When we feel stress, our heart beats faster. A study in a journal shows that heart rate variability is key to cardiovascular health. This variability shows how well our heart handles physical and mental challenges. It often raises the question, “What is the average heart rate when stressed? since stress naturally causes the heart to beat quicker.
The heart rate stress test is a way to check our heart health. It looks at how our heart reacts to stress. Knowing the target heart rate for stress test helps us understand the test results.
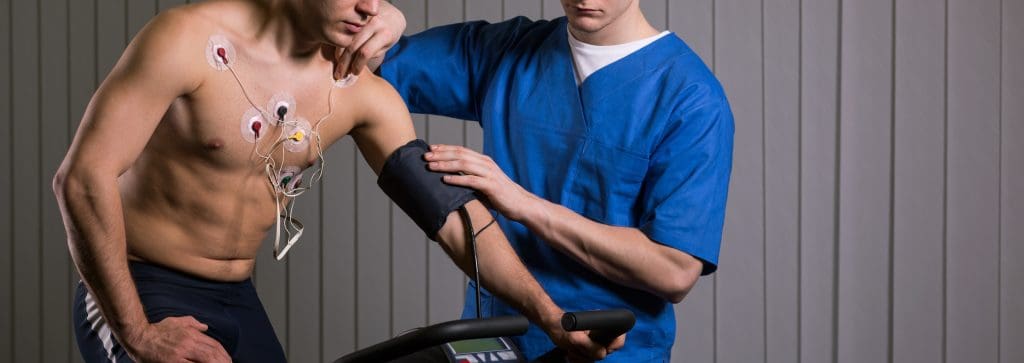
When we feel stressed, our body reacts in many ways. This includes changes in our heart rate. The autonomic nervous system controls these changes, helping us respond to stress.
Stress makes our body release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones get us ready to either fight or run away. A study in a Journal showed how stress affects our heart health.
The autonomic nervous system manages our body’s automatic actions, like our heart rate. When we’re stressed, it activates the sympathetic branch. This makes our heart rate go up, helping us react quickly to threats.
Short-term stress can make our heart rate go up for a bit. But long-term stress can keep our heart rate and blood pressure high. This can harm our heart over time.
Knowing the difference between resting heart rate and heart rate under stress is key. Resting heart rate shows how well your heart works when you’re calm. On the other hand, heart rate under stress shows how your heart and blood vessels react to challenges.
Heart rate at rest changes with age. A study in a Journal found heart rate ranges vary by age group (Jennifer M. H. et al., 2012). For adults, a normal resting heart rate is between 60 to 100 beats per minute.
| Age Group | Normal Resting Heart Rate (bpm) |
| 18-25 years | 60-100 |
| 26-35 years | 60-100 |
| 36-45 years | 60-100 |
| 46-55 years | 60-100 |
| 56-65 years | 60-100 |
| 65+ years | 60-100 |
Stress can make your heart rate jump up a lot. During a stress test, your heart rate goes up to a certain percentage of your maximum heart rate. The average heart rate when stressed can hit 80-90% of your maximum heart rate.
An elevated heart rate during stress is normal. But, if your heart rate stays high even when you’re not stressed, it might be a sign of a problem. If you feel your heart racing, dizzy, or short of breath, see a doctor right away.
It’s important to know what affects heart rate during stress to understand stress test results. Age, gender, and fitness level play a big role (Maradit Kremers et al., 2015). These factors change how the heart reacts to stress, so they’re key when looking at stress test results.
Age and gender greatly influence heart rate during stress. Research shows heart rate responses differ between men and women and across ages. For example, heart rate max decreases with age.
Physical fitness also affects heart rate during stress. People who are more fit tend to have better heart rate responses to stress. This means they might have lower heart rates during stress tests than those who are less fit.
Medical conditions can also change how heart rate responds to stress. Conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes can affect heart rate. It’s important to consider these conditions when looking at stress test results.
Experts say, “When looking at stress test results, we must consider the person’s health. This includes age, gender, fitness level, and any medical conditions.” Knowing these factors helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
A cardiac stress test is a key test that shows how well the heart works when you’re active. It helps doctors spot heart problems that might not show up when you’re just sitting or lying down. This is important for checking on heart health, as Tu et al. found in 2025.
These tests are used for many reasons. They help find heart disease, check if you’re at risk, and see if treatments are working. Doctors often suggest them for people with symptoms like chest pain or trouble breathing.
There are a few kinds of cardiac stress tests. You might have an exercise test, a nuclear test, or a stress echocardiogram. The type you get depends on your health and what your doctor needs to know.
If you have risk factors for heart disease, like high blood pressure or diabetes, you might need a test. Also, if you get chest pain when you’re active, you should talk to your doctor about getting tested.
| Test Type | Description | Indications |
| Exercise Stress Test | Measures heart function during physical exertion | Diagnosing coronary artery disease, assessing heart condition |
| Nuclear Stress Test | Uses imaging to assess heart function under stress | Identifying areas of reduced blood flow to the heart |
| Stress Echocardiogram | Ultrasound imaging of the heart during stress | Evaluating heart valve function and overall heart health |
An exercise treadmill stress test is key for checking heart function under stress. It tests how well the heart works when it’s at its peak, usually by walking on a treadmill.
The Bruce protocol is a set exercise test for heart health. It was made by Robert A. Bruce. It’s a multi-stage treadmill test that checks how the heart reacts to exercise.
The test lasts about 8-12 minutes. The exercise gets harder as it goes on.
Not everyone can do the standard Bruce protocol. Modified protocols are for those who need an easier test. This includes older adults or people with health issues.
These changes make the test safe and useful for more people.
Patients wear an ECG monitor during the test. The treadmill’s speed and incline go up, making it harder. They keep going until they can’t anymore or if they feel bad.
The test shows how well the heart is doing. It helps find any heart problems.
The time you spend on a treadmill stress test changes with age and fitness. Knowing how long you’ll be on the treadmill is key. It helps you get ready for the test.
Test times differ by age. Younger people usually do better and stay on longer. Here’s what you might expect:
Your fitness level affects how long you can stay on the treadmill. Fitter people can go longer. Research shows a clear link between fitness and test time (Shichman et al., 2023).
“The fitter you are, the longer you’ll be able to walk on the treadmill during a stress test.” –
Cardiology Expert
A Treadmill Stress Test Duration Chart helps everyone understand test times. It’s based on age and fitness. These charts are useful for setting realistic goals and understanding results.
Knowing what to expect can reduce anxiety. It makes the test experience better for everyone.
When you have a stress test, hitting the target heart rate is key. This test checks how well your heart works when you’re stressed. It usually happens while you’re exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike.
The target heart rate is important. It makes sure your heart is working hard enough. Doctors figure this out by using the age-predicted maximum heart rate.
To find your age-predicted maximum heart rate, subtract your age from 220. For instance, a 50-year-old would have a predicted rate of 170 beats per minute (bpm).
The goal in a stress test is to hit 85% to 100% of your predicted maximum heart rate. This is your target heart rate zone. For a 50-year-old, this would be between 145 bpm and 170 bpm.
Getting to the target heart rate in a stress test is very important. It lets doctors see how well your heart works under stress. If you don’t reach it, you might need more tests.
A stress test heart rate by age chart shows how our heart reacts during exercise. It helps doctors understand our heart health better. Knowing how our heart rate should change during a test is key.
Our heart rate changes a lot as we get older. Young people usually have higher heart rates than older adults. Studies, like the one by Tu et al. in 2025, show that heart rate changes with age.
| Age Group | Expected Maximum Heart Rate | Average Heart Rate During Stress Test |
| 20-29 | 180-200 bpm | 170-190 bpm |
| 30-39 | 170-190 bpm | 160-180 bpm |
| 40-49 | 160-180 bpm | 150-170 bpm |
| 50-59 | 150-170 bpm | 140-160 bpm |
| 60+ | 130-150 bpm | 120-140 bpm |
How fast our heart rate goes back down after a test is very important. A quicker recovery means better heart health. Doctors look at this to see if we might have heart problems.
If we don’t hit our top heart rate, it might mean our heart isn’t working right. But, it could also be because of medicine, how fit we are, or the test itself. If this happens, doctors might want to do more tests or try different ways to check our heart.
When exercise is not possible, chemical stress tests help check heart health. These tests are great for people who can’t exercise because of health issues or mobility problems
Chemical stress tests use medicine to mimic exercise on the heart. Drugs are given to boost blood flow to the heart or to mimic exercise’s effects on heart rate and blood pressure. This way, doctors can check for heart disease and function in those who can’t exercise.
Several medicines are used in these tests, including:
Each medicine works in its own way to affect the heart. For example, adenosine and regadenoson widen blood vessels to increase blood flow. Dobutamine, on the other hand, makes the heart beat faster and stronger.
Chemical stress tests have many benefits, like helping patients who can’t exercise and giving insights into heart function. But, they also have some downsides, like possible side effects from the medicines and the need for careful dosing.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Assesses heart health in patients unable to exercise | Potential side effects from medication |
| Provides valuable diagnostic information | Requires precise dosing and monitoring |
Knowing how to prepare for a stress test is key. It can greatly affect the test’s outcome. González-Cacheda et al. in 2025 highlighted the importance of preparation. Here are some steps to help you get ready.
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions before the test. You’ll likely be told to avoid eating or drinking anything except water for a few hours before the test. Also, wear comfortable clothing and shoes suitable for exercise.
Tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking. Some might need to be adjusted or stopped before the test. Your doctor will tell you if you should keep taking your regular medication.
On test day, wear loose, comfortable clothing and appropriate footwear for exercise. It’s a good idea to bring a towel and water bottle. Also, be ready to give a list of your medications and any important medical history.
By following these tips, you’ll be well-prepared for your stress test. This ensures the results are accurate and reliable.
A stress test is a key tool that shows how well the heart works when stressed. It checks the heart’s function and finds coronary artery disease (Tu et al., 2025). It helps doctors see how the heart handles effort, showing the patient’s heart health.
The main goal of a stress test is to see how the heart works when active. It looks at heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG readings while the patient exercises. This is usually on a treadmill or stationary bike.
Stress tests are also used to spot coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD happens when heart arteries narrow or block due to plaque. A stress test can show if the heart muscle gets less blood, hinting at CAD.
Stress tests also check how well a patient can exercise and their overall health. They watch how long a patient can exercise and how their heart reacts. This helps doctors see if there are heart issues limiting physical fitness.
| Aspect Assessed | Information Provided |
| Cardiovascular Function | Heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG readings during exercise |
| Coronary Artery Disease Detection | Signs of ischemia or reduced blood flow to the heart muscle |
| Exercise Capacity | Duration of exercise and overall physical fitness level |
Understanding stress test results is key. It involves knowing about age and physical health. These tests show how well the heart works, helping doctors find and treat heart problems.
Stress test results can be normal or abnormal. Normal results mean the heart works well under stress. But, abnormal results might show heart disease or other issues. Signs of trouble include ECG changes and a heart rate that’s not right.
ECG changes during a stress test are important. For example, ST-segment depression can mean the heart is not getting enough blood. Knowing these signs helps doctors understand the test results better.
Age also plays a role in stress test results. A chart helps doctors see what’s normal for different ages. For example:
Using these charts helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Alternative stress tests are key for diagnosing heart issues in those who can’t exercise. They’re essential for people with physical limits or other health issues that stop them from doing traditional stress tests.
Healthcare providers have other ways to check heart function for those who can’t exercise. They use pharmacological stress tests. This method uses medicine to mimic exercise’s effects on the heart.
Nuclear stress tests use a tiny bit of radioactive material to see how the heart works under stress. It’s great for spotting coronary artery disease.
A stress echocardiogram uses ultrasound to check how well the heart pumps blood. It shows if any part of the heart isn’t getting enough blood.
| Test Type | Description | Usefulness |
| Nuclear Stress Test | Uses radioactive material to visualize heart function | Diagnosing coronary artery disease |
| Stress Echocardiogram | Uses ultrasound to show heart muscle function | Revealing areas with poor blood flow |
These tests give important info for patients who can’t do traditional stress tests. They make sure everyone gets the care they need.
Stress tests are important for finding heart problems. But, they can cost a lot. This is something patients and doctors think about a lot.
In the U.S., stress tests can cost between $200 and $3,000. This price changes based on where you are, the type of test, and the place you go.
| Type of Stress Test | Average Cost |
| Exercise Stress Test | $200-$500 |
| Nuclear Stress Test | $1,000-$3,000 |
Most insurance plans pay for stress tests if they’re needed. But, how much they cover can differ. Some plans might ask for approval before they pay.
It’s smart to ask your doctor about the total cost and what your insurance will cover. You should also ask about any money you might have to pay yourself.
Stress significantly affects heart rate, making monitoring important.
A stress test, also known as an exercise stress test or treadmill test, checks how well the heart works when you’re active. It’s done by exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike.
A stress test shows if your heart can handle physical activity. It looks for heart problems like coronary artery disease. It also checks how well your heart works and how long you can exercise.
A stress test usually takes 30 minutes to an hour. This includes getting ready and recovering. The exercise part is about 7-12 minutes.
The time on a treadmill for a stress test varies by age. Younger people can usually exercise longer than older adults. A healthy adult might exercise for 7-12 minutes.
To find your target heart rate for a stress test, subtract your age from 220. This gives you your maximum heart rate.
If you don’t reach your maximum heart rate, it might mean there’s a problem. It could be due to medication or other reasons. The test results will be looked at closely.
There are many types of cardiac stress tests. These include exercise tests, chemical tests, nuclear tests, and stress echocardiograms. Each has its own purpose and way of working.
To get ready for a stress test, follow your doctor’s instructions. This might mean avoiding certain medicines, wearing comfy clothes, and being ready to exercise.
Chemical stress tests are good for people who can’t exercise. But, they might have side effects and aren’t for everyone. The good side is they let you check your heart without exercising. The bad side is the side effects and who they’re not good for.
Yes, there are other tests like nuclear imaging stress tests and stress echocardiograms. They give more info and are good for some people.
Doctors interpret stress test results. They look at ECG changes, heart rate, and symptoms. The results can show if everything is normal or if there’s a problem. More tests might be needed.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!