurately spot the condition. It also helps them tell it apart from other types of urticaria.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing cholinergic urticaria is a detailed clinical evaluation. This includes a thorough medical history and physical exam. Key aspects of the clinical evaluation include:
- Looking at the patient’s symptoms and how they relate to temperature changes or physical activity
- Checking for the characteristic wheals and hives of cholinergic urticaria
- Reviewing the patient’s medical history to find any underlying conditions that might be causing the symptoms
Provocation Tests
Provocation tests are key in diagnosing cholinergic urticaria. These tests involve exposing the patient to specific stimuli to bring on symptoms. Common provocation tests include:
- Exercise testing: Patients are asked to do physical activity to trigger symptoms
- Heat exposure: Patients are put in warm environments or use a warm bath to bring on symptoms
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is important to tell cholinergic urticaria apart from other conditions with similar symptoms. A thorough differential diagnosis may involve:
- Excluding other types of urticaria, like cold urticaria or aquagenic urticaria
- Checking for other skin conditions that might look like cholinergic urticaria
Laboratory Investigations
Laboratory investigations support the diagnosis of cholinergic urticaria. While there’s no specific test for it, certain tests can help rule out other causes. These may include:
|
Test |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
Complete Blood Count (CBC) |
To check for underlying infections or inflammatory conditions |
|
Thyroid Function Tests |
To see if thyroid issues are causing urticaria |
|
Allergy Tests |
To find out if allergies are triggering or making symptoms worse |
By combining clinical evaluation, provocation tests, differential diagnosis, and lab tests, doctors can accurately diagnose cholinergic urticaria. They can then create an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches
Treating cholinergic urticaria needs a custom plan. It’s about knowing the options and fitting them to each person’s needs.
First-Line Medications
The main treatment for cholinergic urticaria is antihistamines. Antihistamines help by blocking histamine receptors. Experts say antihistamines are key in treating this condition.
We start with standard doses of antihistamines. Then, we adjust them as needed to manage symptoms.
Second-Line Therapies
For those not helped by antihistamines, omalizumab is a good next step. Omalizumab is an anti-IgE antibody. It’s shown to help with chronic urticaria, including cholinergic urticaria.
Studies have found it reduces symptoms and improves life quality.
“Omalizumab represents a significant advancement in the treatment of chronic urticaria, giving hope to those with hard-to-treat cases.”
Emerging Treatment Options
New treatments for cholinergic urticaria are being researched. These include new antihistamines, immunosuppressants, and biologics. These target specific parts of the condition.
We keep an eye on these new options. This way, we can offer the latest treatments to our patients.
Understanding the different treatments helps us manage cholinergic urticaria better. This improves life quality for those affected.
When to Seek Medical Help
Knowing when to get medical help is key to managing Cholinergic Urticaria well. Some cases might be mild and handled with self-care. But, others can be serious and need quick medical help.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the warning signs for needing medical help. These include:
- Severe symptoms that don’t get better with antihistamines or other treatments.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing, which can be very dangerous.
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations.
- Dizziness or fainting spells.
- Widespread hives or itching that makes it hard to do daily tasks.
If you see any of these symptoms, you should get medical help right away.
Emergency Situations
Cholinergic Urticaria can sometimes lead to emergency situations. These include:
- Anaphylaxis, a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that needs immediate medical help.
- Severe angioedema, which can cause swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
If you’re facing any of these emergency situations, call emergency services or seek immediate medical help.
Finding the Right Specialist
When you need medical help for Cholinergic Urticaria, seeing a specialist is a good idea. You might start with:
- A dermatologist, who specializes in skin conditions.
- An allergist, who can help manage allergic reactions.
To find the right specialist, ask your primary care doctor for a referral. Or check with your insurance for a list of specialists they cover.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Appointment
To get the most from your doctor’s appointment, prepare by:
- Gathering info about your symptoms, like when they happen and how long they last.
- Listing any medicines you’re taking now.
- Writing down any questions or concerns you have about your condition.
Being ready will help you get the best care for your Cholinergic Urticaria.
Living with Cholinergic Urticaria
People with cholinergic urticaria can improve their life by making lifestyle changes. This condition makes hives appear when body temperature goes up. It needs a detailed plan to manage it.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle is key to managing cholinergic urticaria. Keeping cool is a main strategy. Stay in air-conditioned places, avoid hot showers, and wear loose, cool clothes.
- Avoiding extreme temperatures
- Using cooling packs or cold compresses when experiencing a flare-up
- Choosing loose, breathable clothing to help keep the body cool
Also, watch your stress levels as stress can make symptoms worse. Try meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to help.
Exercise Adaptations
Exercise can trigger symptoms, but you don’t have to stop moving. Adapting exercise routines can help manage symptoms.
- Opting for low-intensity exercises during hot weather
- Exercising in cooler environments, such as air-conditioned gyms
- Swimming in cool water, which can be both a form of exercise and a way to stay cool
It’s good to monitor body temperature during exercise. Have a plan for managing symptoms if they happen.
Managing Flare-Ups
Flare-ups can happen even with good management. Having a management plan is key. Keep antihistamines or other medications ready.
- Recognizing the early signs of a flare-up
- Having a cool compress or cooling pack readily available
- Knowing when to seek medical help if symptoms are severe
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
Cholinergic urticaria can affect your mind. The unpredictability and need to manage your environment can be stressful and isolating.
It’s important to find coping strategies. This includes:
- Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities
- Educating oneself about the condition to better understand and manage it
By using these strategies and working with healthcare providers, people with cholinergic urticaria can live active and fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
Cholinergic urticaria is a complex condition. It causes wheals and hives in response to heat, exercise, and emotional stress. We’ve looked into its definition, how common it is, and what causes it.
We’ve also talked about how it presents itself, how to diagnose it, and how to treat it. Understanding cholinergic urticaria is key to managing it.
Knowing the signs and symptoms is the first step. This way, people can get help and find ways to live better with the condition.
In the end, treating cholinergic urticaria needs a team effort. With the right medical care and lifestyle changes, people can control their symptoms. This improves their daily life a lot.
FAQ
What is cholinergic urticaria?
Cholinergic urticaria is a skin condition. It causes hives when your body gets warmer. This can happen during exercise, hot showers, or when you’re stressed.
What are the symptoms of cholinergic urticaria?
Symptoms include small, itchy hives on your skin. These usually appear on your chest, neck, and arms. You might also feel a burning or stinging sensation.
Is cholinergic urticaria rare?
Yes, cholinergic urticaria is not common. But, we don’t know exactly how rare it is.
What triggers cholinergic urticaria?
Triggers include exercise, hot showers, emotional stress, and rising body temperature.
How is cholinergic urticaria diagnosed?
Doctors use a few methods to diagnose it. They look at your symptoms, do provocation tests, and rule out other conditions.
What is the treatment for cholinergic urticaria?
Treatment includes antihistamines and avoiding triggers. Sometimes, other treatments or new options are used.
Can cholinergic urticaria be managed?
Yes, it can be managed. You can avoid triggers, change your exercise routine, and use medications to help symptoms.
How does cholinergic urticaria differ from other types of urticaria?
It’s different because it’s triggered by heat, not cold or other things. It has its own unique characteristics.
Is cholinergic urticaria a serious condition?
It’s not usually serious but can be uncomfortable. It might mean there’s an underlying issue in some cases.
Can emotional stress trigger cholinergic urticaria?
Yes, stress can trigger it. It can make your body temperature rise and cause symptoms.
What is the role of histamine in cholinergic urticaria?
Histamine is important. It’s released when you’re triggered and causes hives and other symptoms.
How can I prepare for a doctor’s appointment for cholinergic urticaria?
Keep a symptom journal and list your triggers. Be ready to talk about your medical history and any medications you’re taking.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7416524/