Compare viral vs bacterial bronchitis. Read the essential guide to identify symptoms and determine if antibiotics are necessary for cure.
Bronchitis is a common disease of the lungs, affecting about 5 percent of adults in the U.S. each year. Knowing if your bronchitis is viral or bacterial is key to getting better.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the difference between viral and bacterial bronchitis. Most cases are viral and get better with care. But bacterial bronchitis needs antibiotics.
We aim to give our patients the right treatment by accurately diagnosing. This means we can treat viral and bacterial bronchitis effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Bronchitis can be caused by either viral or bacterial infections.
- Distinguishing between the two is key for the right treatment.
- Viral bronchitis usually gets better with care alone.
- Bacterial bronchitis needs specific antibiotics.
- Getting the right diagnosis is vital for managing the disease.
Understanding Bronchitis: An Overview
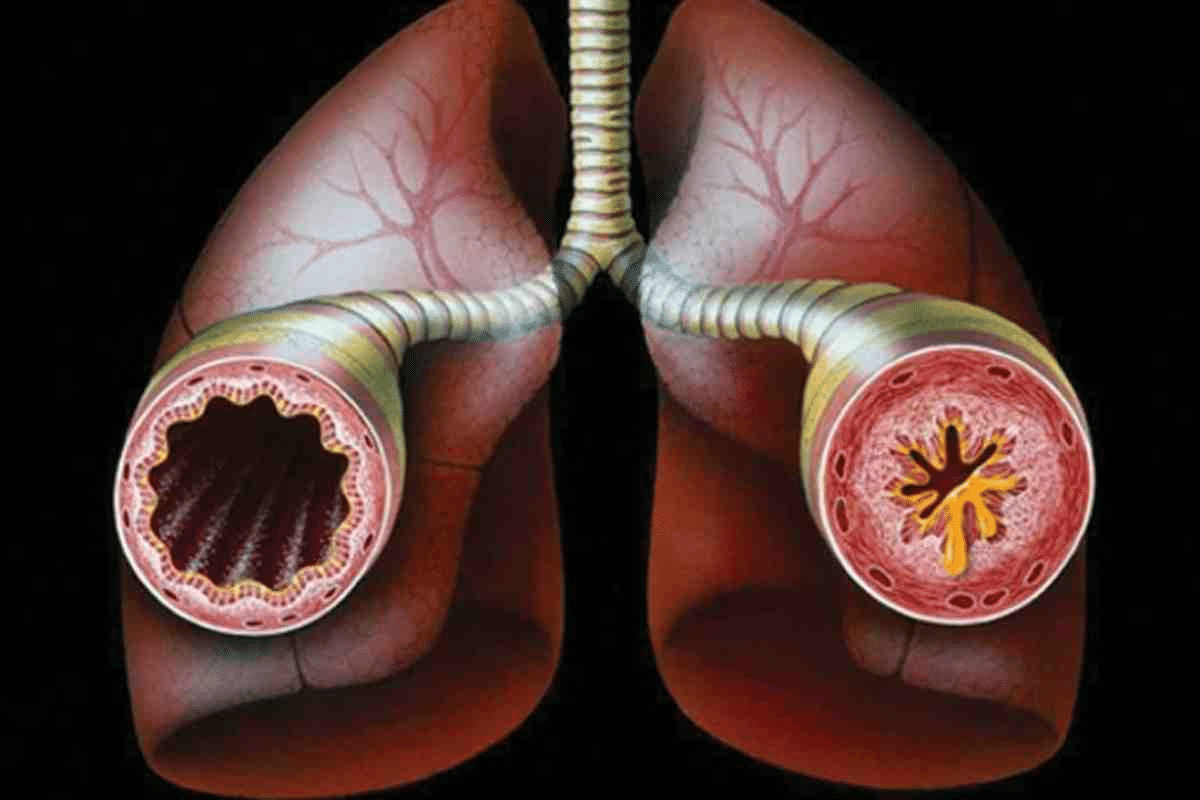
Bronchitis is a common condition that affects the bronchial tubes. These tubes are key for our breathing. They carry air in and out of the lungs. When they get inflamed, it can cause many symptoms and problems.
What Happens During Bronchitis
When bronchitis strikes, the bronchial tubes get inflamed. This can happen due to infection or irritation from things like smoke or pollutants. The tubes then make too much mucus, causing coughing, wheezing, and breathing trouble. The inflammation can be caused by either viral or bacterial pathogens, making it important to know the cause for the right treatment.
Medical Expert, a pulmonologist, says, “Bronchitis can really affect someone’s life, if not treated right.” It can be either acute or chronic. Acute bronchitis usually gets better on its own, but chronic bronchitis lasts longer and is often linked to long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke.
Prevalence and Impact in the United States
Bronchitis is a big health problem in the United States, affecting millions each year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says millions of Americans get bronchitis every year. This leads to many doctor visits and hospital stays.
“Bronchitis is a major public health concern, specially for the elderly and young children,”
the CDC points out.
The cost of bronchitis is also high, with expenses for healthcare, lost work, and more. Knowing how common and impactful bronchitis is helps us find ways to stop and manage it better.
Viral vs Bacterial Bronchitis: The Fundamental Distinction

Viral and bacterial bronchitis share similar symptoms but have different causes. They need different treatments. The main difference is in their causative agents.
Causative Agents
Viruses cause 60-70% of bronchitis cases. The most common viruses include influenza, RSV, and adenovirus. Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis are less common but also play a role.
Infection Mechanisms
Viral bronchitis starts when you breathe in viruses. These viruses infect the cells lining your bronchial tubes. Bacterial bronchitis happens when bacteria grow in your respiratory tract, often in people with weak lungs or after a viral infection.
- Viral bronchitis symptoms come on slowly.
- Bacterial bronchitis symptoms are often more severe, like high fever and thick, yellow sputum.
Initial Presentation Differences
The first signs of viral and bacterial bronchitis can tell you what’s causing it. Both can cause coughing and sputum, but the sputum’s color and symptoms can vary. For example, bacterial infections often have purulent sputum.
Key differences in how it starts include:
- Fever is more common and severe in bacterial infections.
- The color and consistency of sputum are different, with bacterial infections having thicker, more colored sputum.
- The severity of symptoms is also different, with bacterial bronchitis often being more serious.
Viral Bronchitis: The Common Culprit
Viral bronchitis affects millions of people every year. It’s important to know what causes it to treat it right.
Prevalence Statistics
Viruses cause 60 to 70 percent of bronchitis cases. This shows how common viral bronchitis is. It’s key to understand it to treat respiratory infections well.
Anyone can get viral bronchitis, but some are more at risk. This includes older people, those with health issues, or those exposed to smoke.
Common Viral Pathogens
Several viruses are linked to bronchitis, including:
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Influenza virus
- Adenovirus
These viruses can cause mild to severe symptoms. They can also lead to serious problems, mainly in those who are more vulnerable.
Key Facts About Viral Bronchitis:
- Highly contagious and can spread through respiratory droplets
- Can be caused by multiple viral pathogens
- Symptoms can vary in severity and duration
Knowing the viruses behind bronchitis helps in creating better ways to prevent and treat it.
Bacterial Bronchitis: Less Common but Significant
Bacterial bronchitis is less common than viral bronchitis but is very serious. We will look at how often it happens, the bacteria involved, and who is at risk. This will help us understand its impact.
Incidence Rates
Bacterial bronchitis makes up only 1 to 10 percent of acute bronchitis cases. Even though it’s not as common, it’s a big deal because it can be severe. It also needs the right antibiotic treatment.
Common Bacterial Pathogens
The main bacteria causing bronchitis are Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. These bacteria can lead to serious infections. They are a big worry for the elderly and people with health problems.
|
Bacterial Pathogen |
Characteristics |
Commonly Affected Populations |
|---|---|---|
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
Gram-negative coccobacillus, often encapsulated |
Children, individuals with COPD |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Gram-positive coccus, often colonizes the nasopharynx |
Elderly, young children, immunocompromised |
|
Moraxella catarrhalis |
Gram-negative diplococcus, commonly colonizes the respiratory tract |
Individuals with COPD, smokers |
Risk Factors for Bacterial Infection
Some things make you more likely to get bacterial bronchitis. These include:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Immunocompromised status (e.g., HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy)
- Advanced age
- Underlying heart or lung disease
Knowing these risk factors helps us find who needs special care and early treatment.
Symptom Comparison: How to Tell the Difference
Both viral and bacterial bronchitis have similar symptoms, but there are key differences. Knowing these differences helps figure out the cause and the right treatment.
Viral Bronchitis Symptoms
Viral bronchitis has mild symptoms that come on slowly. Common signs include:
- A persistent cough that may produce clear or white mucus
- Mild fatigue
- Slight fever or no fever at all
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
These symptoms are like those of a cold or flu. They usually get better in a few weeks.
Bacterial Bronchitis Symptoms
Bacterial bronchitis has more serious symptoms. These include:
- A cough that produces thick, yellow or green mucus
- High fever
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue that is more pronounced than in viral bronchitis
This type of bronchitis might need antibiotics, depending on how bad the symptoms are.
Phlegm Color and Consistency as Indicators
The color and consistency of phlegm can tell you if it’s viral or bacterial. Viral bronchitis usually has clear or white phlegm. Bacterial bronchitis has thicker, yellow or green phlegm. But, remember, phlegm color alone isn’t always a sure sign.
Doctors look at symptoms, medical history, and tests to diagnose bronchitis. Knowing the symptoms of viral and bacterial bronchitis helps us understand how to treat it.
Diagnostic Approaches for Distinguishing Viral vs Bacterial Bronchitis
Diagnosing bronchitis requires a mix of clinical checks and lab tests. Getting it right is key to picking the right treatment.
Clinical Evaluation
First, we look at the patient’s history and symptoms. This helps us figure out what might be causing the problem. We also do a physical check, like listening to the lungs with a stethoscope. This helps us find signs like wheezing or crackles.
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests are important in telling viral from bacterial bronchitis. We use:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check for signs of infection
- Sputum culture to identify bacterial pathogens
- Nasal swab or throat swab for viral antigen detection
|
Test |
Purpose |
Relevance to Bronchitis Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
|
Complete Blood Count (CBC) |
Checks for signs of infection |
Helps differentiate between viral and bacterial causes |
|
Sputum Culture |
Identifies bacterial pathogens |
Confirms bacterial bronchitis |
|
Nasal/Throat Swab |
Detects viral antigens |
Diagnoses viral bronchitis |
Imaging Studies
Imaging like chest X-rays might be used to check for other issues like pneumonia. They’re not a surefire way to diagnose bronchitis but can spot other problems.
When Misdiagnosis Occurs
Sometimes, it’s hard to tell if bronchitis is viral or bacterial because symptoms can be similar. We use different tests to make sure we get it right. If we’re wrong, it can lead to the wrong treatment, making things worse or causing antibiotic resistance.
By using clinical checks, lab tests, and sometimes imaging, we can accurately figure out what’s causing bronchitis. This helps us choose the best treatment plan.
Treatment Strategies for Viral Bronchitis
Managing viral bronchitis requires a mix of supportive care and over-the-counter medicines. Because it’s caused by a virus, antibiotics won’t work. Instead, we aim to ease symptoms and help the body heal on its own.
Supportive Care
Supportive care is key in treating viral bronchitis. It means getting lots of rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and using a humidifier. We also advise avoiding smoking and harmful irritants to lessen symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Medications
OTC medicines are vital in managing viral bronchitis symptoms. Cough suppressants can lessen coughing, while expectorants help clear mucus. Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also reduce fever and pain.
|
Medication Type |
Purpose |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Cough Suppressants |
Reduce cough frequency and severity |
Dextromethorphan |
|
Expectorants |
Aid in clearing mucus from the lungs |
Guaifenesin |
|
Pain Relievers |
Alleviate fever and discomfort |
Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen |
When Antibiotics Are Not Effective
It’s important to know that antibiotics don’t work on viruses, including viral bronchitis. Misusing antibiotics can make them less effective against real bacterial infections. We stress the need to tell the difference between viral and bacterial bronchitis for proper treatment.
Recovery Timeline
The time it takes to recover from viral bronchitis varies. Symptoms usually get better in 7-10 days, but coughing can last longer. Health, age, and other conditions can affect how fast someone recovers.
By focusing on supportive care and using OTC medicines wisely, we can manage viral bronchitis well. This helps the body heal naturally.
Treatment Approaches for Bacterial Bronchitis
Treating bacterial bronchitis involves antibiotics and supportive care. Doctors must pick the best treatment to fight the infection and avoid complications.
Appropriate Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic therapy is key for bacterial bronchitis. The right antibiotic depends on the bacteria and local resistance. Common choices are amoxicillin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. Antibiotics should only be used after a careful check-up, sometimes with lab tests.
The Problem of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a big challenge in treating bacterial bronchitis. Misusing antibiotics can make bacteria resistant. It’s important to use antibiotics wisely and finish the treatment to avoid this problem.
Supportive Measures
Supportive care is also vital for managing bacterial bronchitis. Drinking plenty of water, using humidifiers, and resting are key. Over-the-counter cough medicines can help with symptoms.
Duration of Treatment
The antibiotic treatment for bacterial bronchitis lasts 7 to 14 days. It depends on the infection’s severity and how well the patient responds. Sticking to the treatment plan is essential for full recovery and preventing future problems.
In summary, treating bacterial bronchitis well needs a mix of antibiotics, awareness of resistance, supportive care, and knowing how long treatment lasts. By using these methods, we can help patients get better and lessen the impact of this condition.
Complications and Prevention Strategies
To manage bronchitis well, we need to know its possible complications. Bronchitis might seem like a simple illness, but it can cause serious problems, mainly for those who are more vulnerable.
Potential Complications
Bronchitis, whether caused by a virus or bacteria, can lead to serious issues. A big worry is pneumonia, which is more common in older people or those with health problems. Other complications include:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) getting worse
- Bronchiolitis
- Respiratory failure in severe cases
Knowing these risks helps both patients and doctors to handle the illness better.
High-Risk Populations
Some groups face a higher risk of bronchitis complications. These include:
|
High-Risk Group |
Reason for Increased Risk |
|---|---|
|
Older Adults |
Decreased lung function and immunity |
|
Young Children |
Developing lungs and immune systems |
|
Individuals with Chronic Health Conditions |
Underlying conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or COPD |
Knowing who is at risk helps us focus on prevention.
Preventive Measures
Preventing bronchitis is more important than treating it after it happens. Here are some ways to prevent or lessen its impact:
- Annual Influenza Vaccination: Helps avoid flu-related bronchitis
- Pneumococcal Vaccination: Guards against pneumococcal disease, which can lead to pneumonia
- Smoking Cessation: Stopping smoking greatly lowers the risk of bronchitis
- Good Hygiene Practices: Washing hands often and staying away from sick people
By understanding bronchitis complications and using preventive steps, we can lessen its impact, mainly in high-risk groups.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Bronchitis Care
It’s key to know the difference between viral and bacterial bronchitis to make good care choices. Knowing which one you have helps pick the right treatment. This ensures you get the best care for your condition.
Viral bronchitis is more common, making up 60-70% of cases. But bacterial bronchitis needs special antibiotics to avoid serious problems.
Understanding the symptoms and treatments for each type helps you get the right help fast. This way, you can follow the treatment plan well. It leads to better health and less chance of serious issues, mainly for those at high risk.
Always talk to a doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan. This way, you get the right care. Whether it’s for viral or bacterial bronchitis, you’ll get the help you need.
FAQ
What is bronchitis and how does it affect the body?
Bronchitis is when the bronchial tubes get inflamed. These tubes carry air to the lungs. This can cause coughing, mucus production, and chest discomfort.
Is bronchitis viral or bacterial?
Bronchitis can come from viruses or bacteria. Knowing the cause is key for the right treatment.
What are the symptoms of viral bronchitis?
Viral bronchitis shows as coughing, clear or white mucus, and mild tiredness. Fever might or might not be there.
What are the symptoms of bacterial bronchitis?
Bacterial bronchitis has more serious signs. These include yellow or green mucus, higher fever, and more tiredness.
How is bronchitis diagnosed?
Doctors use a mix of clinical checks, medical history, and tests to diagnose bronchitis. They look at the cause and how severe it is.
Can the color of phlegm indicate whether bronchitis is viral or bacterial?
The color of phlegm can hint at the cause. Clear or white phlegm often means a virus. Yellow or green phlegm might point to a bacterial infection.
How is viral bronchitis treated?
For viral bronchitis, treatment is supportive. This includes rest, drinking lots of water, and using over-the-counter meds. Antibiotics won’t work on viruses.
How is bacterial bronchitis treated?
Bacterial bronchitis needs antibiotics. The right antibiotic depends on the bacteria and how bad the infection is.
What are the possible complications of bronchitis?
Bronchitis can lead to pneumonia, COPD, or even respiratory failure in severe cases.
Who is at higher risk for developing complications from bronchitis?
People with weak immune systems, older adults, and those with lung problems are at higher risk for complications.
What preventive measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing bronchitis?
To avoid bronchitis, practice good hygiene, stay away from sick people, get flu and pneumonia shots, and don’t smoke.
How long does it take to recover from bronchitis?
Recovery time for bronchitis varies. Viral bronchitis usually gets better in a few weeks. Bacterial bronchitis might need antibiotics and take longer to heal.