Stem cells can develop into many cell types and act as the body’s repair system. They replace or restore damaged tissues, offering new possibilities for treating diseases.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The heart often speaks in whispers before it shouts. Recognizing the early symptoms of heart disease is the most effective way to prevent a major health crisis. Non-invasive cardiology relies heavily on the patient’s ability to report what they are feeling. Because the doctor cannot look inside the heart physically without tools, the patient’s story is the most valuable diagnostic asset. Symptoms can vary widely from person to person; what feels like indigestion to one person might be a heart attack in another.
Risk factors are the silent architects of heart disease. They are the conditions and habits that slowly damage the cardiovascular system over years or decades. Understanding these risks empowers patients to take control of their health. A noninvasive cardiologist evaluates these factors to calculate the statistical likelihood of a future event. This section explores the warning signs that should prompt a visit to the doctor and the hidden dangers that might be lurking in the background.
Chest pain is the most well-known symptom of heart trouble, but it is often misunderstood. In medical terms, this is called angina. It is not always a sharp, stabbing pain. In fact, many patients describe it as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or a heavy weight sitting on the center of the chest. It occurs when the heart muscle is not getting enough oxygen-rich blood.
Stable angina is a predictable chest discomfort. It typically happens during physical exertion, such as climbing stairs or walking briskly. The heart works harder and needs more oxygen, but narrowed arteries cannot supply it. The pain usually subsides quickly when the person rests or takes medication.
Unstable angina is much more dangerous. It can occur while resting, sleeping, or with very little physical effort. This situation signals that an artery is critically blocked or that a clot has formed. The symptoms often feel more severe than those experienced during a strong warning sign that a heart attack could be imminent.
Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is a classic symptom of heart issues, though it is often blamed on age or lack of fitness. If the heart is struggling to pump blood efficiently, fluid can back up into the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. These symptoms might manifest as getting winded after walking a distance that used to be easy or waking up in the middle of the night gasping for air.
Fatigue is another subtle but significant sign. This is not just being tired after a long day; it is a profound exhaustion that does not improve with sleep. It happens because the body’s tissues are not receiving enough oxygenated blood. Patients often report feeling like their limbs are heavy or that they simply lack the energy to perform daily chores.
Many people experience the sensation that their heart is racing, pounding, fluttering, or skipping a beat. These sensations are known as palpitations. While a skipped beat now and then can be normal, frequent or sustained irregularities can indicate an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia is a problem with the heart’s electrical system.
In some cases, the heart beats too fast (tachycardia), leaving the person feeling anxious or dizzy. In other cases, it beats too slowly (bradycardia), causing fatigue. Atrial fibrillation is a common rhythm disorder where the upper chambers of the heart quiver instead of beating effectively. This condition can cause a sensation of a “fish flopping” in the chest and significantly increases the risk of stroke.
Syncope is the medical term for fainting. It happens when blood flow to the brain is temporarily reduced. This process can be caused by a sudden drop in heart rate or blood pressure. While fainting can be caused by dehydration or standing up too quickly, it can also be a sign of a serious heart valve problem or a dangerous heart rhythm.
Dizziness or lightheadedness that does not result in fainting is also a concern. It suggests that the heart is not pumping enough blood to the brain to maintain full alertness. This can occur in conditions like aortic stenosis, where the main valve leaving the heart is narrowed, restricting blood flow. Any unexplained fainting spell warrants an immediate evaluation by a cardiologist.
When the heart weakens, it cannot pump blood effectively throughout the body. This causes blood to back up in the veins, forcing fluid to leak out into the surrounding tissues. This condition is often referred to as congestive heart failure. The fluid typically accumulates in the lowest parts of the body due to gravity.
The most common sign is swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs. Patients might notice that their shoes feel tight by the end of the day or that their socks leave deep indentations in their skin. This swelling, called edema, is often painless but can make the legs feel heavy.
Fluid can also build up in the abdomen, causing bloating and nausea, or in the lungs, causing a persistent cough. This cough might produce frothy or pink-tinged mucus. Sudden weight gain of two or three pounds overnight is a specific sign of fluid retention that needs medical attention.
The most dangerous heart problems are often the ones you cannot feel. High blood pressure (hypertension) is known as the “silent killer” because it damages the arteries and heart muscle for years without causing a single symptom. It forces the heart to work harder, leading to thickened muscle and eventual failure.
High cholesterol is another silent risk. Excess cholesterol circulates in the blood and deposits into the artery walls, forming plaque. This plaque narrows the arteries over time. You cannot feel high cholesterol; it can only be detected with a blood test. Diabetes also silently damages the blood vessels and nerves of the heart, sometimes masking the pain of a heart attack.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Yes. Many people, especially women and those with diabetes, may not experience classic chest pain. Their symptoms might be shortness of breath, extreme fatigue, nausea, or back pain.
A significant family history usually means a father or brother diagnosed with heart disease before age 55, or a mother or sister diagnosed before age 65. Genetics plays a strong role in risk.
Yes, anxiety releases adrenaline, which speeds up the heart. But if your heart races when you’re calm or is very fast and irregular, see a doctor.
Mild swelling can happen when standing all day, but persistent swelling can indicate that the heart is not pumping blood back up from the legs efficiently. It is a common sign of heart weakness.
It can be difficult to tell. However, shortness of breath that worsens when you lie flat or wakes you up at night is more commonly associated with heart issues. A doctor can use tests to tell the difference.

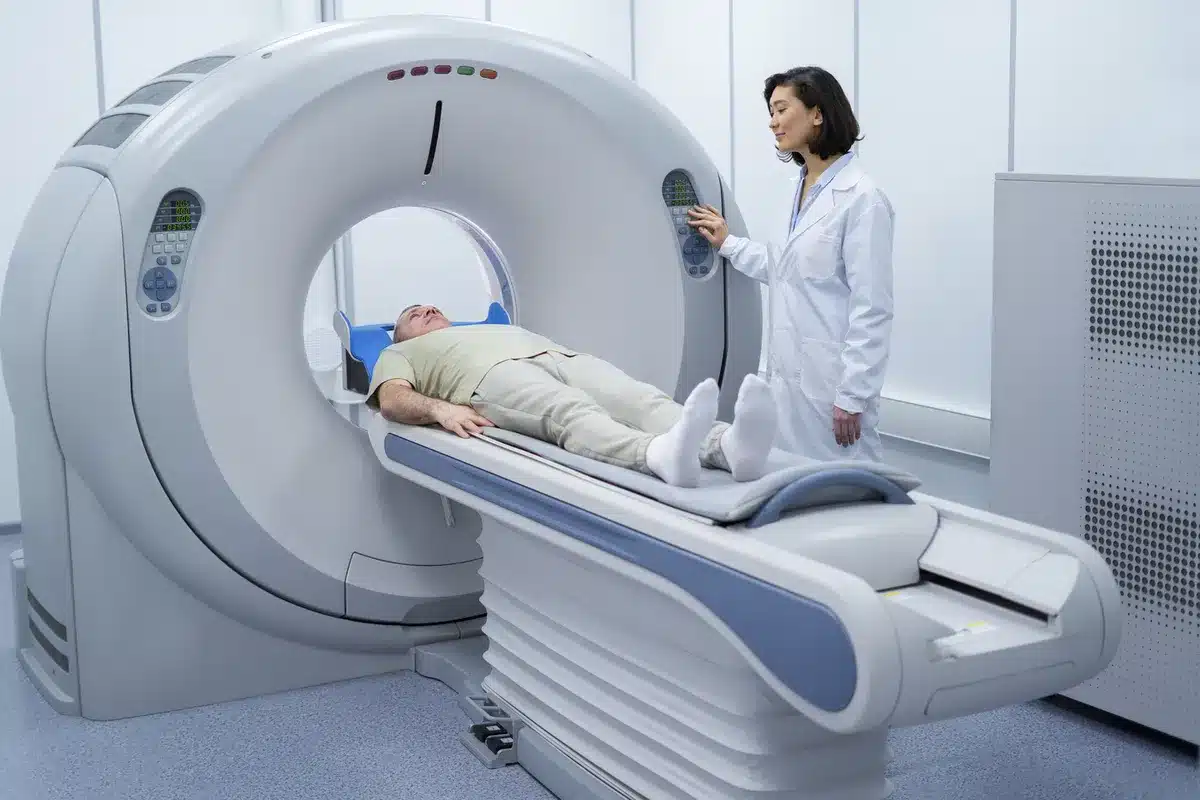
Heart disease is a big problem worldwide. To find and treat heart problems, cardiologists use advanced tests like the Cardiac MRI. Cardiac MRI makes detailed
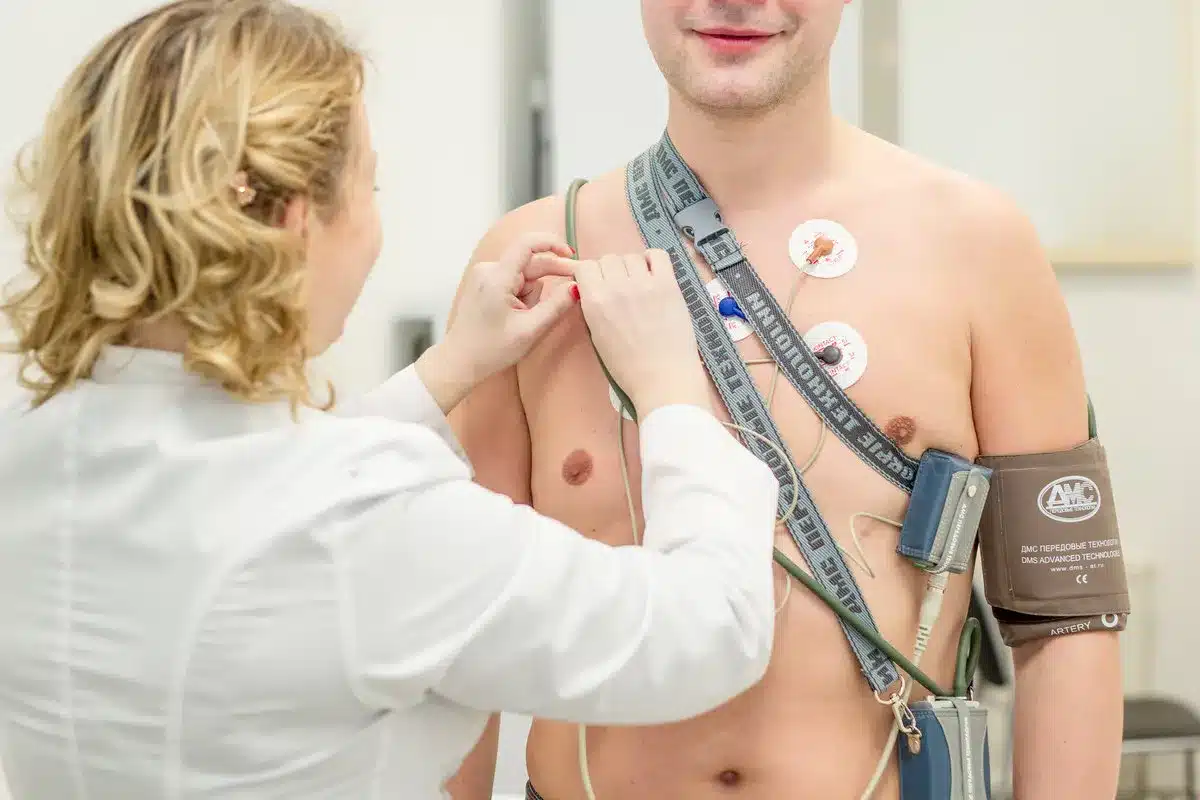
Did you know walking can change your heart rate in big ways? This is key for people in cardiac rehab with a Holter monitor on
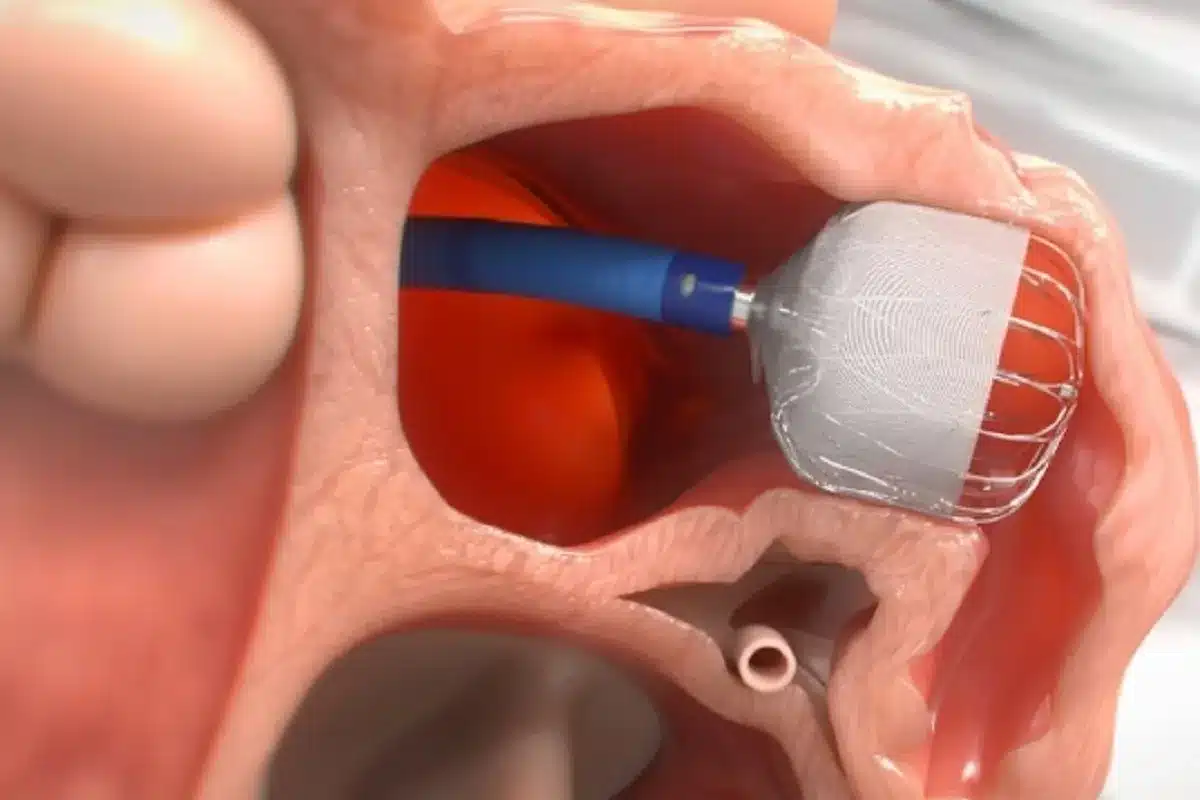
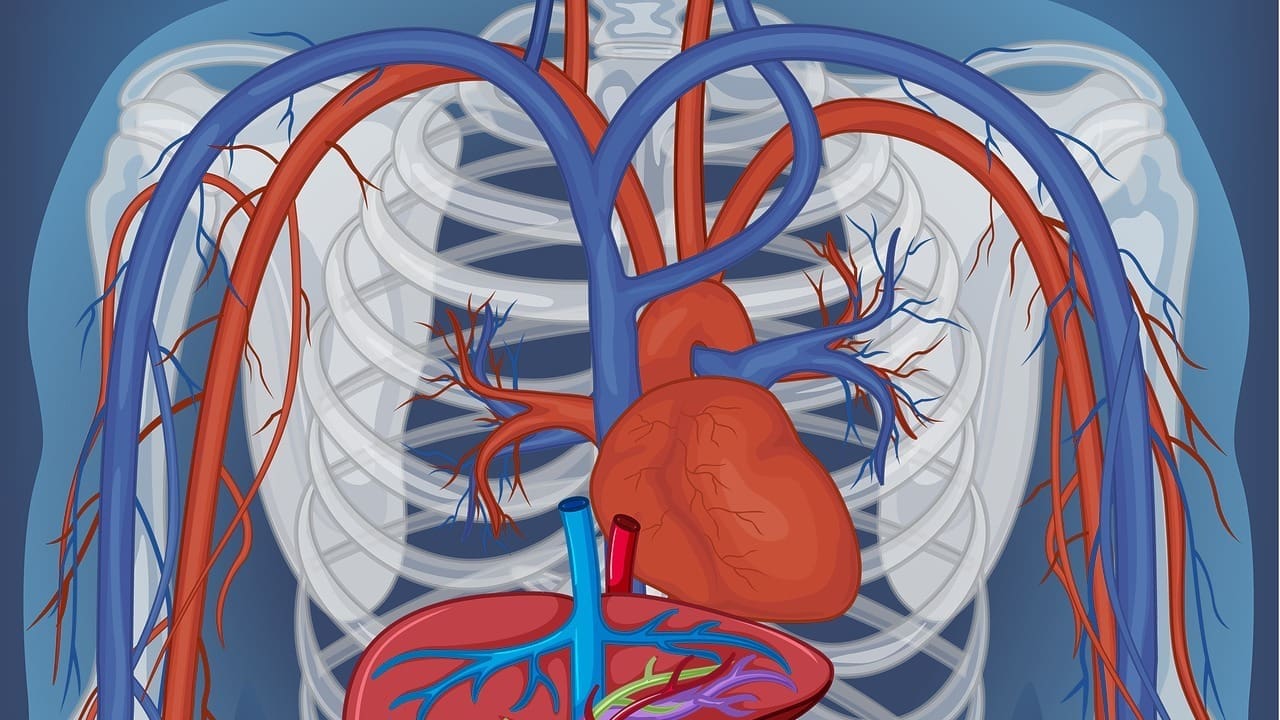
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart condition that makes the heart beat irregularly and fast. Did you know that AFib is a leading cause of
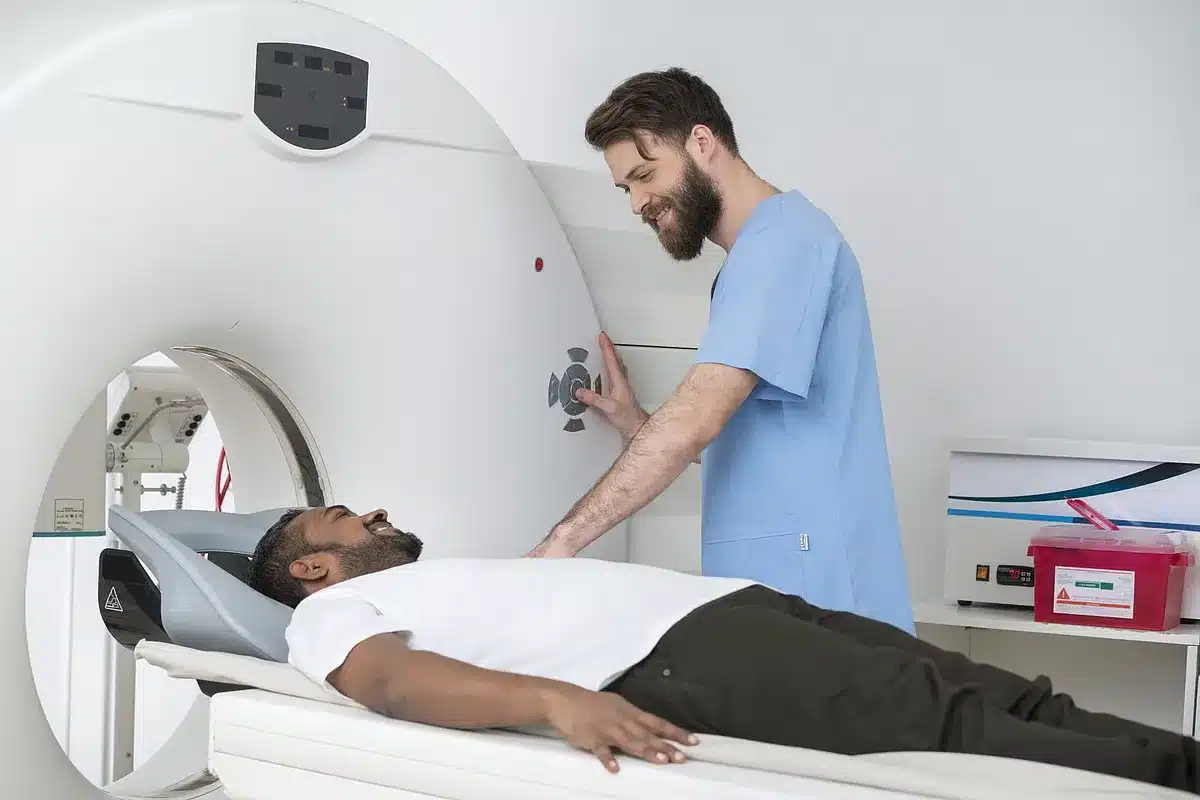
Nearly 1 in 5 adults in the United States will face heart disease at some point. This makes heart health very important cat scan vs
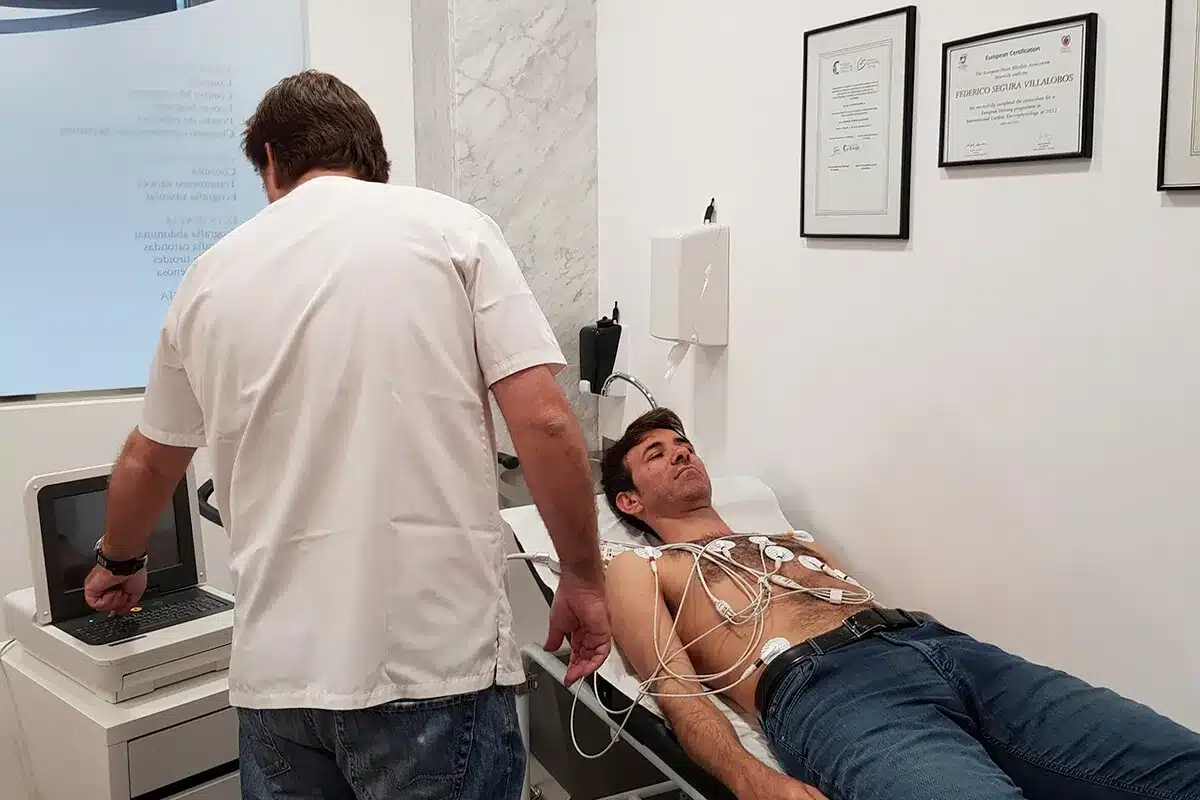
Heart disease is a big problem worldwide, with coronary artery disease leading to many heart attacks. A Holter monitor is a small device that tracks