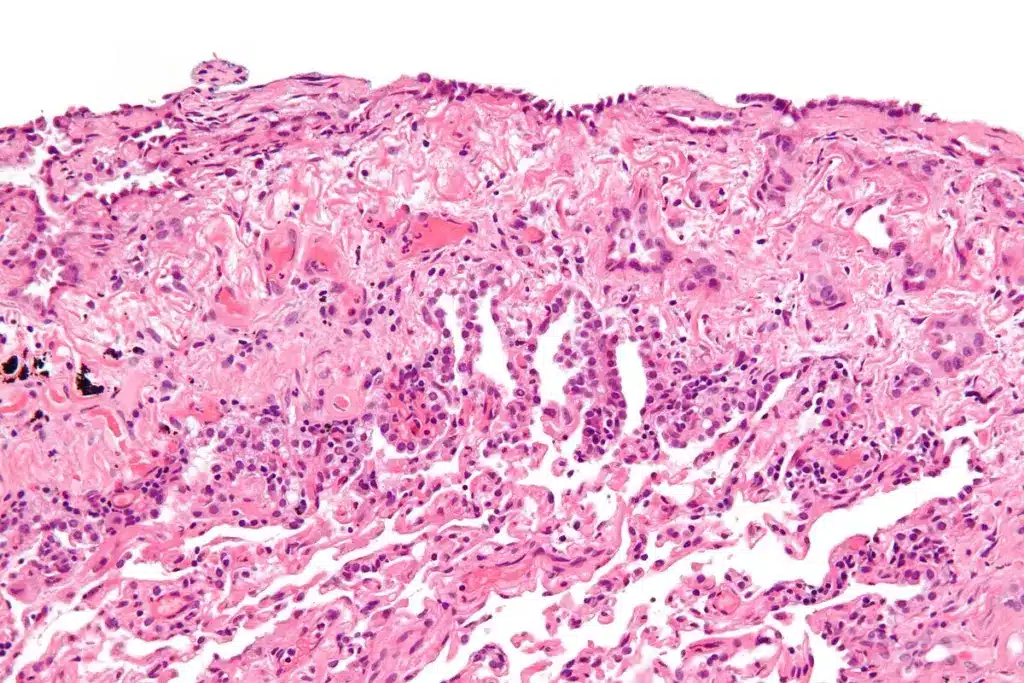
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common type of mesothelioma, making up about 60-70% of cases. It is usually caused by asbestos and has the best chance of recovery among all mesothelioma cell types.
Knowing the important facts about epithelioid mesothelioma helps patients and their families understand the disease better. We will look into its causes, symptoms, and how it is treated. This will give you key insights into this serious asbestos-related disease.
Key Takeaways
- Epithelioid mesothelioma accounts for 60-70% of all mesothelioma cases.
- Asbestos exposure is the primary cause of epithelioid mesothelioma.
- This subtype has the best prognosis among all mesothelioma cell types.
- Treatment options include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation, and surgery.
- Average life expectancy after surgery is about 18 months.
Understanding Epithelioid Mesothelioma Cancer: Prevalence and Causes
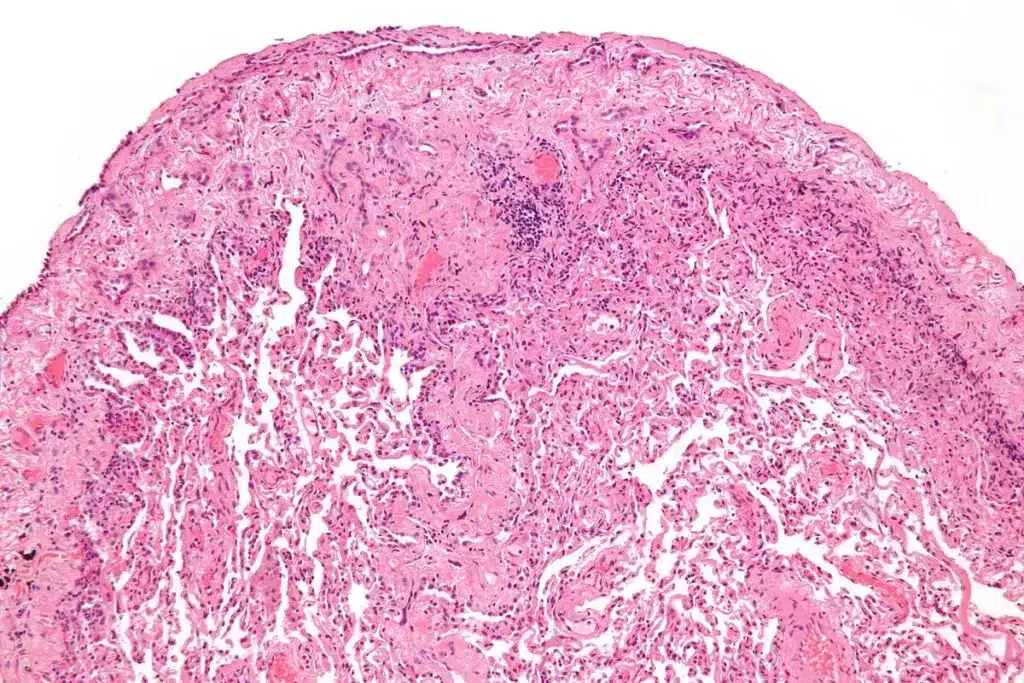
Epithelioid mesothelioma is a serious cancer type. It’s important to know how common it is, what causes it, and how it develops. Knowing these details helps doctors treat it better.
The Most Common Mesothelioma Cell Type
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common type, making up 50-70% of cases. It looks like epithelial cells under a microscope. This type often has a better chance of being treated successfully.
A study by Medical organization shows it has a better outlook. This is because it grows slower and responds well to treatment.
Asbestos Exposure and Mesothelium Tissue Damage
Asbestos is the main cause of epithelioid mesothelioma. When asbestos fibers are breathed in, they damage mesothelial cells. This can lead to cancer. It can take 20 to 60 years for symptoms to show up, making early detection hard.
Medical Expert, a leading thoracic surgeon, says, “Asbestos exposure is the biggest risk for mesothelioma, including the epithelioid type.”
Asbestos damage to mesothelium tissue is complex. Here’s a brief explanation:
| Stage | Description |
| Asbestos Inhalation | Asbestos fibers are inhaled, causing physical damage to mesothelial cells. |
| Chronic Inflammation | Persistent inflammation is triggered, leading to genetic mutations. |
| Cancer Development | Genetic alterations result in the development of epithelioid mesothelioma. |
Understanding epithelioid mesothelioma is key to better treatment and patient care. By knowing how asbestos causes this cancer, we can improve how we manage it.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy Factors
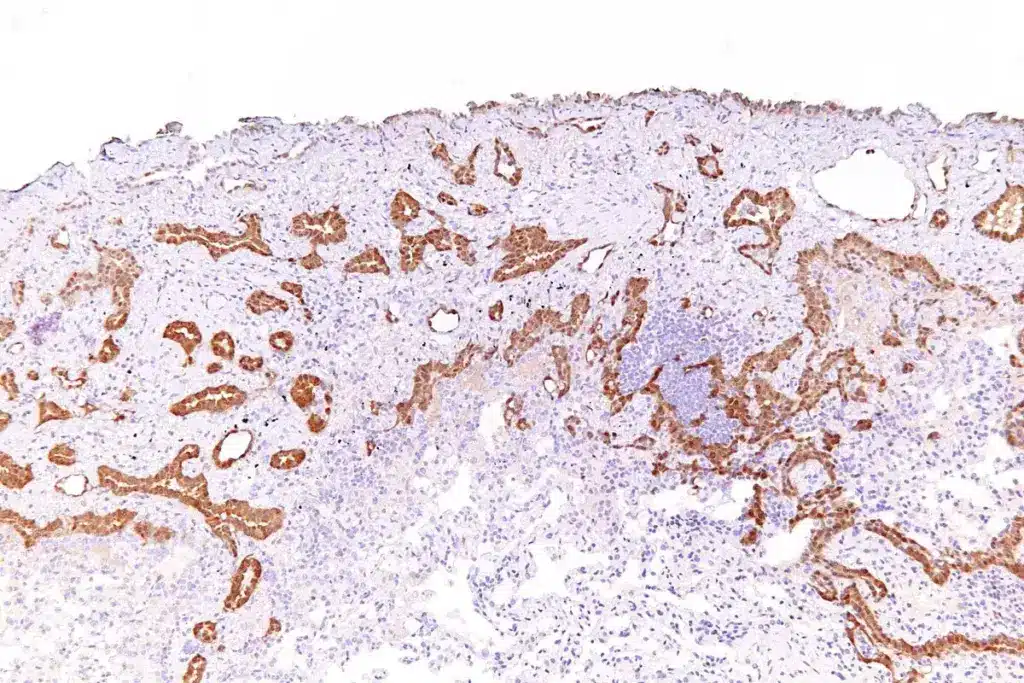
Knowing the prognosis for epithelioid mesothelioma is key for patients and their families. The disease’s outlook depends on several factors. These include the stage at diagnosis and the patient’s overall health.
Average Survival Rates and Comparative Prognosis
Patients with epithelioid mesothelioma usually live about 2.5 years. But, with aggressive treatment, some can live up to 6 years or more. The epithelioid subtype has a better prognosis than other types of mesothelioma. This is because it grows slower and spreads less aggressively.
Comparative survival rates show the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Patients with epithelioid mesothelioma often have better outcomes than those with other subtypes.
Why Epithelioid Type Has Better Outcomes
The epithelioid type of mesothelioma has malignant epithelial cells. These cells are more responsive to treatment than cells in other subtypes. This responsiveness is a key reason for the better outcomes in epithelioid mesothelioma patients.
Several factors contribute to the better prognosis of epithelioid mesothelioma. These include:
- The slower growth rate of the tumor
- The less aggressive nature of the disease
- The higher likelihood of successful surgical intervention
Understanding these factors helps patients and their families make informed decisions about their care and treatment options.
Effective Treatment Approaches
There are several ways to treat epithelioid mesothelioma, a cancer of epithelial tissue. We look at surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy. These methods help manage this malignant mesothelioma cancer.
Treatment for mesotelioma often combines two or more therapies. The choice depends on the disease stage, patient health, and other factors. For example, surgery might remove a tumor. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy help ease symptoms and slow the disease.
Immunotherapy is a promising method. It uses the immune system to fight cancer. By knowing the treatment options, patients can make informed decisions. They work with their healthcare team to get the best results.
FAQ
What is epithelioid mesothelioma?
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common histological subtype of mesothelioma (50%–70% of cases), occurring when epithelial cells in the protective lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart become cancerous.
What causes epithelioid mesothelioma?
The primary cause is the inhalation or ingestion of asbestos fibers, which lodge in the mesothelium and cause chronic inflammation and genetic damage over several decades.
What are the symptoms of epithelioid mesothelioma?
Common symptoms include persistent chest or abdominal pain, shortness of breath, a chronic cough, unexplained weight loss, and fluid buildup known as pleural or peritoneal effusion.
How is epithelioid mesothelioma diagnosed?
Diagnosis is confirmed through a combination of imaging scans (CT, MRI, or PET) and a tissue biopsy, followed by immunohistochemistry to identify specific protein markers like calretinin.
What is the prognosis for epithelioid mesothelioma?
Epithelioid mesothelioma has a more favorable prognosis than other types because the cells spread more slowly and respond better to treatment, with an average life expectancy of 18 to 36 months.
What are the treatment options for epithelioid mesothelioma?
Treatment often involves a multimodal approach combining surgery (to remove visible tumors), chemotherapy (like cisplatin and pemetrexed), and radiation to target remaining cancer cells.
Can epithelioid mesothelioma be treated with surgery?
Yes, eligible patients may undergo aggressive surgeries such as a Pleurectomy/Decortication (P/D) to remove the diseased lining while sparing the lung, or an Extrapleural Pneumonectomy (EPP).
What is the role of immunotherapy in treating epithelioid mesothelioma?
Immunotherapy drugs like Nivolumab (Opdivo) and Ipilimumab (Yervoy) help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells and are now a standard first-line treatment for advanced cases.
[Image showing immunotherapy drugs blocking checkpoint proteins to allow T-cells to attack mesothelioma tumors]
How does asbestos exposure lead to epithelioid mesothelioma?
Asbestos fibers trigger “frustrated phagocytosis,” where immune cells fail to digest the fibers, leading to a release of mutagenic free radicals and chronic inflammation that mutates DNA over 20–50 years.
What is the average survival rate for epithelioid mesothelioma?
With surgery and multimodal therapy, the 2-year survival rate is approximately 45% and the 5-year survival rate is about 14%, significantly higher than the rates for sarcomatoid or biphasic subtypes.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12860938/























