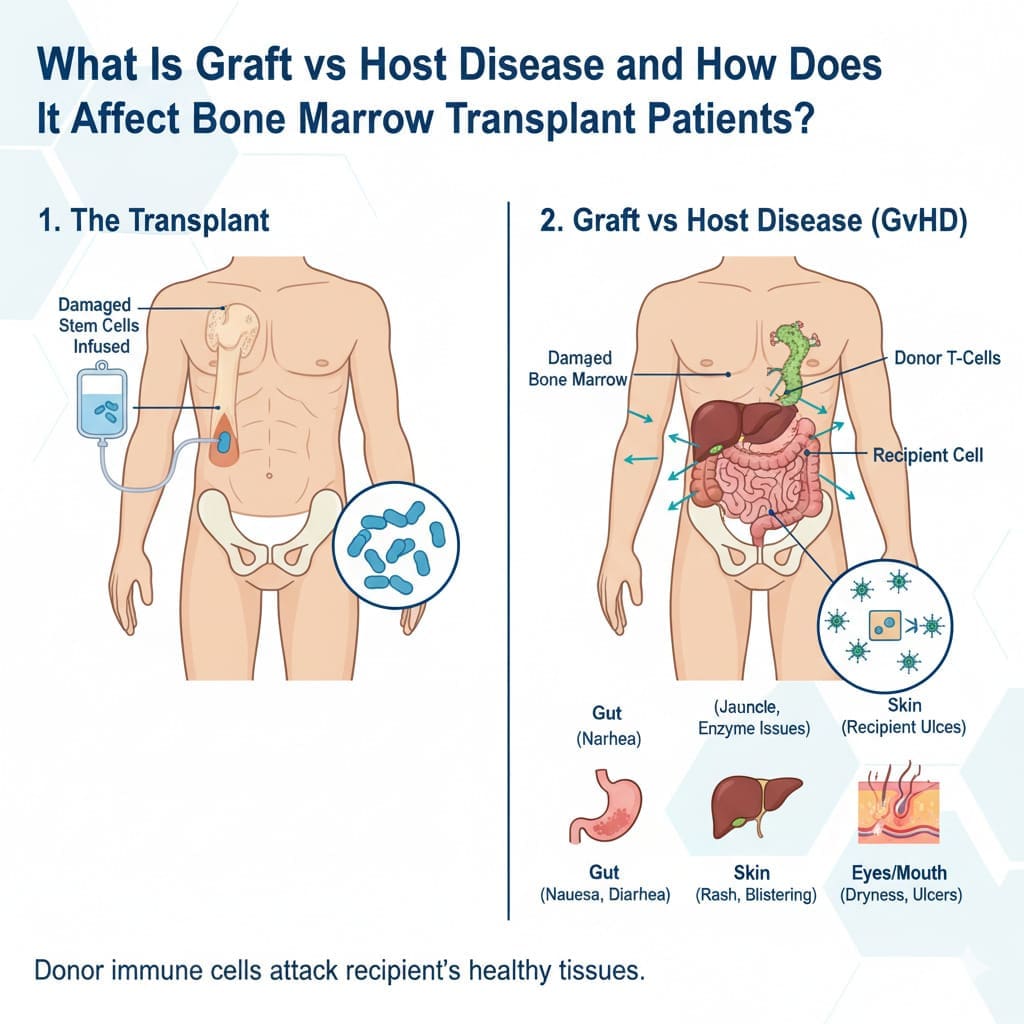
Graft vs host disease (GVHD) is a complex immune disorder. It happens when donor immune cells attack the recipient’s tissues after a bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the risks associated with GVHD and its impact on patient recovery. GVHD can be a significant complication of allogeneic stem cell transplants. It’s important for patients to get expert care and the latest treatment protocols.
We are committed to providing patient-centered innovation and internationally recognized clinical outcomes. We ensure each step in the transplantation journey is guided by trust, quality, and leading medical expertise.
Key Takeaways
- GVHD is a complex immune disorder that occurs after a bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
- Donor immune cells can attack the recipient’s tissues, leading to GVHD.
- Liv Hospital provides expert care and up-to-date treatment protocols for GVHD.
- Patient-centered innovation and internationally recognized clinical outcomes are our priority.
- Trust, quality, and leading medical expertise guide our transplantation services.
Understanding Graft vs Host Disease
Graft vs Host Disease (GVHD) is a big problem with the immune system. It happens when the cells from the transplant see the host’s body as different. This makes the immune system attack the host’s tissues, causing many issues. It’s a big worry for those getting allogeneic stem cell transplants.
Definition and Basic Mechanism
GVHD is when the donor’s immune cells attack the host’s tissues. This is because of T cells and other immune parts in the graft. The process starts with the donor T cells seeing the host’s histocompatibility antigens.
This seeing leads to an immune attack on the host’s body. This can harm many parts, like the skin, liver, and gut. Knowing how it works helps us find ways to stop and treat it.
Prevalence and Impact on Transplant Success
GVHD is a big problem after allogeneic stem cell transplant, hitting up to 50% of patients. How common it is depends on things like how well the donor and recipient match, the treatment before the transplant, and how they prevent GVHD.
GVHD really affects how well a transplant works. It makes life harder for patients and raises the chance of death from the transplant. GVHD can be either acute or chronic, each with its own effects on patients.
Handling GVHD well is key to helping transplant patients. We need to prevent it, catch it early, and treat it right. By understanding GVHD, we can help those getting allogeneic stem cell transplants more.
The Science Behind Graft vs Host Disease
GVHD is a complex immune disorder that happens when the donor’s immune cells see the recipient’s body as foreign. This leads to an immune attack on the host.
Immune System Dynamics in GVHD
The immune system’s fight in GVHD involves many steps. Donor T cells are key, as they start the immune attack. They grow and become cells that fight the host’s tissues.
Cytokines are important too. They help cells talk to each other. In GVHD, they can either help or stop the immune fight, affecting how bad the disease is.
Risk Factors for Developing GVHD
Several things can make someone more likely to get GVHD. A big one is how different the HLA is between the donor and the recipient. A bigger difference means a higher risk of GVHD.
Being older also raises the risk. Older people’s immune systems don’t work as well, leading to more inflammation. The type of medicine used before the transplant can also play a role.
Knowing these risk factors helps us find better ways to prevent and treat GVHD. We can focus on those at higher risk to make the disease less likely and less severe.
Acute Graft vs Host Disease
Acute Graft vs Host Disease (GVHD) is a serious issue after a bone marrow transplant. We will look into acute GVHD’s key points. This includes when it happens, its symptoms, and how severe it is.
Timeframe and Onset Within 100 Days
Acute GVHD usually happens in the first 100 days after a transplant. It’s most risky during this time. We need to watch symptoms closely to manage them well.
Common Symptoms and Affected Organs
The symptoms of acute GVHD vary but often include a skin rash, diarrhea, and liver issues. These happen because of the immune system reacting to the new cells. The skin, gut, and liver are the main organs affected.
| Organ/System | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Skin | Rash, itching |
| Gastrointestinal Tract | Diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Liver | Jaundice, elevated liver enzymes |
Grading System for Acute GVHD Severity
The severity of acute GVHD is graded using a system. It looks at how much of the body is affected and how bad the symptoms are. This grading helps decide the best treatment and care plan.
Chronic Graft vs Host Disease
Chronic GVHD is a big challenge for those who have had transplants. It shows up more than 100 days after the transplant. This condition makes recovery harder and affects many parts of a patient’s life.
Distinguishing Features and Timeframe Beyond 100 Days
Chronic GVHD starts usually after 100 days after a transplant. It’s different from acute GVHD because it involves a more complex fight between donor cells and the recipient’s body. It has a wider range of symptoms and lasts longer.
Organ Systems Affected in Chronic GVHD
Chronic GVHD can hit many parts of the body, causing a variety of symptoms. Common areas include:
- The skin, where it can cause rashes, lesions, and changes in skin pigmentation.
- The mouth, leading to dryness, ulcers, and difficulties in eating and speaking.
- The eyes, resulting in dryness, irritation, and sensitivity to light.
- The liver, where it can cause abnormalities in liver function tests and, in severe cases, liver failure.
Managing chronic GVHD well means treating all affected areas. This helps improve the patient’s life quality.
Long-term Impact on Quality of Life
Chronic GVHD can deeply affect a patient’s life. Symptoms can be mild or very severe, impacting physical health, emotions, and social life. Patients might feel tired, in pain, and struggle with daily tasks. A care plan that includes medical treatment, mental support, and lifestyle changes is needed.
| Aspect of Life | Impact of Chronic GVHD |
|---|---|
| Physical Health | Fatigue, pain, and organ dysfunction |
| Emotional Well-being | Anxiety, depression, and stress related to chronic illness |
| Social Life | Limited social interactions due to health constraints and hospital visits |
It’s key to understand chronic GVHD to create good GVHD management strategies. By tackling this condition’s many sides, doctors can help patients live better lives after transplants.
Diagnosis and Assessment of GVHD
Diagnosing GVHD requires a detailed approach. This includes clinical evaluation, biopsy, and lab tests. Getting the diagnosis right is key to treating the disease effectively.
Clinical Evaluation Methods
First, doctors evaluate the patient’s symptoms and medical history. They look for signs of GVHD. They check for skin rashes, stomach problems, and liver issues. The severity of these symptoms helps grade the disease.
Doctors use special tools to measure GVHD’s extent and severity. These tools help decide the best treatment and predict how well the patient will do.
Biopsy and Laboratory Testing
Biopsy and lab tests are vital for confirming GVHD. A biopsy examines tissue samples from affected areas like the skin or stomach. This helps spot GVHD changes.
Lab tests, including blood work, check organ damage and treatment response. They also help rule out other diseases with similar symptoms.
By combining clinical checks with biopsy and lab tests, we can accurately diagnose GVHD. This allows us to create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Treatment Approaches for Graft vs Host Disease
Treating GVHD needs a custom plan, mixing old and new treatments. It’s important to know all the options, from basic to new ones.
First-Line Therapies
The first step in treating GVHD is often corticosteroids. They help lower inflammation and calm the immune system. These drugs are usually the first choice for both acute and chronic GVHD.
Immunosuppressive medications also play a big role. They help control the immune system’s attack on the body, making the disease less severe.
Advanced Treatment Options
For those who don’t get better with first-line treatments, there are more options. Extracorporeal photopheresis is one. It takes blood cells, treats them, and then puts them back. It’s shown to help in tough cases.
Targeted therapies are another advanced method. They aim to fix specific problems in GVHD. This can lead to better results and fewer side effects.
Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
New treatments for GVHD are coming, like cellular and gene therapies. These aim to fix or replace immune cells causing GVHD. They might offer lasting solutions.
Research on novel immunosuppressive agents and other new strategies is growing. As we learn more about GVHD, we get more ways to treat it.
Prevention Strategies for GVHD
Preventing GVHD is a complex task. It involves choosing the right donor and using special medicines before the transplant. These steps are key to better results for bone marrow transplant patients.
Donor Selection and Matching
Finding the right donor is very important. We use advanced tests to match the donor and recipient closely. This greatly lowers the chance of GVHD.
Recent studies show that even with less than perfect matches, stem cell transplants can work better. A study on Targeted Oncology highlights this. It says using alternative donors and better medicines can help more patients.
Immunosuppressive Therapies
Medicines are a big part of preventing GVHD. We use drugs like calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids. These help control the immune system and stop GVHD from starting.
Our plan also includes watching for GVHD signs and changing treatments if needed. Experts agree that a personalized approach is best. It takes into account each patient’s unique situation and how they react to treatment.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Donor Selection | Advanced HLA typing for optimal donor-recipient matching | Reduces GVHD risk |
| Immunosuppressive Therapy | Use of calcineurin inhibitors and corticosteroids | Controls immune response, prevents GVHD onset |
| Monitoring and Adjustment | Regular monitoring for GVHD signs, adjusting treatment as needed | Enhances prevention efficacy, improves patient outcomes |
In summary, stopping GVHD needs a detailed plan. This includes picking the right donor, using medicines, and keeping a close eye on the patient. By doing these things, we can make bone marrow transplants safer and more successful.
Advanced GVHD Management at Specialized Centers
Specialized centers like Liv Hospital lead in GVHD management. We use a team approach and follow the latest care standards. Our goal is to give the best care possible.
Multidisciplinary Team Approach
Our GVHD management strategy involves a multidisciplinary team. This team includes hematologists, oncologists, immunologists, and more. They work together to give patients the care they need.
- Hematologists and oncologists handle the blood-related parts of GVHD.
- Immunologists help understand and manage the immune system in GVHD.
- Nurses and support staff are key in patient care and teaching.
Evidence-Based Treatment Pathways
We use evidence-based treatment pathways that keep up with new research. Our treatments aim to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Our approach includes:
- Assessing risk to tailor treatment plans.
- Using medicines to prevent GVHD.
- Starting treatment quickly when GVHD symptoms appear.
International Standards in GVHD Care
We follow international standards in GVHD care. This ensures our patients get the best care available.
At Liv Hospital, we combine a team approach, evidence-based treatments, and international standards. This way, we offer top-notch GVHD management.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing graft vs host disease (GVHD) is key for better outcomes in bone marrow transplant patients. GVHD is a big problem after allogeneic stem cell transplant. It affects how well the transplant works and the patient’s quality of life.
We’ve covered the main points about GVHD, how to diagnose it, treat it, and prevent it. Our goal is to give a complete guide for patients and healthcare workers. Handling GVHD well needs a team effort, using the newest treatments and proven methods.
At Liv Hospital, we have a team ready to give top-notch care to patients from around the world. We focus on giving the best healthcare with full support. By tackling GVHD head-on and using a proactive approach, we can make stem cell transplants more successful. This way, we can also improve care for our patients.
What is Graft vs Host Disease (GVHD)?
GVHD is a problem that can happen after a stem cell transplant from someone else. The donor’s immune cells attack the body of the person who got the transplant.
What are the symptoms of acute GVHD?
Acute GVHD symptoms show up within 100 days after the transplant. They can include a skin rash, diarrhea, feeling sick to the stomach, and liver problems.
How is chronic GVHD different from acute GVHD?
Chronic GVHD happens more than 100 days after the transplant. It can affect many parts of the body, like the skin, liver, lungs, and mouth.
What are the risk factors for developing GVHD?
Some things increase the chance of getting GVHD. These include how well the donor and recipient match, using donors who aren’t family, and having certain infections.
How is GVHD diagnosed?
Doctors use a few ways to find out if someone has GVHD. They look at how the person feels, do biopsies, and check blood and tissue samples.
What are the treatment options for GVHD?
Doctors have a few ways to treat GVHD. They might use steroids, medicines to calm the immune system, and other treatments to help with symptoms.
Can GVHD be prevented?
While we can’t stop GVHD from happening completely, we can try to lower the risk. This includes using special medicines and choosing donors carefully.
What is the role of a multidisciplinary team in managing GVHD?
A team of doctors, including hematologists and immunologists, work together. They help take care of patients with GVHD in a complete way.
How does Liv Hospital approach GVHD management?
Liv Hospital uses a team of doctors to manage GVHD. They follow the best treatments and stick to international standards for care.
References
Cancer Research UK: Graft versus host disease (GVHD) symptoms
Canadian Cancer Society (Cancer.ca): Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)
NCBI Bookshelf (StatPearls): Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD)




































