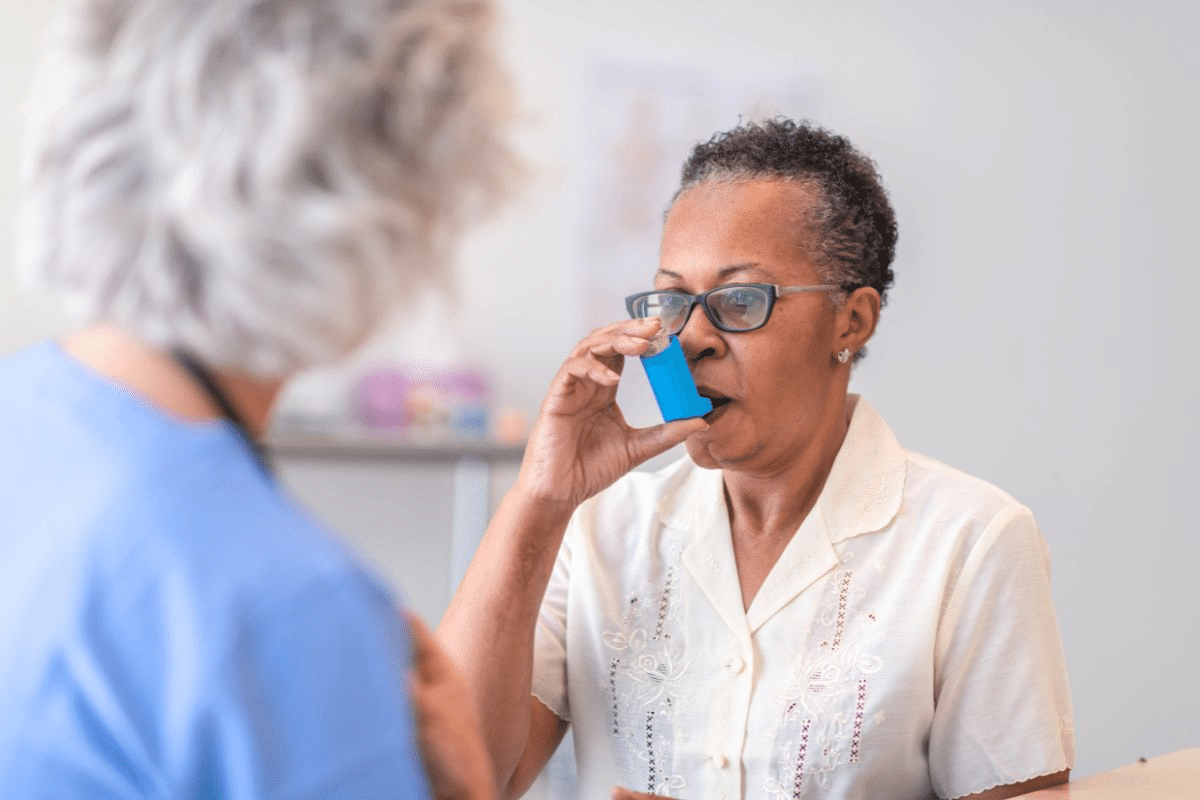
We are seeing more people diagnosed with Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS). This condition mixes the problems of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Five key facts concerning chronic obstructive asthma and its relationship to the Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS).
ACOS brings its own set of challenges for doctors to diagnose and treat. People with ACOS have symptoms of both asthma and COPD. These symptoms can be worse than those of either condition alone.
At our healthcare organizations, we aim to provide top-notch care to patients worldwide. It’s key to understand ACOS for the right diagnosis and treatment. This helps improve how well patients do.
Key Takeaways
- ACOS is a complex respiratory condition that combines asthma and COPD.
- Understanding ACOS is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
- People with ACOS face more severe symptoms than those with asthma or COPD alone.
- ACOS needs a special approach because of its unique traits.
- Good management of ACOS can greatly help patients.
Understanding Asthma and COPD as Separate Conditions
To grasp Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS), we need to know about asthma and COPD separately. Both are long-term lung diseases but differ in how they work, symptoms, and treatment.
Asthma: Characteristics and Pathophysiology
Asthma is a long-term inflammation of the airways. It causes recurring episodes of reversible airflow blockage. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
The inflammation in asthma makes airways more sensitive to triggers. This can be due to allergens, irritants, or infections. Asthma can affect anyone at any age, with severity ranging from mild to severe.
COPD: Characteristics and Pathophysiology
COPD is a progressive lung disease with airflow obstruction that’s not fully reversible. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, leading to breathing problems. These conditions can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life.
COPD’s cause is long-term exposure to irritating gases or particles, often from smoking. This leads to chronic inflammation and structural changes in the airways. These changes narrow the airways, causing airflow limitation.
COPD usually affects people over 40 with a history of smoking or lung irritant exposure. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, and chronic cough. These symptoms can get worse over time without proper management.
What is Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS)?

ACOS is a condition where you have both asthma and COPD symptoms. It’s hard to diagnose because it has traits from both diseases.
Definition and Diagnostic Criteria
The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) have guidelines for ACOS. It’s diagnosed by looking at symptoms, spirometry results, and patient history. The main criteria are:
- Persistent airflow limitation
- Features of both asthma and COPD
- Significant bronchodilator responsiveness
ACOS is often seen in people with a history of asthma, COPD, or both. Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to managing the condition well.
Historical Recognition of the Condition
The idea of ACOS has changed over time. At first, asthma and COPD were seen as separate diseases. But, some patients showed signs of both, leading to ACOS being recognized as its own condition.
Studies have shown that ACOS patients have more symptoms and exacerbations. This has led to the creation of specific guidelines for diagnosis and treatment.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ACOS involves inflammation, airway changes, and breathing problems. It combines asthma’s eosinophilic inflammation with COPD’s neutrophilic inflammation and emphysema.
|
Pathophysiological Feature |
Asthma |
COPD |
ACOS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Inflammatory Cells |
Eosinophils |
Neutrophils |
Both eosinophils and neutrophils |
|
Airway Remodeling |
Present |
Present |
Complex, with features of both |
|
Bronchodilator Responsiveness |
Significant |
Variable |
Often significant |
Knowing how ACOS works is vital for finding the right treatments. It helps meet the complex needs of ACOS patients.
Key Fact #1: ACOS Affects 27% of COPD Patients
ACOS, or Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome, is a big deal for those with COPD. It makes diagnosing and treating respiratory diseases harder.
Overall Prevalence Statistics
About 27% of COPD patients also have ACOS. This mix of asthma and COPD symptoms makes treatment tricky.
Here’s a look at the data:
|
Study |
Prevalence of ACOS in COPD Patients |
|---|---|
|
Study 1 |
25% |
|
Study 2 |
30% |
|
Meta-Analysis |
27% |
Age-Related Prevalence Patterns
ACOS gets more common with age, mainly in older adults. This is important for doctors to know when treating the elderly.
Geographic and Demographic Variations
Where you live and who you are can affect ACOS rates. Things like air pollution, smoking, and genes play a part.
Places with more smokers often see more COPD and ACOS. Knowing this helps in making health plans better.
Understanding ACOS helps doctors plan better care for those with chronic respiratory issues.
Key Fact #2: Chronic Obstructive Asthma Has Distinct Patient Characteristics
People with asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) have unique traits. These traits help doctors diagnose and treat them. They are different from those with just asthma or COPD.
Typical Age and Smoking History Profile
ACOS patients are usually older adults who have smoked a lot. Research shows ACOS gets more common with age, in those who have smoked. Knowing this helps doctors spot at-risk patients.
Bronchodilator Responsiveness Patterns
ACOS patients often react well to bronchodilators. This is a key sign of ACOS. It helps doctors decide how to treat them. Using bronchodilators can make breathing easier and reduce symptoms.
Elevated Peripheral Eosinophil Counts
ACOS patients also have high eosinophil counts. Eosinophils are white blood cells linked to inflammation. Their high levels in ACOS show how much inflammation is in the airways. This helps doctors choose the right treatments.
In short, ACOS patients have certain traits like being older, having smoked a lot, reacting to bronchodilators, and high eosinophil counts. Knowing these traits is key to diagnosing and treating ACOS. It helps doctors tailor treatments to meet each patient’s needs.
Key Fact #3: ACOS Carries Higher Disease Burden Than Either Condition Alone
Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) is a big challenge. It has a complex mix of symptoms and a higher disease burden. Patients with ACOS face a more severe condition than those with asthma or COPD alone.
Frequency and Severity of Exacerbations
ACOS is known for its more frequent and severe exacerbations. These exacerbations have a big impact on patients’ lives and healthcare costs. Research shows that ACOS patients are more likely to need hospital care than COPD patients.
“The overlap syndrome is associated with a higher risk of exacerbations and a greater decline in lung function,” as noted in recent clinical studies. This highlights the need for careful management and monitoring of patients with ACOS to prevent and promptly treat exacerbations.
Impact on Quality of Life Measures
ACOS also affects quality of life. Patients with ACOS often have a lower quality of life. The mix of asthma and COPD symptoms makes life harder for them.
- Increased symptoms and reduced lung function
- Greater healthcare utilization
- Impact on daily activities and overall well-being
Accelerated Lung Function Decline
ACOS leads to faster lung function loss than asthma or COPD alone. This is a big worry because it can cause more health problems and death. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to slowing this decline.
Elevated Mortality Rates
ACOS also means a higher risk of death than asthma or COPD alone. The complex nature and higher disease burden are to blame. We need to use all the right treatments to lower this risk and help ACOS patients live better.
In summary, ACOS is a serious condition with more severe symptoms, lower quality of life, faster lung function loss, and higher death rates. Understanding these points is key to finding better ways to manage ACOS.
Key Fact #4: Diagnostic Challenges and Approaches
Diagnosing Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) is complex. It needs a detailed approach. We will look at the challenges and how to accurately identify ACOS.
Clinical Assessment and History Taking
A thorough clinical assessment is key for diagnosing ACOS. We consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle. This helps spot any overlap between asthma and COPD.
Important parts of the assessment include:
- Symptom evaluation: cough, wheeze, shortness of breath
- Smoking history and exposure to environmental factors
- Family history of respiratory diseases
- Previous diagnoses and treatments
Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are vital for diagnosing ACOS. They help us see lung function and spot any issues.
|
Pulmonary Function Test |
Asthma |
COPD |
ACOS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
FEV1/FVC Ratio |
Reduced |
Reduced |
Reduced |
|
Reversibility Testing |
Significant reversibility |
Limited reversibility |
Variable reversibility |
Biomarkers and Laboratory Investigations
Biomarkers and lab tests help tell asthma, COPD, and ACOS apart. They show specific traits of each condition.
Some important biomarkers are:
- Eosinophil count: high in asthma and ACOS
- Neutrophil count: high in COPD
- IgE levels: high in asthma
Imaging Studies and Their Interpretation
Imaging like chest X-rays and CT scans gives us lung details and comorbidities. We use these images to spot signs of asthma, COPD, or ACOS.
Key findings include:
- Air trapping and hyperinflation in COPD and ACOS
- Bronchial wall thickening in asthma and ACOS
- Emphysema in COPD
Key Fact #5: Treatment Strategies Differ from Pure Asthma or COPD
The treatment for ACOS is special because it’s different from asthma or COPD. It needs a detailed plan to handle its unique challenges.
Pharmacological Management Guidelines
Medicine is key in treating ACOS. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and bronchodilators are the mainstay of therapy. They help control symptoms and reduce flare-ups, improving life quality.
The choice of ICS, LABAs, or LAMAs depends on the patient’s needs and how severe their disease is. We suggest starting with ICS and LABAs or LAMAs and adjusting as needed. Regular monitoring is key to customize treatment.
Inhaler Therapy Considerations
Inhaler therapy is vital in managing ACOS. The right inhaler depends on the patient’s preference and ability to use it. Proper inhaler technique is essential to get the most benefit and avoid side effects.
- Metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) are often used with spacers for better drug delivery.
- Dry powder inhalers (DPIs) are easy to use and portable.
- Soft mist inhalers release medication slowly, which helps some patients.
Role of Corticosteroids and Bronchodilators
Corticosteroids and bronchodilators have different roles in ACOS treatment. Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory agents that help control symptoms and reduce exacerbations. Bronchodilators (LABAs and LAMAs) relax airway muscles, improving airflow.
Together, these medications tackle ACOS’s inflammation and airway constriction. They provide full symptom control and enhance lung function.
Comprehensive Management of ACOS
Managing Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) needs a detailed plan. It’s not just about medicine. We know a full approach is key to better health and happiness for patients.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Pulmonary rehab is a big help for ACOS. It has exercise, education, and ways to change behavior. These help patients feel better, move easier, and live better lives.
Benefits of Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
- Improved exercise tolerance
- Enhanced quality of life
- Better disease management
- Reduced hospitalization rates
Lifestyle Modifications and Smoking Cessation
Changing your lifestyle is important for ACOS. Quitting smoking is a must. It makes symptoms worse and speeds up the disease. We help with counseling and medicine to quit smoking.
|
Lifestyle Modification |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Smoking Cessation |
Reduces disease progression and symptom severity |
|
Dietary Changes |
Supports overall health and well-being |
|
Increased Physical Activity |
Improves physical function and reduces symptoms |
Exacerbation Prevention Strategies
Stopping bad episodes is a big part of managing ACOS. It’s about sticking to your medicine, avoiding bad things, and keeping away from sickness.
Exacerbation Prevention Measures:
- Adherence to prescribed medication regimens
- Avoidance of environmental triggers
- Regular monitoring of lung function
- Staying up-to-date with recommended vaccinations
Vaccination Recommendations
Vaccines are very important for ACOS. They help stop infections that can make symptoms worse. We tell patients with ACOS to get flu shots and pneumococcal shots every year.
With a plan that includes rehab, lifestyle changes, quitting smoking, stopping bad episodes, and vaccines, ACOS patients can get better and live better lives.
Living with ACOS: Patient Perspectives
Living with Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) is tough. It affects not just your body but also your mind and feelings. To manage ACOS well, you need to tackle both the physical and emotional sides of it.
Daily Management Challenges
People with ACOS have big daily challenges. They must stick to their meds and avoid things that make their symptoms worse. Effective management means taking your meds, making lifestyle changes, and watching your symptoms.
It’s also important to watch out for things like air quality, allergens, and pollutants. These can set off your symptoms. Patient education is key to helping you manage your ACOS well.
Psychological Impact and Mental Health
ACOS can really affect your mind and mental health. The constant worry and unpredictability of flare-ups can lead to anxiety and depression.
Healthcare providers need to help with the mental side of ACOS. They should offer support and resources to help you cope. Mental health support is a big part of caring for ACOS patients.
Support Resources and Patient Education
Support resources and patient education are very important for ACOS patients. They give you the latest info on treatments, lifestyle changes, and coping strategies.
Patient education is essential for better outcomes. By understanding your ACOS and how to manage it, you can live a more active and happy life despite your diagnosis.
Conclusion
It’s key to understand asthma-COPD overlap syndrome (ACOS) for effective care. ACOS needs a special approach, different from treating asthma or COPD alone.
Our look into ACOS shows it has big clinical effects. It means a higher disease load and special patient traits. ACOS needs a detailed management plan, using both medicines and other treatments.
As we learn more about ACOS, focusing on education and research is vital. This will improve patient results and life quality. Healthcare teams can meet the unique needs of ACOS patients with a broad strategy.
FAQ
What is Asthma and COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS)?
ACOS is a condition where people have symptoms of both asthma and COPD. This makes it hard to diagnose and treat.
How common is ACOS among COPD patients?
About 27% of COPD patients also have ACOS. This shows a big overlap between the two conditions.
What are the typical characteristics of patients with ACOS?
People with ACOS often smoked a lot, are older, and respond well to bronchodilators. They also have high eosinophil counts.
How does ACOS impact the quality of life?
ACOS leads to more and worse attacks, faster lung damage, and higher death rates. It really affects how well someone lives.
What are the challenges in diagnosing ACOS?
Diagnosing ACOS is hard because it shares symptoms with asthma and COPD. Doctors need to use many tests and look at biomarkers.
How is ACOS treated?
Treating ACOS means using medicines like steroids and bronchodilators. It also includes non-medical steps like exercise and changing lifestyle habits.
Can ACOS be managed effectively?
Yes, with the right treatment plan, ACOS can be managed well. This improves how patients feel and live.
What is the role of pulmonary rehabilitation in ACOS management?
Pulmonary rehab is key in managing ACOS. It helps improve lung health, reduces symptoms, and boosts quality of life.
Are there specific vaccination recommendations for ACOS patients?
Yes, ACOS patients should get vaccinated against flu and pneumococcus. This helps prevent attacks.
How does smoking cessation impact ACOS management?
Quitting smoking is very important for ACOS patients. It slows lung damage and cuts down on attacks.
What is the psychological impact of living with ACOS?
ACOS can really affect a person’s mind, causing anxiety and depression. It’s important to have support and learn about the condition.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/
































