Pneumonia is a serious infection that makes it hard to breathe. It inflames the air sacs in the lungs. At Liv Hospital, we know it’s key to tell bacterial from viral pneumonia to treat it right.Is pneumonia viral or bacterial? Read our best guide on fever, sputum color, and X-ray differences for a quick home assessment.
Both kinds of pneumonia start with similar symptoms like cough, fever, and trouble breathing. But they need different treatments. Knowing the cause is essential for the right care. Misdiagnosis can slow down recovery and make antibiotics less effective.
We figure out if pneumonia is from a virus or bacteria to treat each patient uniquely. This way, we offer top-notch healthcare and support.
Key Takeaways
- Distinguishing between bacterial and viral pneumonia is critical for effective treatment.
- Pneumonia symptoms can be similar, regardless of the cause.
- Bacterial pneumonia requires antibiotics, while viral pneumonia relies on supportive care.
- Misdiagnosis can lead to delayed recovery and antibiotic resistance.
- Understanding the cause of pneumonia enables tailored treatment.
Understanding Pneumonia: An Overview
Pneumonia is a big health issue that affects people of all ages. Its impact changes based on where you live, how old you are, and your health. It’s important to know about pneumonia to understand its effects.
Definition and Basic Pathophysiology
Pneumonia is often divided by where you got it and the germ that caused it. Community-acquired pneumonia can be from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. We’ll look at the main differences between bacterial and viral pneumonia, as they are the most common.
Pneumonia happens when germs infect the lungs. This causes inflammation and fluid in the air sacs. Symptoms include cough, fever, and trouble breathing.
Global Impact and Prevalence
Pneumonia affects the world a lot, with viral pneumonia causing about one-third of cases. It’s a big reason for sickness and death, mainly in the elderly, young kids, and those with weak immune systems. Knowing how widespread pneumonia is and its causes helps in fighting it.
Knowing the difference between bacterial and viral pneumonia is key for treatment. Both can have similar symptoms, but their causes and treatments are different. This knowledge helps doctors give better care and improve patient results.
Is Pneumonia Viral or Bacterial? Understanding the Pathogens

Knowing if pneumonia is viral or bacterial is key to treating it right. Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can be deadly. It’s caused by different pathogens, and knowing the difference is important for treatment.
Common Bacterial Causes
Bacterial pneumonia is often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. This bacterium can cause severe illness, mainly in people with weak immune systems or health issues. Other bacteria like Haemophilus influenzae and Klebsiella pneumoniae can also lead to pneumonia, with varying severity.
“The most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae,” says experts. This shows how important this bacterium is in respiratory infections.
Common Viral Causes
Viral pneumonia is usually caused by respiratory viruses. Influenza viruses are a major cause, mainly during flu season. Other viruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), coronaviruses (like SARS-CoV-2), and adenoviruses can also cause pneumonia. These viruses can spread and affect people of all ages, with different levels of severity.
- Influenza viruses
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Coronaviruses (including SARS-CoV-2)
- Adenoviruses
Knowing the specific virus is key to managing the infection well. Treatment plans can differ a lot between viruses.
By figuring out the cause, whether bacterial or viral, doctors can create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs. This can help improve outcomes and lower the chance of complications.
Bacterial Pneumonia: Characteristics and Causes
Bacterial pneumonia can start suddenly, with severe symptoms that need quick care. It’s an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs.
This condition can be severe because it often affects just one lung lobe. It often comes after a viral infection, making it harder to treat.
Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Other Common Bacteria
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the main cause of bacterial pneumonia. Other bacteria, like Haemophilus influenzae and Klebsiella pneumoniae, can also cause it.
|
Bacteria |
Common Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Gram-positive, lancet-shaped diplococci |
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
Gram-negative, coccobacillus |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
Gram-negative, encapsulated bacilli |
How Bacterial Pneumonia Develops
Bacterial pneumonia starts when bacteria are inhaled into the lungs. It can also spread through the bloodstream or from nearby areas.
The process of getting bacterial pneumonia involves several steps. First, bacteria colonize the upper respiratory tract. Then, they invade the lung tissue. Knowing these steps helps doctors diagnose and treat it early.
Understanding the causes and signs of bacterial pneumonia helps doctors treat it better. This improves patient outcomes.
Viral Pneumonia: Characteristics and Causes
Viral pneumonia is a big health issue that affects many people worldwide. It can be hard to tell apart from bacterial pneumonia. Knowing the causes and differences is key.
Influenza, RSV, Coronaviruses, and Other Viral Agents
Viral pneumonia can be caused by many viruses. These include influenza, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), and coronaviruses. These viruses cause lung inflammation, leading to pneumonia.
Influenza virus is a common cause, mainly during flu season. RSV is big in young kids and older adults. Coronaviruses, like SARS-CoV-2, also cause viral pneumonia.
“Understanding the specific viral cause of pneumonia is key for the right treatment.”
Medical Expert, Pulmonologist
How Viral Pneumonia Develops
Viral pneumonia happens when a virus attacks the lung tissue. This causes inflammation and fluid in the air sacs. It can make breathing hard and lead to cough, fever, and shortness of breath.
The symptoms can get worse over time. This makes it hard to breathe.
|
Viral Agent |
Common Symptoms |
High-Risk Groups |
|---|---|---|
|
Influenza |
Fever, cough, body aches |
Older adults, young children |
|
RSV |
Runny nose, cough, wheezing |
Young children, older adults |
|
Coronaviruses |
Fever, cough, shortness of breath |
All ages, those with health issues |
The table shows common viruses, symptoms, and who’s at risk. Knowing this helps in treating viral pneumonia better.
Understanding viral pneumonia is vital for better treatment. By knowing the differences, doctors can give better care.
Symptom Differences Between Bacterial and Viral Pneumonia
It’s important to know the differences between bacterial and viral pneumonia to treat them right. Both types have similar symptoms, but they start and get worse in different ways.
Onset and Progression Patterns
Bacterial pneumonia hits fast and hard. “Bacterial pneumonia can strike quickly, with symptoms escalating rapidly.” Viral pneumonia starts like a bad cold or flu and gets worse slowly.
A study found that bacterial pneumonia starts suddenly with high fever and chills. “The rapid progression of bacterial pneumonia necessitates prompt medical attention.”
Fever and Respiratory Symptoms
Both types cause fever, cough, and chills. But, how bad these symptoms are can vary. Bacterial pneumonia has a higher fever and more severe respiratory symptoms, like coughing up rust-colored or greenish mucus.
“The presence of rust-colored sputum is a classic sign of bacterial pneumonia, particularlly when caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae.”
Viral pneumonia has a dry cough or coughs up clear mucus. Its fever is usually not as high as bacterial pneumonia’s.
Physical Examination Findings
Healthcare providers can tell bacterial and viral pneumonia apart during a physical exam. Bacterial pneumonia shows signs of lung consolidation, like crackles or dullness to percussion.
- Bacterial pneumonia often shows signs of lung consolidation.
- Viral pneumonia may present with more diffuse findings.
- Physical examination findings can guide further diagnostic testing.
By looking at how symptoms start, what they are, and what the physical exam shows, doctors can figure out what kind of pneumonia it is. Then, they can start the right treatment.
Diagnostic Approaches: Identifying the Culprit
Diagnosing pneumonia requires a mix of clinical checks, lab tests, and imaging. Knowing the cause is key to picking the right treatment. This is true for both bacterial and viral pneumonia.
Laboratory Tests and Biomarkers
Labs are essential in finding out what’s causing pneumonia. Important tests include:
- Blood Tests: Look for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Shows how severe the infection is.
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP): High levels suggest a bacterial infection.
- Procalcitonin: Helps tell if it’s bacterial or viral.
These tests guide doctors in diagnosing and treating pneumonia.
|
Test |
Purpose |
Indications |
|---|---|---|
|
Blood Culture |
Find bacteria in the blood |
Think it’s bacterial pneumonia |
|
CBC |
Check how severe the infection is |
Have severe symptoms or are at high risk |
|
CRP |
Show if it’s a bacterial infection |
High in bacterial pneumonia |
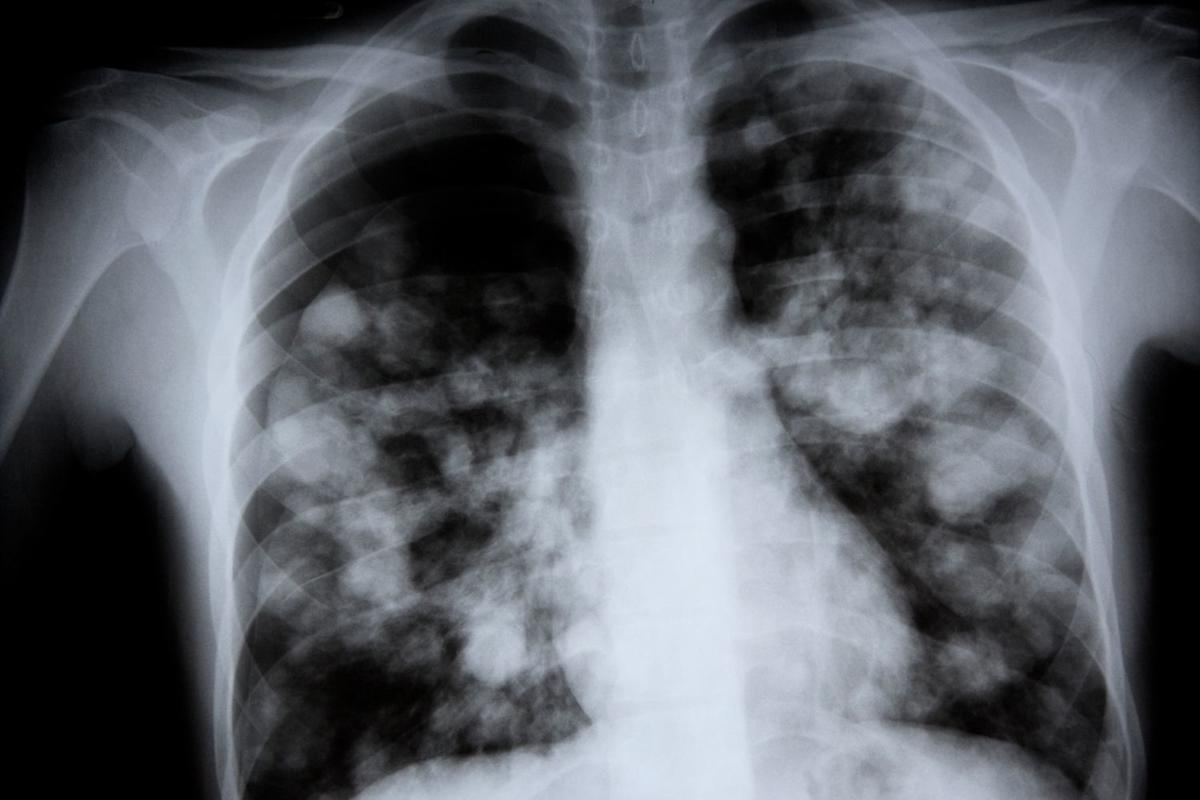
Imaging Differences
Imaging, like chest X-rays, is vital for diagnosing pneumonia. They help by:
- Confirming pneumonia.
- Seeing how much of the lung is affected.
- Finding complications like pleural effusion.
Microbiological Testing
Microbiological tests directly find the pneumonia cause. These include:
- Sputum Culture: Finds bacteria or fungi in respiratory secretions.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Detects viral or bacterial DNA/RNA.
- Serology: Looks for antibodies against specific pathogens.
These tests are key for confirming the diagnosis and creating a treatment plan.
In conclusion, diagnosing pneumonia needs a team effort. It includes clinical checks, lab tests, and imaging. By using these tools, doctors can accurately find the cause and treat it effectively.
Treatment Strategies for Bacterial vs. Viral Pneumonia
Knowing how to treat bacterial and viral pneumonia is vital for good care. These two types of pneumonia need different treatments. This is not just a detail; it’s a big deal for patient care.
Antibiotic Therapy for Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics. The right antibiotic depends on the pneumonia’s severity, the patient’s age, and health conditions. For example, amoxicillin is often the first choice for adults with community-acquired pneumonia.
In serious cases or when the cause is unknown, stronger antibiotics might be given. It’s important to finish all antibiotics to clear the infection and avoid resistance.
Management of Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia needs a different strategy. Antibiotics don’t work on viruses, but antiviral medications might be used for certain viruses like influenza.
For viral pneumonia, the main focus is on supportive care. This includes rest, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter meds for symptoms. In severe cases, hospital care may be needed for oxygen and other treatments.
Supportive Care Approaches
Supportive care is key for both bacterial and viral pneumonia. It helps manage symptoms, prevent complications, and aids in recovery. Drinking enough water, eating well, and getting plenty of rest are essential.
In summary, treating pneumonia depends on its cause. Understanding these differences is essential for effective care.
Recovery and Prognosis: What to Expect
Recovering from pneumonia is a journey that varies based on the type of pneumonia and your health. Knowing the typical recovery times and possible complications is key for both patients and doctors.
Typical Recovery Timeline for Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia recovery is usually more predictable than viral pneumonia. Most people start feeling better in 3-5 days after starting antibiotics. But, it can take several weeks to fully recover.
Key milestones in bacterial pneumonia recovery include:
- Reduction in fever within 2-3 days
- Improvement in cough and breathing within 4-6 days
- Return to normal activities within 3-6 weeks
Typical Recovery Timeline for Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia recovery can vary a lot. It often depends on the virus causing the infection. People may start feeling better in 1-2 weeks. But, some might have symptoms for up to 6 weeks or more.
Key considerations for viral pneumonia recovery include:
- The risk of getting a secondary bacterial infection
- The impact of any underlying health conditions
- The role of antiviral medications in managing symptoms
When to Seek Additional Medical Care
It’s important for patients to know when to get more medical help after pneumonia. Warning signs that need immediate care include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Chest pain or pressure
- Fever above 102°F (39°C)
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus
We advise patients to watch their symptoms closely. Seek medical care if they see any of these warning signs or if their condition gets worse.
|
Recovery Aspect |
Bacterial Pneumonia |
Viral Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
|
Initial Improvement |
3-5 days with antibiotics |
1-2 weeks, variable |
|
Full Recovery |
3-6 weeks |
Up to 6 weeks or more |
|
Common Complications |
Bacterial resistance, sepsis |
Secondary bacterial infections, exacerbation of underlying conditions |
Complications and Co-infections
It’s key to know the possible complications of pneumonia to manage it well. Both bacterial and viral pneumonia can cause serious issues. These are more common in the elderly, young kids, and those with weak immune systems.
Potential Complications of Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia can lead to serious problems. One big issue is respiratory failure, where the lungs can’t get enough oxygen. Other serious issues include:
- Septicemia: Bacteria get into the blood, which can cause sepsis, a very dangerous condition.
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid builds up around the lungs, which might need to be drained.
- Lung Abscess: A pocket of pus forms in the lung, needing antibiotics or drainage.
Potential Complications of Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia can also cause serious problems, mainly for those who are more vulnerable. Common issues include:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A severe lung condition that can be very dangerous.
- Secondary Bacterial Infection: Patients might get a secondary bacterial pneumonia, making treatment harder.
- Multi-organ Failure: In severe cases, viral pneumonia can cause failure of other organs.
When Both Types Occur Together
When both bacterial and viral pneumonia happen at the same time, it makes diagnosis and treatment harder. These cases are often more serious and have a higher risk of complications. It’s important to know about co-infections to tailor treatment properly.
|
Complication |
Bacterial Pneumonia |
Viral Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
|
Respiratory Failure |
Common |
Common |
|
Septicemia |
Frequent |
Rare |
|
Secondary Infection |
Less Common |
Frequent |
We need to understand the complications of both bacterial and viral pneumonia to give the best care. Early treatment and management of these complications can greatly improve patient outcomes.
Special Populations and Risk Factors
Pneumonia hits different groups in different ways. We look at how it affects children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. We’ll talk about their special risks and challenges.
Pneumonia in Children: Viral vs. Bacterial Differences
Children are more at risk for pneumonia because their immune systems are not fully grown. Viral pneumonia is common in kids under 5, with Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) being a big cause. On the other hand, bacterial pneumonia, often from Streptococcus pneumoniae, can be more serious.
It’s hard to figure out what kind of pneumonia a child has. Doctors use tests, lab work, and sometimes pictures to find out.
Pneumonia in the Elderly
The elderly face a higher risk of pneumonia because their immune systems weaken with age. Bacterial pneumonia is more common in older adults, and they are more likely to get very sick. They often don’t show clear symptoms, making it tough to diagnose.
“Pneumonia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the elderly, stressing the need for quick diagnosis and treatment.”
– Medical Expert
Immunocompromised Patients
People with weakened immune systems, due to illness or treatment, are more likely to get pneumonia. Opportunistic infections are a big worry, with pathogens like Pneumocystis jirovecii causing pneumonia in those with weak immune systems.
Dealing with pneumonia in people with weakened immune systems needs careful thought. It’s important to consider their immune status and the possible germs causing the infection.
|
Population |
Common Causes |
Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
|
Children |
RSV, Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Young age, developing immune system |
|
Elderly |
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Influenza |
Age-related immune decline, comorbidities |
|
Immunocompromised |
Pneumocystis jirovecii, CMV |
Immunosuppression due to disease or treatment |
It’s key to understand the unique challenges and risks in special groups to manage pneumonia well. By knowing these differences, doctors can give better care and improve health outcomes.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Clinical Implications
It’s important to know the difference between bacterial and viral pneumonia. This knowledge helps in treating and managing the condition. Accurate diagnosis is key to figure out if pneumonia is caused by bacteria or a virus. This is because the treatment varies greatly.
Bacterial pneumonia has more severe symptoms and needs antibiotics. On the other hand, viral pneumonia might need antiviral drugs and supportive care. The symptoms and how they are treated differ significantly.
When diagnosing pneumonia, the treatment options depend a lot on the patient’s health. We must consider the patient’s overall health, age, and any underlying conditions. This helps in choosing the right treatment.
Healthcare providers can offer better care by understanding the differences between bacterial and viral pneumonia. This targeted approach improves patient outcomes and lowers the risk of complications.
FAQ
What is the difference between bacterial and viral pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia is caused by bacteria and has sudden, severe symptoms. Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses and has symptoms that come on more slowly.
Is pneumonia bacterial or viral?
Pneumonia can be either bacterial or viral, depending on the cause.
What are the common bacterial causes of pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common cause of bacterial pneumonia. Other bacteria like Haemophilus influenzae and Klebsiella pneumoniae also cause it.
What are the common viral causes of pneumonia?
Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and coronaviruses are common viral causes of pneumonia.
How is bacterial pneumonia diagnosed?
Bacterial pneumonia is diagnosed with lab tests like blood cultures and sputum analysis. Chest X-rays are also used.
How is viral pneumonia diagnosed?
Viral pneumonia is diagnosed with lab tests like PCR and serology. Chest X-rays are also used.
What is the treatment for bacterial pneumonia?
Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics like beta-lactam and macrolides.
What is the treatment for viral pneumonia?
Viral pneumonia is managed with rest, hydration, and oxygen therapy. Antiviral medications may be used in some cases.
Can pneumonia be both bacterial and viral?
Yes, pneumonia can be caused by both bacteria and viruses, known as co-infection.
What are the possible complications of bacterial pneumonia?
Complications of bacterial pneumonia include respiratory failure, sepsis, and lung abscess.
What are the possible complications of viral pneumonia?
Complications of viral pneumonia include respiratory failure, ARDS, and secondary bacterial infections.
How long does it take to recover from bacterial pneumonia?
Recovery from bacterial pneumonia takes several weeks. Most people recover in 4-6 weeks.
How long does it take to recover from viral pneumonia?
Recovery from viral pneumonia varies. It usually takes several weeks, with some recovering in 2-4 weeks.
When should I seek additional medical care for pneumonia?
Seek additional medical care if symptoms worsen, breathing is difficult, or if you have underlying health conditions.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/pneumonia/about/index.html























