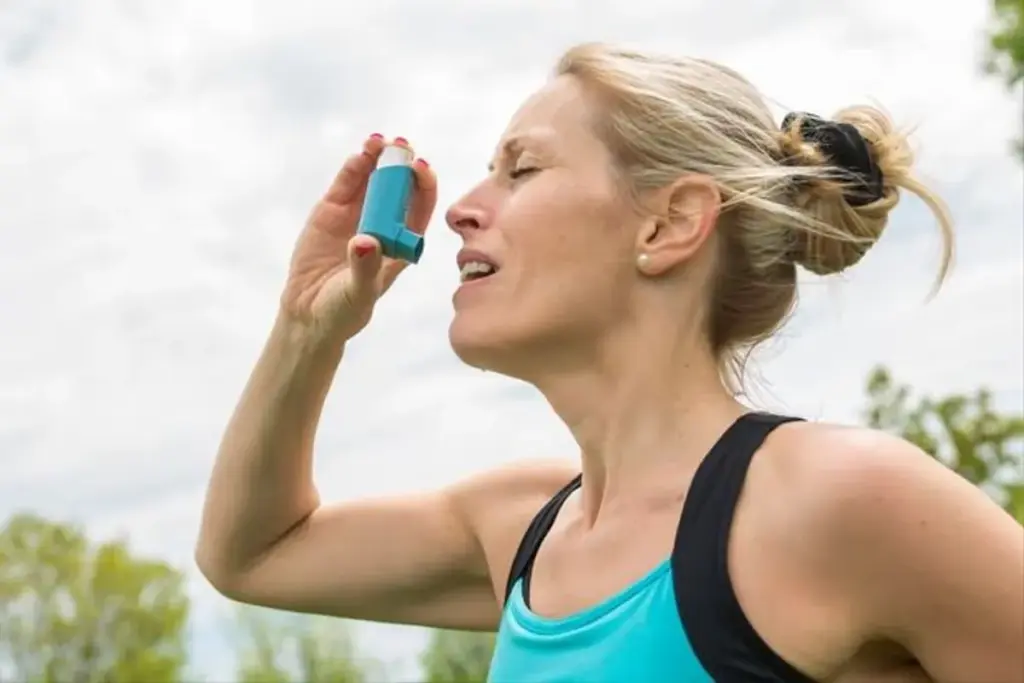
Nocturnal asthma is a big problem for millions around the world. It makes asthma symptoms worse at night, messing up sleep and health. Studies show that about 75 percent of asthma sufferers see their symptoms get worse at night at least once a week.
At Liv Hospital, we know how bad nocturnal asthma can be. Our team works hard to help manage its symptoms. By figuring out why it happens and using the right strategies, people can get better sleep at night.
Key Takeaways
- Nocturnal asthma affects a significant portion of the asthma population.
- Worsening asthma symptoms at night can disrupt sleep and overall health.
- Effective management strategies can provide relief from nighttime asthma symptoms.
- Comprehensive care is available at Liv Hospital to address nocturnal asthma.
- Understanding the causes of nocturnal asthma is key to managing it.
Understanding Nocturnal Asthma

For many with asthma, nighttime can trigger symptoms, known as nocturnal asthma. This condition makes asthma symptoms worse during sleep. It can really affect how well you live.
What is Nocturnal Asthma?
Nocturnal asthma means asthma symptoms like wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath get worse at night. Up to 60 percent of asthma patients deal with this, making it a big issue for them.
Prevalence and Statistics
Nocturnal asthma is more common than people think, affecting a lot of asthma patients. It can happen because of changes in circadian rhythms that affect lung function and inflammation. Knowing how common it is helps us see why managing it well is so important.
Recognizing Nighttime Asthma Symptoms
It’s key to know the symptoms of nocturnal asthma to manage it. Common signs include:
- Waking up with coughing or wheezing
- Experiencing chest tightness or shortness of breath at night
- Feeling like one is breathing through a narrow passage
Spotting these symptoms early can help prevent them and get the right treatment. This can make nighttime asthma relief better.
Why Does Asthma Flare Up at Night?

Asthma symptoms often get worse at night due to many reasons. Knowing these reasons is key to controlling asthma better at night.
Circadian Rhythm and Hormone Fluctuations
Our bodies have a natural rhythm that affects how we breathe and fight off inflammation. Studies show that epinephrine levels, which relax airway muscles, are lowest around 4 a.m. This is when most people have their worst asthma symptoms. Also, cortisol levels, which help control asthma, are usually lower at night.
Bedroom Environmental Triggers
The things in our bedrooms can also make asthma symptoms worse at night. Dust mites, pet dander, and mold are common allergens that can make asthma worse. These can cause asthma attacks, making symptoms like wheezing worse when lying down.
To fight these triggers, making our bedrooms asthma-friendly is important. This means using allergen-proof bedding, removing carpets, and ensuring good air flow.
Physical Factors During Sleep
Physical things that happen while we sleep can also make asthma symptoms worse. For example, lying down can cause mucus to build up in the airways, which can trigger asthma attacks. Some people also get gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptoms at night, which can make asthma worse.
Understanding these physical factors and taking steps to address them can help reduce asthma symptoms at night. This includes elevating the bed or managing GERD symptoms.
Effective Strategies for Nighttime Asthma Relief
To help with nighttime asthma, you need a plan that includes medicine, changes to your bedroom, and breathing exercises. It’s important to manage asthma with a mix of medical care, lifestyle changes, and making your environment better.
Medical Treatments and Prevention
Medical care is key in fighting nighttime asthma. Stick to your doctor’s advice on medicines, like inhalers or pills. Working with your doctor to tailor your treatment is vital. For more tips, check out Baptist Health’s guide on sleeping better with asthma.
Creating an Asthma-Friendly Bedroom
Make your bedroom safe from asthma triggers. Use allergen-proof bedding and clean your room often. Keep it cool and dry. An air purifier and humidifier can also help.
Sleep Position and Breathing Techniques
Your sleep position and breathing can affect your asthma at night. Try different sleep positions to keep your airways open. Breathing exercises can also help your lungs. Diaphragmatic breathing is a good choice.
Emergency Action Plan
It’s important to have an emergency plan for severe asthma attacks at night. Know when to use your rescue medicine and when to call for help. Practice your plan with your doctor to be ready for emergencies.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing nocturnal asthma is key to a better life for those with asthma. If your asthma gets worse at night, tell your doctor. Nocturnal asthma can hurt your sleep and health a lot.
Asthma can get worse at night for many reasons. This includes changes in your body’s clock and things in your bedroom that trigger it. In rare cases, asthma attacks at night can be deadly. It’s important to manage asthma well to avoid this.
Knowing the signs of nocturnal asthma, like wheezing at night, is important. By knowing why it happens and how to manage it, you can feel better. If your asthma symptoms at night don’t go away, see a doctor. They can help you avoid serious problems.
By managing nocturnal asthma, you can lower the risk of serious problems. If you wheeze only at night or have asthma symptoms that keep you awake, talk to your doctor. They can help you make a plan to control your asthma at night.
FAQ
What is nocturnal asthma?
Nocturnal asthma is a common condition where asthma symptoms—such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath—significantly worsen or only appear during the night or early morning hours.
How common is nocturnal asthma among asthma patients?
It is estimated that 44% to 61% of people with asthma experience nocturnal symptoms, making it one of the most frequent indicators of poorly controlled asthma.
Can you have an asthma attack in your sleep?
Yes, asthma attacks can occur during sleep and are particularly dangerous because you may not wake up immediately to use rescue medication, leading to delayed treatment.
Why do I wake up wheezing?
Waking up wheezing is often caused by a combination of natural lung function “nadir” (the lowest point) around 4 a.m., increased mucus buildup, and exposure to bedroom triggers like dust mites.
What triggers asthma attacks at night?
Common triggers include reclining (which increases airway resistance), cooler bedroom air, acid reflux (GERD) irritating the throat, and allergens trapped in pillows or mattresses.
Can asthma kill you in your sleep?
While rare with proper management, nighttime asthma is serious; research suggests that up to 70% of asthma-related deaths occur during the night or early morning hours due to severe airway obstruction.
How can I alleviate nighttime asthma symptoms?
You can reduce symptoms by using dust-mite-proof covers, elevating your head with extra pillows to assist drainage, and discussing “chronotherapy” (adjusting the timing of your meds) with your doctor.
What is the role of circadian rhythm in nocturnal asthma?
The body’s internal clock causes natural drops in protective hormones like adrenaline and cortisol at night, while increasing inflammatory markers, all of which narrow the airways during sleep.
How can I create an asthma-friendly bedroom?
An asthma-friendly bedroom involves washing bedding weekly in 130°F (54°C) water, keeping pets off the bed, using a HEPA air purifier, and keeping the windows closed to block pollen.
What should be included in an emergency action plan for nocturnal asthma?
Your plan should include keeping a rescue inhaler on your nightstand, knowing the signs of a severe attack (like blue lips), and having a pre-planned route to the nearest 24-hour emergency room.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9536586/