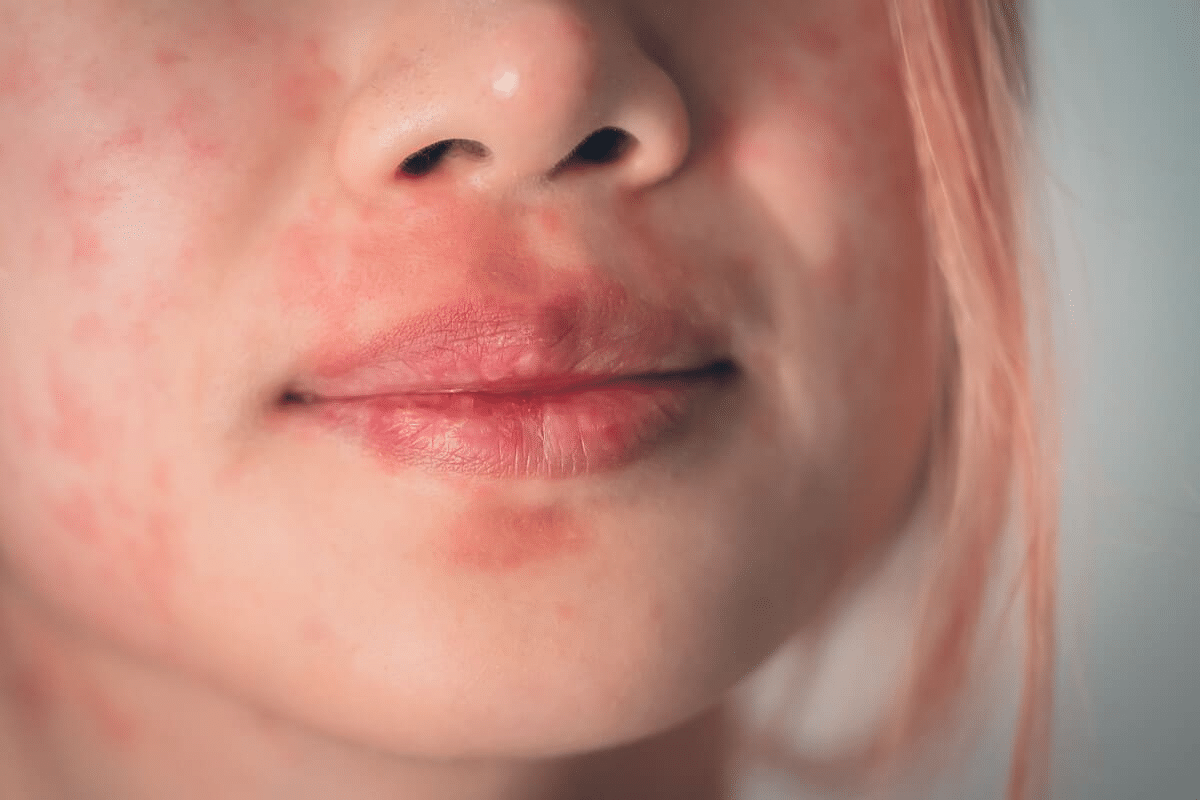
Every second counts when anaphylaxis strikes. This severe, life-threatening allergic reaction can start in seconds to minutes after exposure to an allergen. It can quickly get worse, reaching critical stages in just 15 minutes. Track anaphylaxis signs and symptoms speed. Learn why rapid onset is a severe warning and demands immediate EpiPen use.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important prompt medical attention is for these dangerous reactions. We have the expertise and emergency plans to quickly spot and handle allergic reactions.
It’s key to know how fast allergic reactions can happen, for those at risk or looking after someone with allergies. We’ll talk about how fast anaphylactic reactions can unfold and why getting medical help quickly is so vital.
Key Takeaways
- Anaphylaxis is a severe and sudden allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention.
- Allergic reactions can develop in seconds to minutes after allergen exposure.
- Prompt medical attention is key in managing anaphylaxis.
- Liv Hospital offers expert knowledge and detailed emergency plans for allergic reactions.
- Knowing the timeline of anaphylactic reactions is vital for effective treatment.
The Speed of Allergic Reactions: From Mild to Severe
Knowing how fast allergic reactions happen is key to treating them well. Reactions can start right away or take hours to show up. How fast they happen depends on the allergen, how you’re exposed to it, and how sensitive you are.
How Quickly Does an Allergic Reaction Occur?
Most anaphylactic reactions start quickly, within seconds to minutes. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can begin in minutes to hours and get worse fast. For example, reactions to insect stings or some medicines can happen in minutes. Food allergies might take longer to show up.
Immediate reactions happen fast with things like insect venom or certain drugs given by injection. On the other hand, delayed reactions can happen with food allergies or oral medicines. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat allergic reactions better.
Differences Between Mild, Moderate, and Severe Reactions
Allergic reactions can be mild, moderate, or severe. The severity often depends on how fast the reaction starts. Mild reactions might cause skin rashes or itching, taking hours to appear. Moderate reactions can cause more widespread symptoms like stomach issues or breathing problems, happening faster. Severe reactions, or anaphylaxis, are very dangerous and can happen in just minutes.
- Mild reactions: Localized symptoms, often developing over hours.
- Moderate reactions: Systemic symptoms, occurring within a shorter timeframe.
- Severe reactions: Life-threatening, usually occurring within minutes.
Why Timing Matters in Allergic Responses
The timing of an allergic reaction is very important. It affects how quickly and what treatment you need. Fast reactions, like anaphylaxis, need immediate help. Slower reactions also need quick diagnosis and treatment to avoid getting worse.
Doctors can give the right treatment fast if they know how and when reactions happen. For example, using epinephrine auto-injectors for anaphylaxis can save lives if done quickly.
Understanding Anaphylaxis: A Life-Threatening Emergency
Anaphylaxis is a serious medical emergency. It happens quickly and can be deadly. It’s a severe allergic reaction that needs quick medical help.
What Happens in the Body During Anaphylaxis
When anaphylaxis occurs, the body’s immune system releases a lot of chemicals. These chemicals cause blood vessels to widen and muscles to tighten. This can lead to symptoms like low blood pressure, tight airways, and heart problems.
Doctors say, “Anaphylaxis is a complex, multi-system reaction that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly and properly.”
This condition requires immediate recognition and treatment to prevent serious outcomes.
How Anaphylaxis Differs from Regular Allergic Reactions
Anaphylaxis is more severe and happens faster than regular allergic reactions. While regular allergies might cause local symptoms, anaphylaxis affects many parts of the body. It can lead to serious and life-threatening problems.
|
Characteristics |
Regular Allergic Reactions |
Anaphylaxis |
|---|---|---|
|
Severity |
Mild to Moderate |
Severe, Life-Threatening |
|
Speed of Onset |
Variable, often slower |
Rapid, often within minutes |
|
Body Systems Involved |
Usually localized |
Multiple systems |
Risk Factors for Severe Reactions
Some people are more likely to have severe anaphylactic reactions. These include those with a history of anaphylaxis, allergies to common triggers like peanuts or bee stings, and people with asthma.
- History of anaphylaxis or severe allergic reactions
- Known allergies to common triggers (e.g., peanuts, shellfish, bee stings)
- Presence of asthma or other respiratory conditions
- Cardiovascular disease
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and being prepared. For example, carrying an EpiPen or other epinephrine auto-injector is advised for those at high risk.
The Timeline of Anaphylactic Reactions
Knowing when anaphylactic reactions happen is key for doctors and those at risk. Anaphylaxis is a serious emergency that needs quick help.
When Do Allergic Reactions Start: The First Moments
Anaphylactic reactions start seconds to minutes after being exposed to an allergen. This quick start is what makes anaphylaxis different from other allergic reactions. Symptoms can include skin issues, breathing problems, or heart changes.
Statistical Patterns: 70% Within 20 Minutes, 90% Within 40 Minutes
About 70% of anaphylactic reactions happen within 20 minutes of being exposed to an allergen. Around 90% occur within 40 minutes. These numbers show how important it is to be quick and alert when someone is exposed to an allergen.
- Rapid onset: Most reactions start quickly.
- High-risk period: The first 20-40 minutes are very important.
- Vigilance is key: Quick recognition and action are vital.
Delayed Reactions: Up to Two Hours After Exposure
While most reactions happen right after exposure, some can be delayed. They can happen up to two hours later. This delayed reaction can make people think it’s safe, but it’s not. It’s important to keep watching after exposure.
“Delayed anaphylactic reactions, though rare, show why we must watch closely after exposure.”
— Expert in Allergy and Immunology
Biphasic Anaphylaxis: When Symptoms Return
Some people might have biphasic anaphylaxis. This means symptoms come back after they seem to go away. This can happen 4-8 hours later, or even up to 24 hours. This means we need to keep watching and be ready to act again.
By knowing when anaphylactic reactions happen, doctors and those at risk can get ready and respond fast. This can save lives.
Factors Affecting How Long for an Allergic Reaction to Start
Understanding what affects the start of allergic reactions is key. The time it takes for an allergic reaction to start can change a lot. We’ll look at these factors to understand how they speed up or slow down allergic responses.
Exposure Route: Why Injections and Stings Act Faster
The way an allergen enters the body greatly affects how fast a reaction happens. Injections and stings cause quicker reactions because they go straight into the blood or tissues. This skips some of the body’s natural defenses.
Key factors influencing reaction speed via exposure route:
- Injections: Medications given through injection can cause fast reactions.
- Insect stings: Venom from stings can trigger quick allergic responses.
- Direct entry into bloodstream: This bypasses digestive processes, leading to quicker reactions.
Food Allergies: Why They May Take Longer
Food allergies take longer to show up because the body has to digest the food first. This digestion process delays the symptoms.
Reasons for delayed reactions in food allergies:
- Digestion time: The time it takes for food to be broken down and absorbed.
- Processing through the gut: The allergen must pass through the gastrointestinal tract before entering the bloodstream.
Individual Sensitivity and Prior Sensitization
How sensitive someone is and past exposure to an allergen can greatly affect reaction timing and severity. People who have been exposed before may react faster the next time.
Factors influencing individual sensitivity:
- Previous exposure: Sensitization from past encounters can lead to faster reactions.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may be more prone to allergic reactions due to genetic factors.
Medication and Health Factors
Certain medications and health conditions can also change how fast an allergic reaction happens. For example, beta-blockers can make reactions worse, while certain health conditions can change how the body reacts to allergens.
Health factors and medications that can influence allergic reaction timing:
|
Factor |
Effect on Allergic Reaction |
|---|---|
|
Beta-blockers |
Can worsen allergic reactions |
|
Underlying health conditions |
Can alter the body’s response to allergens |
Common Triggers of Rapid-Onset Allergic Reactions
Knowing what causes quick allergic reactions is key to staying safe. These reactions happen when our immune system fights off something it shouldn’t. Spotting these enemies is the first step to controlling allergies.
Foods Most Likely to Cause Immediate Reactions
Some foods can lead to severe allergic reactions right away. These include peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish, milk, and eggs.
- Peanuts and tree nuts are common culprits of food-induced anaphylaxis.
- Fish and shellfish can cause severe reactions, often with stomach problems.
- Milk and eggs are big allergens, often hitting kids hard.
|
Food Item |
Common Reaction |
|---|---|
|
Peanuts |
Anaphylaxis |
|
Tree Nuts |
Anaphylaxis, Hives |
|
Fish and Shellfish |
Anaphylaxis, Gastrointestinal Symptoms |
Medications and Injectable Drugs
Some medicines and shots can also cause severe allergic reactions. This includes antibiotics like penicillin, NSAIDs, and contrast agents for medical scans.
- Penicillin and other antibiotics can lead to allergic reactions.
- NSAIDs can cause reactions, from mild to severe.
Insect Stings and Venom
Stings from bees, wasps, hornets, and fire ants can cause serious allergic reactions. The venom can lead to anaphylaxis in those who are very sensitive.
Latex, Exercise, and Environmental Triggers
Other things that can trigger reactions include latex, which is a problem in healthcare settings. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis and certain environmental factors also play a role.
By knowing these common triggers, we can take steps to avoid severe allergic reactions. This includes swelling of the tongue or throat issues.
Anaphylaxis Signs and Symptoms
Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It shows different symptoms. Knowing these signs is key to getting help fast and avoiding serious problems.
Skin Manifestations
Skin symptoms are common in anaphylaxis. They include:
- Hives (urticaria): Itchy, raised welts on the skin that can appear anywhere on the body.
- Flushing: Redness of the skin due to increased blood flow.
- Angioedema: Swelling of the deeper layers of the skin, often around the eyes, lips, and tongue.
Respiratory Symptoms
Respiratory symptoms are serious and need quick action. They include:
- Wheezing: A high-pitched sound while breathing out, indicating airway constriction.
- Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath or feeling like the airway is constricting.
Cardiovascular Changes
Anaphylaxis can affect the heart and blood pressure. Symptoms include:
- Rapid Weak Pulse: A fast heartbeat that may be weak or thready.
- Hypotension: Low blood pressure, which can lead to dizziness or fainting.
|
System |
Symptoms |
|---|---|
|
Skin |
Hives, Flushing, Angioedema |
|
Respiratory |
Wheezing, Difficulty Breathing |
|
Cardiovascular |
Rapid Weak Pulse, Hypotension |
|
Gastrointestinal |
Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Abdominal Cramps |
|
Neurological |
Confusion, Loss of Consciousness, Seizures |
Gastrointestinal and Neurological Symptoms
Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Neurological symptoms can be confusion, loss of consciousness, or seizures in severe cases.
It’s important to know these symptoms to diagnose anaphylaxis and start treatment quickly.
Allergic Reaction Throat Swelling: A Critical Warning Sign
Throat swelling is a dangerous sign of an allergic reaction. It can lead to serious problems if not treated quickly. This swelling is a warning that a severe allergic reaction might be happening, which could turn into anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition.
What Does an Allergic Reaction Feel Like in the Throat?
When an allergic reaction happens, people might feel their throat getting tight or swollen. It can feel like there’s a lump or something is squeezing the throat. This makes it hard to swallow or breathe. It’s a scary feeling, often with other symptoms like hives or itching.
Key symptoms to watch for include:
- A feeling of tightness or constriction in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Changes in voice
- Sensation of a lump in the throat
Progression from Throat Tightness to Airway Compromise
Throat tightness can quickly turn into a serious problem if not treated fast. As swelling gets worse, it can block the airway. This can make breathing very hard. This can happen very quickly, so it’s very important to get medical help right away.
It’s vital to know the signs of airway trouble, which include:
- Wheezing or stridor (a high-pitched sound while breathing)
- Increased difficulty breathing
- Cyanosis (a bluish discoloration of the skin due to lack of oxygen)
Anaphylaxis Tongue Swelling: Recognition and Significance
Tongue swelling is a key sign of anaphylaxis. It happens in about 20% of cases. It’s important to notice tongue swelling because it can block the airway. The swelling can be so bad that it fills the mouth, making it hard to speak or swallow.
Voice Changes and Stridor as Danger Signs
Changes in voice or stridor are big warning signs. A hoarse voice or trouble speaking clearly means severe swelling. Stridor, a high-pitched sound when inhaling, is a very bad sign that needs quick action.
If you or someone else is experiencing these symptoms, it’s essential to:
- Administer epinephrine using an EpiPen if available
- Call emergency services immediately
- Stay calm and try to stay as upright as possible to ease breathing
What Finding Most Clearly Indicates Anaphylaxis
Healthcare providers must watch closely for signs of anaphylaxis. This severe allergic reaction is diagnosed by symptoms after exposure to an allergen. They look for specific signs that point to this condition.
Key Diagnostic Indicators for Healthcare Providers
Doctors diagnose anaphylaxis by looking for certain symptoms. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) says anaphylaxis is likely if any of these are present:
|
Criteria |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Acute onset with skin/mucosal involvement and respiratory compromise or reduced BP |
|
2 |
Two or more: skin/mucosal, respiratory, reduced BP, or GI symptoms after allergen exposure |
|
3 |
Reduced BP after exposure to a known allergen |
Multiple System Involvement
Anaphylaxis affects many parts of the body. Symptoms can include skin issues like hives, respiratory problems, and heart issues. Seeing symptoms in different areas of the body is a big clue.
The timely recognition of multiple system involvement is key for diagnosing anaphylaxis and starting treatment.
Distinguishing from Panic Attacks and Other Conditions
It’s hard to tell anaphylaxis apart from other conditions like panic attacks. But, specific symptoms like widespread hives and a history of allergies can help tell them apart.
Emergency Response: When Seconds Count
Anaphylaxis is a serious allergic reaction that needs quick action. It’s a life-threatening condition that requires immediate response. Knowing what to do can save lives.
Immediate Steps When Symptoms First Appear
Recognizing symptoms of anaphylaxis is the first step. Look for signs like trouble breathing, a fast heartbeat, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If you see these, act fast.
Call for help right away if you think someone is having an anaphylactic reaction. In the U.S., dial 911 or your local emergency number. If you have an EpiPen, use it while waiting for help.
Epinephrine Administration: Why Timing Is Critical
Epinephrine is the main treatment for anaphylaxis. It helps by making blood vessels smaller, improving breathing, and reducing the reaction’s severity. Using an EpiPen can save lives. It’s important to use it as soon as symptoms start.
When to Call 911 and What to Tell Dispatchers
Calling 911 is key when dealing with anaphylaxis. Be ready to give your location and describe the symptoms. Tell the dispatcher you think it’s anaphylaxis and if you’ve used epinephrine.
- State your location clearly.
- Describe the symptoms being experienced.
- Mention if epinephrine has been administered.
Hospital Treatment and Observation
After using epinephrine, go to the hospital fast. Doctors can give more treatment and watch for biphasic reactions. These are when symptoms come back.
At the hospital, you might get more epinephrine, antihistamines, and corticosteroids. These help manage the reaction and prevent more problems.
Long-term Management and Prevention Strategies
Managing severe allergies needs a full plan. This includes avoiding allergens, being ready for emergencies, and treatments to lessen sensitivity.
Allergen Identification and Avoidance Planning
Finding out what causes allergic reactions is the first step. Then, making a plan to stay away from these allergens is key. This means reading labels, asking about food ingredients, and being careful with products.
Avoidance strategies depend on the person’s allergies. For example, someone allergic to peanuts must avoid them and products made in places where peanuts are handled.
Emergency Action Plans for Different Settings
Having an emergency action plan is very important for those with severe allergies. It should cover what to do in case of an allergic reaction, like using epinephrine and when to get medical help.
These plans need to be made for different places, like home, school, or work. It’s also key that family, caregivers, and colleagues know the plan and how to act.
Immunotherapy and Desensitization Options
For some, immunotherapy or desensitization might be an option. It’s about slowly getting used to the allergen. Oral immunotherapy (OIT) is used for some food allergies.
Talking to a healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of immunotherapy is important. They can help decide if it’s right for you.
Living with Severe Allergy Risk
Living with a severe allergy means always being careful and ready. Regular doctor visits, staying up-to-date with new treatments, and having an emergency kit are important. This kit should have epinephrine auto-injectors.
By following these steps, people with severe allergies can lower their risk of anaphylaxis. They can live full and active lives.
Conclusion: Being Prepared for Rapid-Onset Allergic Reactions
Being ready is key to handling anaphylaxis, a serious emergency that needs quick action. Knowing the signs, symptoms, and treatments helps manage this dangerous condition well.
To get ready for anaphylaxis, it’s vital to spot rapid-onset allergic reactions. We’ve talked about the timeline of anaphylactic reactions, factors that speed up allergic reactions, and common triggers.
Having an emergency plan helps people act fast and right when an anaphylactic reaction happens. This includes knowing how to use epinephrine, when to call 911, and what to say to dispatchers.
In short, being ready for rapid-onset allergic reactions is key to managing anaphylaxis well. By knowing the risks and taking steps ahead, people and families can lower the risk of serious harm and get better results.
FAQ
How quickly do allergic reactions occur?
Allergic reactions can start in minutes after being exposed to an allergen. But, how fast it happens can vary. It depends on the person and the allergen.
What is the typical timeline for anaphylactic reactions?
Anaphylactic reactions usually happen between 20-40 minutes after exposure. About 70% happen in 20 minutes, and 90% in 40 minutes.
Can allergic reactions be delayed?
Yes, some allergic reactions can be delayed. They can happen up to two hours after exposure.
What is biphasic anaphylaxis?
Biphasic anaphylaxis is when symptoms come back after treatment. This often happens a few hours later.
How does the route of exposure affect the timing of an allergic reaction?
Injections and stings can cause reactions faster. Food allergies might take longer to show symptoms.
What are the common triggers of rapid-onset allergic reactions?
Common triggers include foods, medications, insect stings, latex, and environmental factors.
What are the signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis?
Symptoms include skin issues, breathing problems, heart changes, stomach issues, and brain symptoms.
What does an allergic reaction feel like in the throat?
Throat swelling can make it feel tight or constricted. This can lead to breathing problems.
What is the significance of tongue swelling in anaphylaxis?
Tongue swelling is a big warning sign of anaphylaxis. It means there could be breathing problems.
How is anaphylaxis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on symptoms in multiple systems. This includes skin, breathing, heart, and stomach symptoms.
What is the emergency response to anaphylaxis?
Immediate steps include giving epinephrine, calling 911, and getting hospital treatment.
How can anaphylaxis be managed long-term?
Long-term management includes finding the allergen, making emergency plans, and considering treatments like immunotherapy.
When do allergic reactions start?
Allergic reactions can start in minutes after exposure. But, the timing can vary.
How long does it take for an allergic reaction to start?
The time for an allergic reaction to start can range from minutes to hours. It depends on the person and the allergen.
How soon do allergic reactions occur?
Allergic reactions can happen right away or be delayed. It depends on the person and the allergen.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21296257/



































