IVF offers hope for couples facing infertility. Learn about the diagnosis, advanced techniques like ICSI and PGT, and the step-by-step treatment process.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Overview and Definition
The journey to parenthood is often envisioned as a natural, effortless path. But for millions of couples worldwide, that path is interrupted by medical hurdles, biological clocks, or unexplained delays. Infertility is not a failure of will or a twist of fate; it is a medical condition of the reproductive system, and like any other medical condition, it deserves scientifically proven treatment.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is the gold standard of reproductive medicine. It is the bridge that helps families cross the gap between “trying” and “conceiving.” At Liv Hospital, our IVF Center is more than a laboratory; it is a sanctuary of hope built on a foundation of rigorous science. We understand that by the time you reach us, you may have already endured months or years of disappointment. Our mission is to end that cycle. By combining Turkey’s world-renowned expertise in reproductive endocrinology with cutting-edge technologies like Embryoscope monitoring and Genetic Screening (PGT-A), we offer success rates that rival the top clinics in Europe and the US.
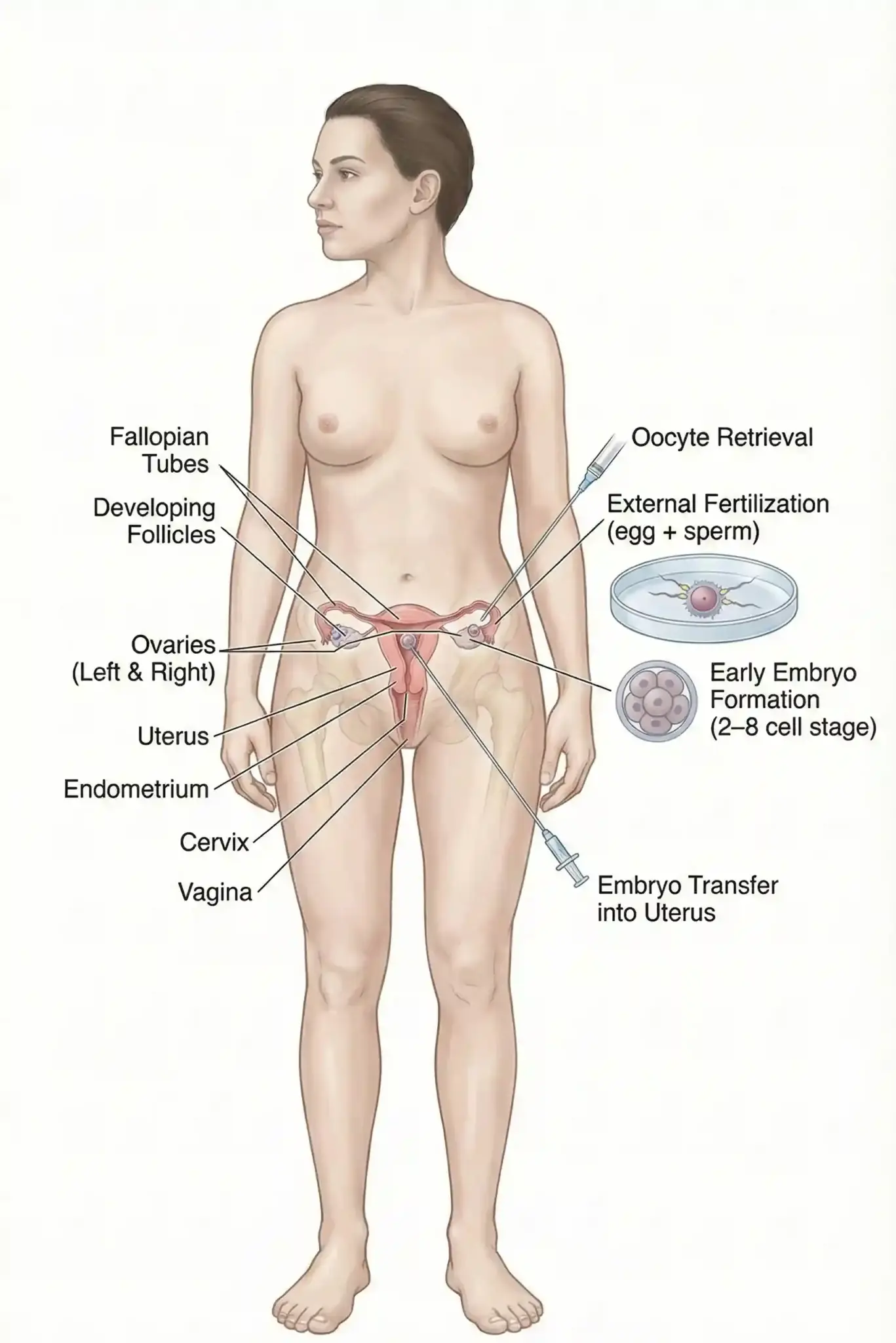
The term “In Vitro” literally means “in glass.” It refers to the process where fertilization—the meeting of the egg and sperm—occurs outside the human body in a controlled laboratory environment.

In a natural pregnancy, an egg is released from the ovary and meets sperm in the fallopian tube. If the tubes are blocked, the sperm count is low, or the egg quality is compromised, this meeting never happens.

Stimulation: We use medication to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs instead of just one.
Retrieval: These eggs are gently collected from the body under light sedation.
Fertilization: In our lab, our embryologists introduce sperm to the eggs.
Culture: The resulting embryos are grown in incubators for 3–5 days until they reach the “Blastocyst” stage.
Transfer: The healthiest embryo is carefully placed back into the uterus to implant and grow.
IVF is not just for blocked tubes. It is a versatile solution for a wide range of fertility challenges. You should consider a consultation at Liv Hospital if you have been trying to conceive for 12 months (or 6 months if you are over 35) without success.
Common Indications Include:


Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

In the world of IVF, the laboratory is the “engine room.” A skilled doctor can retrieve eggs, but it is the laboratory environment that determines whether those eggs become healthy babies. Liv Hospital invests in the absolute latest reproductive technology.
Standard incubators require embryologists to remove the embryos daily to check their progress under a microscope. This disturbs the temperature and pH environment.
For severe male factor infertility, standard magnification isn’t enough.

“Success” in IVF can be defined in many ways. At Liv Hospital, we focus on the Live Birth Rate, not just the positive pregnancy test.
While success depends heavily on the woman’s age and ovarian reserve, our cumulative success rates (after 3 cycles) are consistently high:
Note: These are statistical averages. Your personal prognosis will be determined after your evaluation.

Infertility is stressful, and stress produces cortisol, a hormone that can negatively impact reproductive health. At Liv Hospital, we treat the whole person, not just the reproductive organs.

Turkey has become a global hub for fertility treatment, attracting thousands of couples from Europe, the UK, and the Middle East annually.

Under Turkish law, IVF treatment is strictly limited to legally married couples. We cannot treat single women or unmarried couples. Additionally, Egg Donation, Sperm Donation, and Surrogacy are strictly prohibited. All treatments must use the couple’s own biological gametes.
Most of the process is painless. The daily hormone injections use tiny needles (like insulin pens) that cause minimal discomfort. The egg retrieval is performed under sedation (anesthesia), so you are asleep and feel nothing. You may experience some cramping or bloating for a day or two afterward.
IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) involves placing washed sperm into the uterus during ovulation. It is cheaper but has a much lower success rate (10–15%). IVF involves fertilization in the lab and has much higher success rates (40–60%). We usually recommend moving to IVF after 2–3 failed IUI cycles or immediately if tubes are blocked.
No. Gender selection for “family balancing” is illegal in Turkey. We can only screen for gender if there is a specific sex-linked genetic disease (like Hemophilia) that needs to be avoided.
A full IVF cycle typically requires a stay of 15–20 days.

Choosing how many embryos to transfer in IVF is key in fertility care.how many embryos are transferred in ivfWhere do embryonic stem cells come from?
Period after ivf egg retrieval, many women wonder when their period will come back. We know this can be a worrying time. It’s important to
Guide to the ideal location where in the uterus does the embryo implant (upper posterior wall). Knowing embryo implantation location is key for a healthy
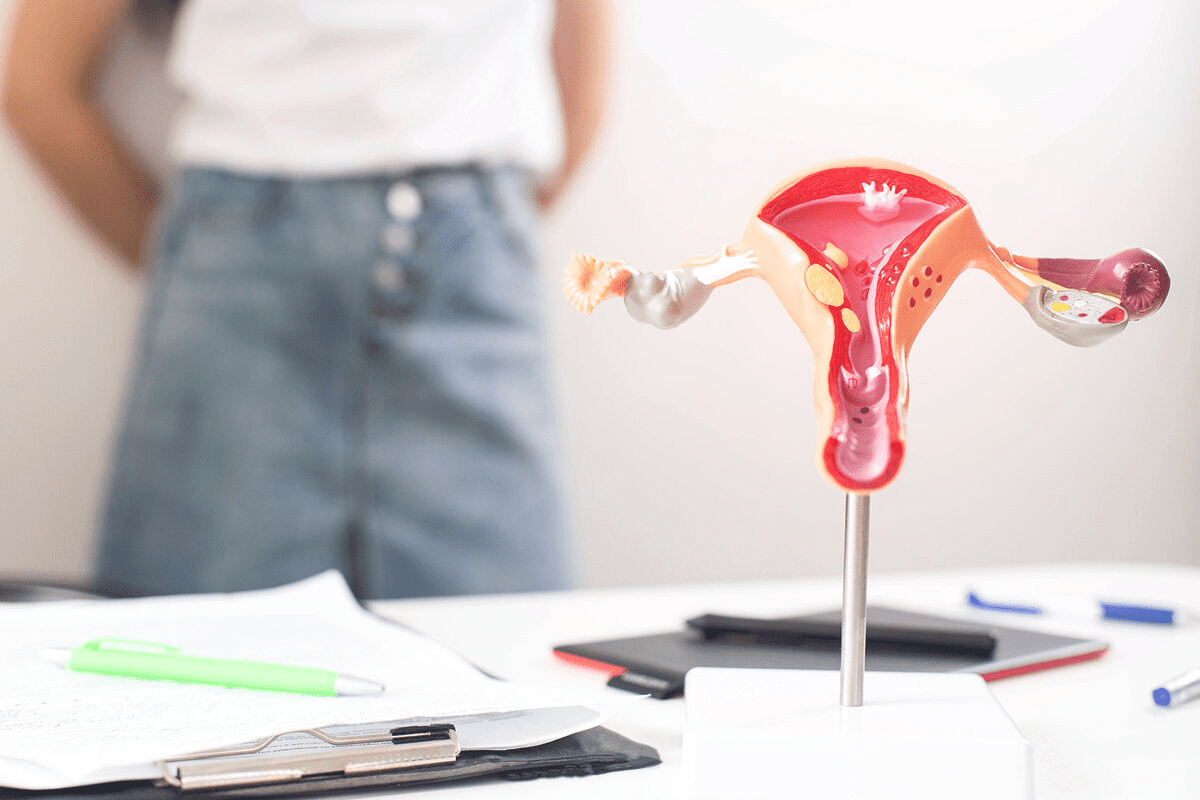
Explaining the best location where do embryos implant in the uterus for successful pregnancy. Embryo implantation is a key step in human reproduction, starting a
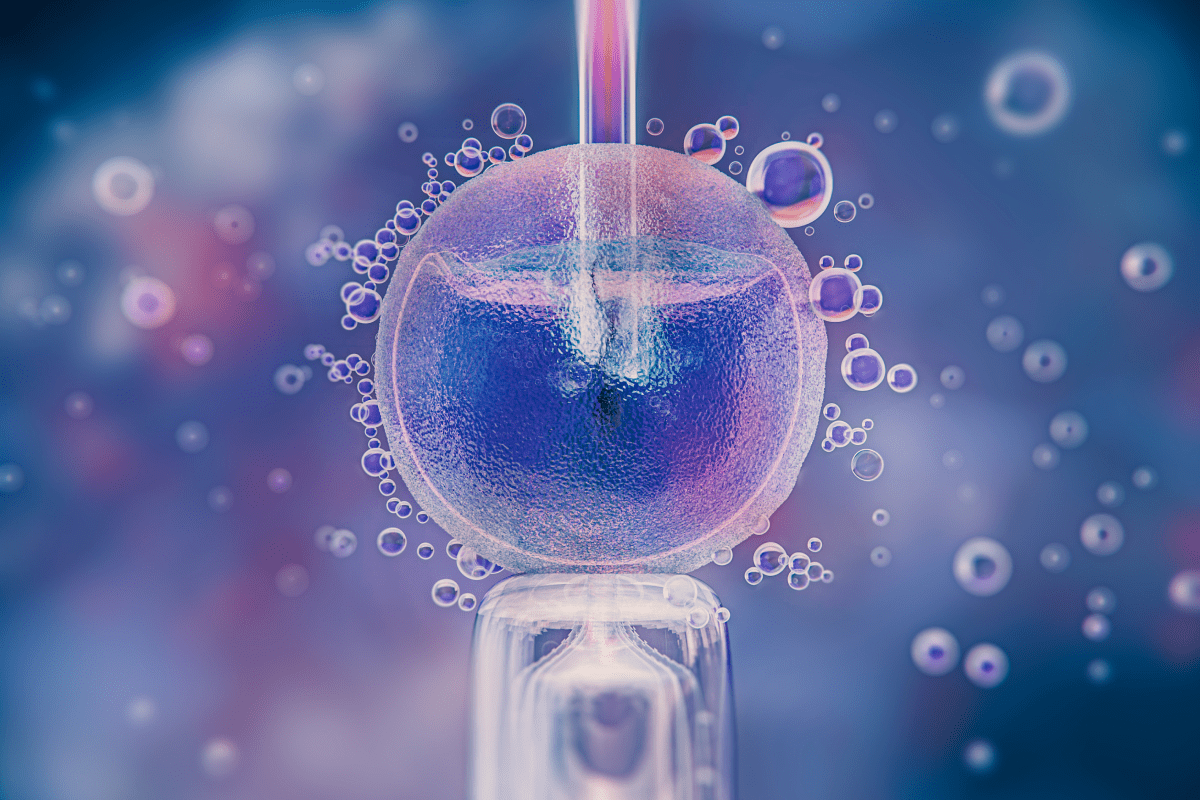
The bloating after embryo transfer is filled with hope and worry. People watch their bodies for signs of a successful embryo implantation. Knowing what to
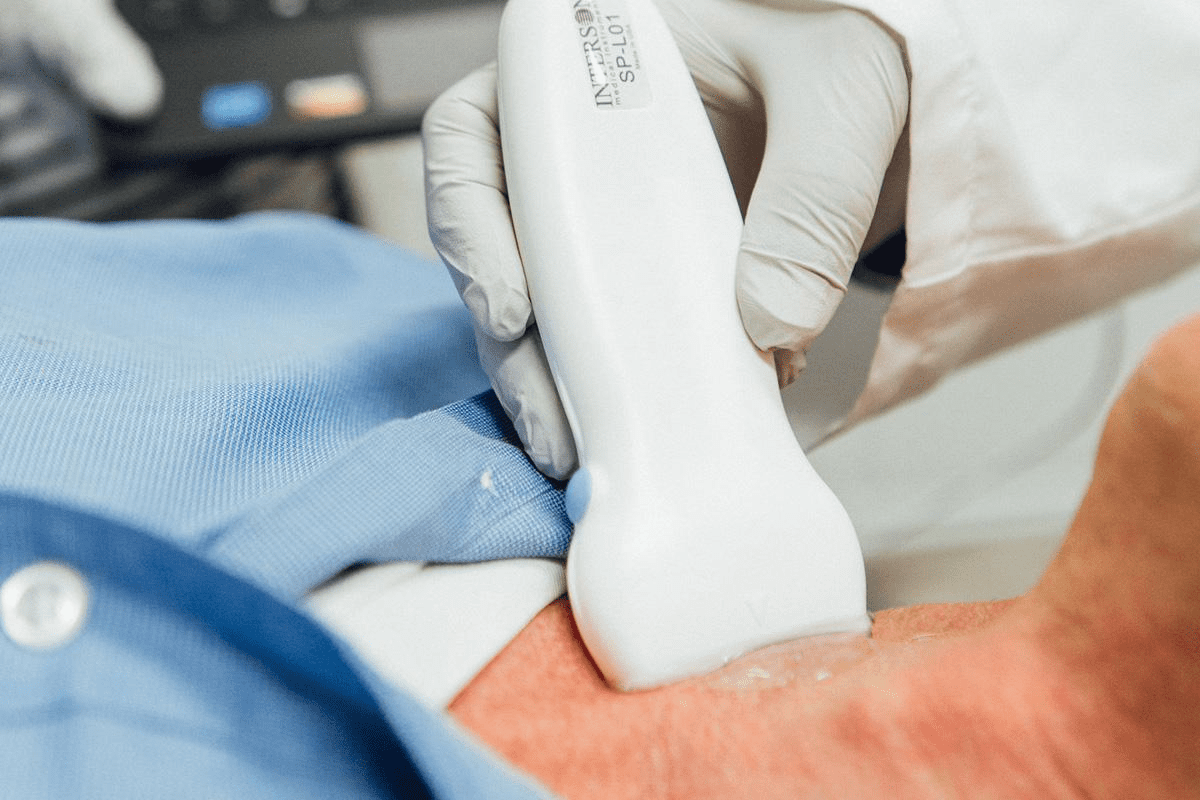
FET ultrasound is key in modern fertility treatments. It helps place embryos exactly in the uterus. This makes IVF treatments more successful for many people.

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)