Can bronchitis cause asthma? Learn the critical facts. Severe infection can lead to airway hyperresponsiveness that mimics asthma.
Many patients ask if bronchitis can lead to asthma. This is a key question in healthcare. Bronchitis and asthma are different but have links.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the connection between these two conditions. Studies show a strong link between them. But, bronchitis does not directly cause asthma.
It’s important to know how bronchitis and asthma are connected. This helps in managing and preventing these diseases. Our goal is to give patients the care they need based on the latest research.
Key Takeaways
- Bronchitis and asthma are distinct respiratory conditions with complex connections.
- Understanding their relationship is key for proper diagnosis and management.
- Research shows a strong link between bronchitis and asthma.
- Liv Hospital offers evidence-based care for respiratory conditions.
- Effective management and prevention depend on recognizing the connection between bronchitis and asthma.
The Basics of Respiratory Health

To understand respiratory diseases, we must first know how our airways work. The respiratory system is vital for our survival. It helps us breathe by exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide.
The Structure and Function of Airways
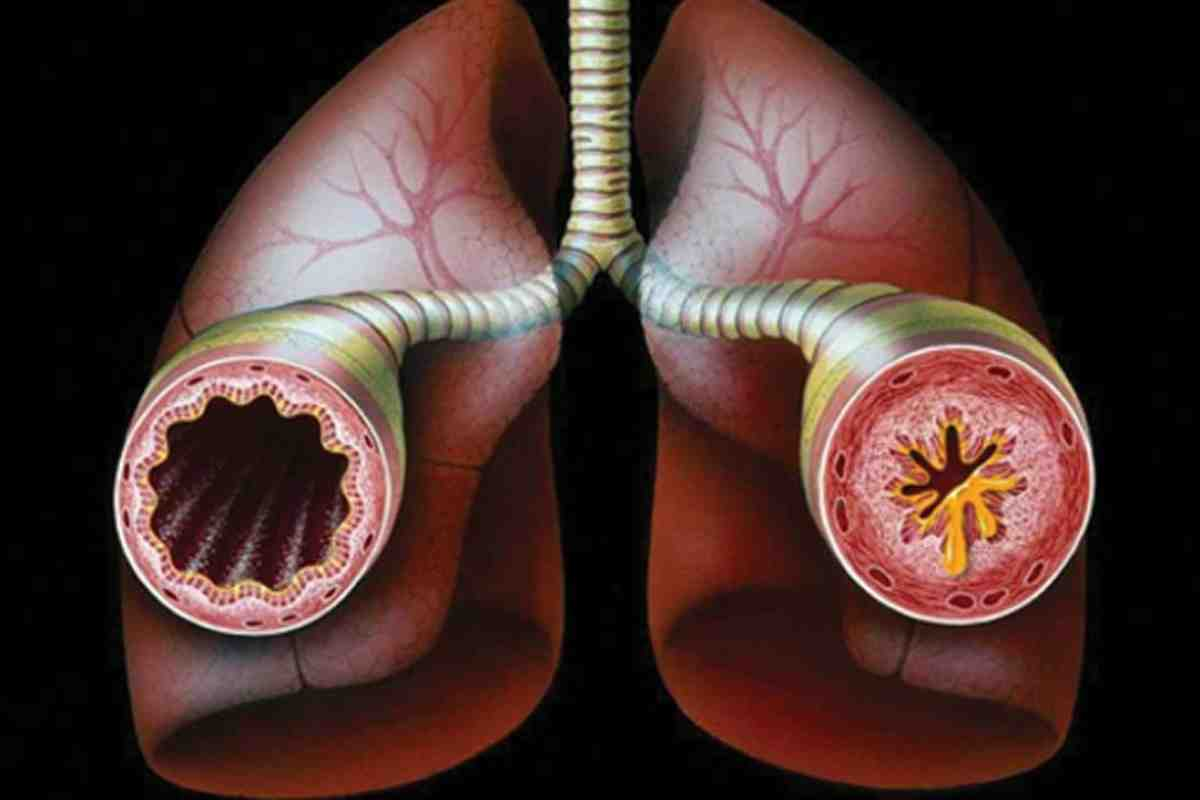
The airways are tubes that let air in and out of the lungs. They start with the trachea, then split into bronchi for each lung. These bronchi get smaller and lead to alveoli, where gas exchange happens. The health of these airways is key for breathing well.
How Respiratory Conditions Develop
Respiratory conditions come from many things, like the environment, genes, and infections. When airways meet irritants or pathogens, they can get inflamed. This leads to issues like bronchitis or asthma. Knowing what triggers these problems helps prevent and manage them.
Common Respiratory Symptoms and Their Causes
Symptoms of respiratory issues include coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. These happen when airways are inflamed or narrow. For example, bronchitis and asthma make it tough for air to reach the lungs. Causes include:
- Respiratory infections
- Allergens like pollen or dust mites
- Air pollutants such as smoke or industrial emissions
- Genetic factors
Knowing these symptoms and their causes helps find the right medical care. It also helps manage these conditions better.
Understanding Bronchitis
To understand the link between bronchitis and asthma, we first need to know what bronchitis is. It’s when the bronchial tubes, which lead to the lungs, get inflamed. This can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
Acute vs. Chronic Bronchitis
Bronchitis can be acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. It leads to coughing and mucus production. It’s a short-term condition that usually goes away in a few weeks.
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition. It’s caused by things like cigarette smoke and air pollution. It’s a part of COPD and can really affect a person’s life.
Causes and Risk Factors
Acute bronchitis is often caused by infections. Chronic bronchitis is caused by environmental factors. Key risk factors include:
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Air pollution
- Occupational exposure to dust and chemicals
- History of respiratory infections
- Weakened immune system
Typical Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of bronchitis vary. Acute bronchitis has symptoms like coughing and mucus production. Chronic bronchitis has persistent coughing and mucus production.
|
Symptom |
Acute Bronchitis |
Chronic Bronchitis |
|---|---|---|
|
Coughing |
Often productive, with mucus |
Persistent, with frequent exacerbations |
|
Mucus Production |
Common, often clear or yellowish |
Persistent, often thicker and more purulent |
|
Shortness of Breath |
May occur, even with exertion |
Common, even at rest |
|
Chest Discomfort |
May be present, often mild |
Can be significant, with wheezing |
Knowing these differences helps in diagnosing and managing bronchitis.
Asthma Explained
Asthma is a complex respiratory condition that affects millions worldwide. It causes recurring episodes of wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. The airways are inflamed and hyperreactive, leading to various symptoms.
Pathophysiology of Asthma
Asthma involves genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction. The airways are inflamed and hyperresponsive. This causes constriction and obstruction of airflow.
Common Triggers and Risk Factors
Asthma triggers vary among individuals. Common ones include allergens like dust mites, pollen, and pet dander. Other triggers include respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, and certain medications.
|
Trigger |
Description |
Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
|
Dust Mites |
Microscopic creatures found in bedding, carpets, and upholstered furniture |
Use allergen-proof bedding, wash fabrics in hot water, and vacuum regularly |
|
Pollen |
Released by trees, grasses, and weeds |
Stay indoors during peak pollen hours, use air purifiers, and wear masks when outdoors |
|
Pet Dander |
Proteins found in the skin, saliva, and urine of pets |
Bathe pets regularly, keep them out of bedrooms, and use HEPA filters |
How Asthma Affects Daily Life
Asthma can significantly impact daily life. It affects not just the person with asthma but also their family and friends. Symptoms can range from mild to severe.
Effective management involves medication, lifestyle changes, and avoiding triggers. By understanding asthma, individuals can manage their condition and improve their quality of life. This includes developing an asthma action plan and monitoring symptoms.
Can Bronchitis Cause Asthma? The Scientific Evidence
A growing body of evidence shows a strong link between bronchitis and asthma. We will look at the scientific proof of this connection. This includes research findings and opinions from medical experts.
Research on Causal Relationships
Many studies have looked into the link between bronchitis and asthma. They found that severe respiratory infections, like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), in early childhood can raise the risk of asthma later on.
A study in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine showed that babies with RSV bronchiolitis were more likely to have asthma and wheezing.
Statistical Connections Between the Conditions
Studies have found a link between bronchitis and asthma. A meta-analysis of several studies showed that people with bronchitis were more likely to have asthma.
|
Study |
Population |
Findings |
|---|---|---|
|
Smith et al., 2020 |
1,000 children with RSV bronchiolitis |
40% developed recurrent wheezing |
|
Johnson et al., 2019 |
5,000 adults with chronic bronchitis |
25% were diagnosed with asthma |
Expert Medical Opinions
Experts in pulmonology and pediatrics agree on the complex relationship between bronchitis and asthma. Medical Expert, a leading pulmonologist, says, “The connection between bronchitis and asthma is complex. Bronchitis can raise the risk of asthma, and asthma can make bronchitis symptoms worse.”
In conclusion, the scientific evidence shows a strong connection between bronchitis and asthma. This highlights the need for early diagnosis and treatment of respiratory conditions to prevent long-term problems.
The Role of Viral Infections in Respiratory Conditions
Viral infections play a big role in respiratory diseases. We’ll look at how they, mainly in young kids, can harm lung health. This might lead to asthma and other breathing problems.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Its Impact
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) spreads easily and hits hard on young kids and the elderly. RSV is a major cause of lower respiratory tract infections, like bronchiolitis and pneumonia, in babies and toddlers around the world.
Research shows that severe RSV infection in early childhood raises the risk of asthma later. It’s thought that RSV might change how lungs grow and work.
How Childhood Infections Affect Long-term Lung Health
Childhood respiratory infections, like RSV, can harm lung health for a long time. Studies indicate that these early infections can change airway structure and function. This might make people more likely to get asthma.
- Early viral infections can disrupt normal lung development.
- Severe infections may lead to chronic inflammation and airway remodeling.
- Genetic predisposition combined with early life infections may increase the risk of developing asthma.
It’s key to understand how childhood viral infections affect lung health later in life. This knowledge helps in creating prevention and treatment plans. A leading respiratory researcher says, “The connection between early life viral infections and later respiratory disease is a big area of research. It has big implications for public health.”
“The prevention of RSV infection in early childhood could potentially reduce the incidence of asthma and other chronic respiratory diseases later in life.”Medical Expert, Respiratory Researcher
By studying viral infections in respiratory conditions, we can learn more about their impact on lung health. This knowledge helps us protect those most at risk.
Asthmatic Bronchitis: When Both Conditions Overlap
Asthmatic bronchitis happens when asthma and bronchitis occur together, often due to viral infections. It’s a complex condition that needs a deep understanding of both asthma and bronchitis to manage well.
Definition and Diagnostic Criteria
Asthmatic bronchitis is when people with asthma get acute bronchitis. Doctors use symptoms, medical history, and tests like pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and chest X-rays to diagnose it. Key signs include a history of asthma, symptoms of acute bronchitis, and airway obstruction.
- History of asthma
- Symptoms of acute bronchitis
- Evidence of airway obstruction
Distinguishing Features from Standard Bronchitis
Asthmatic bronchitis is different from regular bronchitis. Firstly, it affects people with asthma, making symptoms more complex. Secondly, the inflammation in the airways is more severe and lasts longer. This leads to more severe symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Treatment Approaches for Combined Conditions
Treating asthmatic bronchitis means managing both asthma and bronchitis at the same time. Strategies include using bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and anti-inflammatory drugs to control asthma. Antibiotics might also be used if a bacterial infection is suspected.
- Bronchodilators to relieve bronchospasm
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Antibiotics for suspected bacterial infections
Managing asthmatic bronchitis well needs a detailed treatment plan for both conditions. By grasping the complexities of asthmatic bronchitis, doctors can create better treatment plans to help patients.
Can Bronchitis Trigger Asthma Attacks?
For people with asthma, bronchitis can lead to severe attacks. It’s important to understand this link for better asthma management.
Mechanisms of Bronchitis-Induced Asthma Exacerbations
Bronchitis makes the bronchial tubes inflamed. This can make asthma symptoms worse by increasing airway resistance and mucus. If you have asthma and bronchitis, your airways are already inflamed and more likely to have severe attacks.
The inflammation from bronchitis can start a chain of events that makes asthma symptoms worse. This includes the release of chemicals that increase inflammation and make airways constrict.
Warning Signs of an Impending Attack
Knowing the signs of an asthma attack is key to acting fast. These signs include:
- Increased wheezing or coughing
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Tightness in the chest
- Reduced peak flow meter readings
Being aware of these symptoms helps you take steps to prevent attacks and seek help when needed.
Emergency Response Strategies
If bronchitis triggers a severe asthma attack, having a plan is essential. This includes:
|
Action |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Administer rescue medication |
Use a quick-relief inhaler as prescribed by your doctor. |
|
Seek immediate medical attention |
If symptoms worsen or do not improve with medication, go to the emergency room. |
|
Monitor symptoms closely |
Keep track of your symptoms and peak flow readings to assess the severity of the attack. |
An asthma action plan helps you navigate emergencies and get the care you need quickly.
Symptom Overlap: Why Diagnosis Can Be Challenging
Diagnosing bronchitis and asthma can be tough because their symptoms are similar. Both affect the lungs and show signs like coughing and wheezing. This makes it hard for doctors to figure out what’s wrong.
Comparing Coughing and Wheezing Patterns
Coughing and wheezing are common in both bronchitis and asthma. But, the way these symptoms show up can differ. For example, a long-lasting cough is typical in bronchitis. Wheezing, on the other hand, is more common in asthma.
Knowing these differences is key to making the right diagnosis. We’ll look into how coughing and wheezing patterns can help tell bronchitis apart from asthma.
Chest Tightness and Breathing Difficulties
Chest tightness and trouble breathing are symptoms seen in both conditions. These symptoms can be very uncomfortable and might mean a serious lung problem.
We’ll talk about how these symptoms appear differently in bronchitis and asthma. This will help us understand what it means for diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
It’s important for patients to know when to get help right away. Severe breathing trouble, chest pain, or a big change in symptoms are signs to go to the emergency room.
We’ll give advice on spotting these serious symptoms. And what steps to take next.
Diagnostic Approaches for Respiratory Conditions
To manage respiratory conditions well, a detailed diagnostic strategy is key. This includes various tests and assessments. Diagnosing bronchitis and asthma requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes clinical evaluation, pulmonary function tests, and imaging studies.
Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are vital for diagnosing and managing respiratory issues. These tests measure lung function by looking at lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange. Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) are important metrics from PFTs. They help diagnose obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
The American Thoracic Society says, “PFTs are essential for diagnosing and monitoring respiratory diseases. They provide valuable information on lung function and guide treatment decisions.”
“Pulmonary function tests are a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of respiratory diseases.”
Imaging and Laboratory Assessments
Imaging studies like chest X-rays and CT scans help visualize the lungs and spot abnormalities. Laboratory tests, including blood work and sputum analysis, check for infections or inflammation. These tests are key to finding the cause of respiratory symptoms.
The Importance of Medical History in Diagnosis
A detailed medical history is essential for diagnosing respiratory conditions. It helps identify risk factors, understand symptom onset and progression, and guide further testing. By looking at a patient’s medical history, healthcare providers can make better diagnosis and treatment decisions.
A study in the European Respiratory Journal highlights the importance of a detailed medical history. It says, “A detailed medical history is critical for accurate diagnosis and management of respiratory diseases. It provides context for interpreting diagnostic test results.” This shows the importance of a complete patient evaluation.
By combining pulmonary function tests, imaging and laboratory assessments, and a thorough medical history, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose and manage respiratory conditions like bronchitis and asthma.
Treatment Strategies for Both Conditions
Managing bronchitis and asthma needs a detailed plan. We’ll look at how to treat these conditions. This includes medicines, how they’re given, and other non-medical ways.
Medication Options and Their Mechanisms
Medicines are key in treating bronchitis and asthma. Bronchodilators help relax airway muscles, making breathing easier. They come in short-acting and long-acting types, based on what the patient needs.
Corticosteroids help by reducing airway inflammation. They can be taken by mouth or inhaled. Inhaled corticosteroids are best for controlling asthma long-term.
- Short-acting bronchodilators for quick relief
- Long-acting bronchodilators for ongoing management
- Inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Inhalers, Nebulizers, and Other Delivery Methods
How medicine is given is very important. Inhalers are a common way to get medicine directly to the lungs. There are different types, like metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) and dry powder inhalers (DPIs).
Nebulizers turn medicine into a mist that’s inhaled over time. They’re good for those who can’t use inhalers or need more medicine.
- Metered-dose inhalers for precise dosing
- Dry powder inhalers for ease of use
- Nebulizers for patients with severe symptoms or difficulty using inhalers
Non-Pharmaceutical Approaches to Management
There are also non-medical ways to manage bronchitis and asthma. Breathing exercises can help improve lung function. It’s also important to stay away from things that can trigger symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs offer a full package. They include exercise, education, and support to help manage the conditions well.
- Breathing exercises to improve lung function
- Avoiding triggers to prevent exacerbations
- Pulmonary rehabilitation for a complete care approach
Living with Chronic Respiratory Conditions
Living with chronic respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis needs a detailed plan. We know managing these conditions well is key to a good life.
Creating an Asthma and Bronchitis Action Plan
Creating a personal action plan is vital for managing chronic respiratory conditions. It should cover daily treatments, identify triggers, and guide through bad episodes. An effective plan can greatly lessen symptoms and boost well-being.
To make a plan, it’s best to work with a healthcare provider. They can help:
- Watch symptoms and lung health
- Find and avoid triggers
- Change medications when needed
- Plan for emergencies
Environmental Modifications for Better Breathing
Changing your environment can greatly help your breathing. Simple steps like using air purifiers, removing allergens, and staying away from pollution can help a lot. Creating a cleaner, healthier space is a big step in managing chronic respiratory conditions.
Some good changes include:
- Using HEPA filters to clean the air
- Removing carpets and upholstered furniture to cut down on dust
- Staying away from strong chemicals and smells
Support Resources for Patients and Families
Dealing with chronic respiratory conditions is tough, not just for patients but for their families too. Finding support is key to handling these challenges. Support groups, educational materials, and counseling can offer a lot of help.
We suggest checking out these support options:
- Local and online support groups
- Workshops and educational programs
- Counseling services
By using these resources and a detailed management plan, people with chronic respiratory conditions can live full and meaningful lives.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Respiratory Health
Keeping your respiratory health in check is key to avoiding and managing issues like bronchitis and asthma. We’ve looked into how these conditions relate and why it’s vital to know their causes, signs, and treatment choices.
To keep your lungs healthy, it’s smart to steer clear of triggers, get all your vaccinations, and live a healthy lifestyle. Simple respiratory health tips include not smoking, using air purifiers, and staying active.
By being proactive about your respiratory health, you can lower the chance of getting chronic diseases. This can also make your life better overall. We suggest talking to doctors to make a plan that’s right for you to keep your lungs healthy and manage any respiratory issues.
FAQ
Can bronchitis cause asthma?
Research shows a link between bronchitis and asthma. Some studies suggest bronchitis might lead to asthma in some people.
Can bronchitis lead to asthma?
The exact link between bronchitis and asthma is being studied. But, evidence suggests bronchitis might raise the risk of asthma, mainly in those with respiratory infections.
Can bronchitis turn into asthma?
Bronchitis and asthma are different conditions. But, bronchitis can make asthma symptoms worse or trigger them in some.
Does bronchitis lead to asthma?
The connection between bronchitis and asthma is complex. More research is needed. But, studies hint that bronchitis might contribute to asthma in some.
Can bronchitis cause an asthma attack?
Yes, bronchitis can cause asthma attacks in people with asthma. The inflammation and airway constriction from bronchitis can worsen asthma symptoms.
Can you get asthma from bronchitis?
Having bronchitis might increase the risk of getting asthma. The risk depends on health, medical history, and environmental factors.
What is the difference between asthmatic bronchitis and bronchitis?
Asthmatic bronchitis combines bronchitis and asthma symptoms. The main difference is the presence of asthma-like symptoms like wheezing, in addition to bronchitis symptoms.
Can asthma turn into bronchitis?
Asthma and bronchitis are different conditions. But, unmanaged asthma might increase the risk of bronchitis.
Can you have asthma and bronchitis?
Yes, it’s possible to have both asthma and bronchitis. Some people experience asthmatic bronchitis, with symptoms of both conditions.
Can bronchitis kill you if you have asthma?
Bronchitis is serious, but it’s not usually life-threatening with proper care. Seek medical help if symptoms worsen or breathing is hard.
Can bronchitis trigger asthma?
Yes, bronchitis can trigger asthma symptoms. The inflammation and airway constriction from bronchitis can make asthma worse.
Asthmatic bronchitis vs asthma: what’s the difference?
Asthmatic bronchitis combines bronchitis and asthma symptoms. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. Asthmatic bronchitis adds bronchitis symptoms like coughing and mucus.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Bronchitis and Asthma: Exploring the Connection. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7118846/