Asthma and acid reflux often go hand in hand. Studies show that more than half of asthma patients also have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This condition happens when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus. It can set off asthma attacks.
It’s key to understand how GERD and asthma are connected. This knowledge helps manage both conditions better. We must tackle the main cause of asthma symptoms, which acid reflux can worsen.
Key Takeaways
- GERD is common among asthma patients, affecting over half of those with difficult-to-control asthma.
- Acid reflux can trigger asthma symptoms by causing airway inflammation and constriction.
- Treating GERD may help improve asthma management.
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight management and avoiding triggers, can help alleviate GERD symptoms.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are available over-the-counter and by prescription to treat GERD.
The Bidirectional Relationship Between Gastroesophageal Reflux Asthma
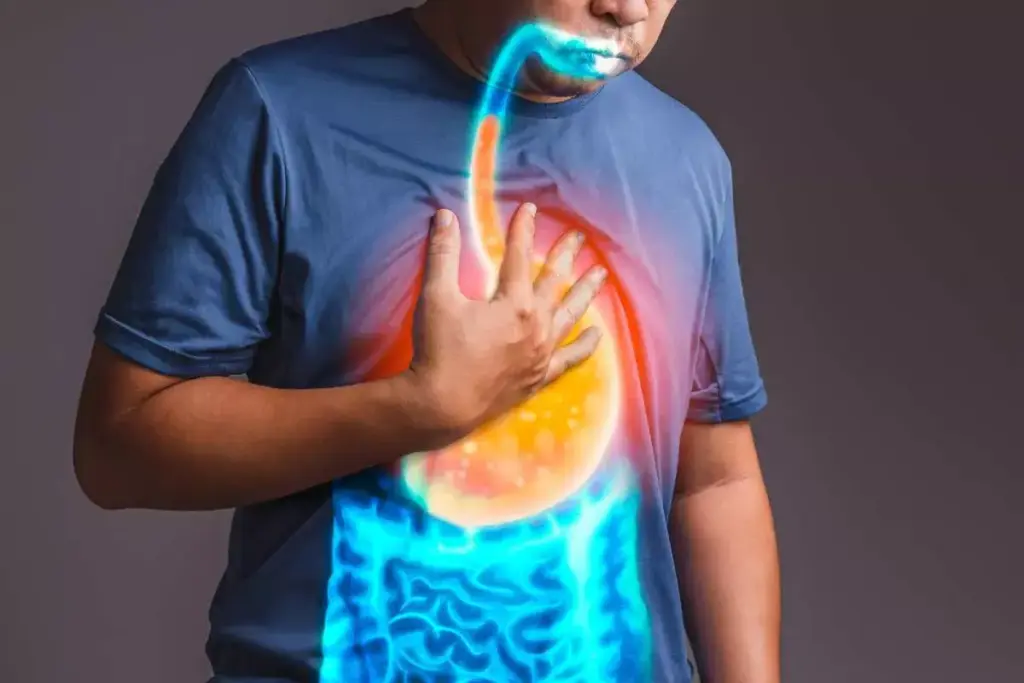
It’s important to understand how GERD and asthma work together. They often happen together and affect each other. GERD can make asthma harder to control, and asthma can make GERD worse.
Prevalence Statistics in Asthma Patients
Research shows that many asthma patients also have GERD. About 89% of asthma patients have symptoms of GERD. This can make it harder to control asthma.
Studies say up to 55% of patients with hard-to-control asthma have GERD. This shows how important it is to treat GERD in asthma patients.
| Condition | Prevalence in Asthma Patients | Impact on Asthma Control |
| GERD | Approximately 89% | Significant impact due to overlapping symptoms |
| Difficult-to-control Asthma | Up to 55% GERD prevalence | GERD exacerbates asthma symptoms |
The Two-Way Connection
GERD and asthma are connected through airway sensitivity and inflammation. Stomach acid from GERD can reach the lungs and trigger asthma. On the other hand, asthma can make GERD worse by increasing pressure in the stomach.
A strategy that tackles both GERD and asthma is needed. By managing GERD in asthma patients, doctors can help control asthma better.
Exploring the link between GERD and asthma shows we need a detailed plan to manage them. This approach is key to treating these conditions effectively.
Mechanisms Linking GERD and Asthma
GERD and asthma are linked through direct and indirect ways. Knowing these connections helps in creating better treatments for both.
How Acid Reflux Triggers Asthma Symptoms
Acid reflux can start asthma symptoms in several ways:
- Irritation of Nerve Endings: Stomach acid in the esophagus irritates nerves. This can cause the airways to tighten, leading to asthma.
- Microaspiration: Tiny bits of stomach acid can get into the lungs. This irritates the airways and triggers asthma.
- Increased Airway Reactivity: Long-term exposure to stomach acid makes airways more sensitive. This increases the chance of asthma symptoms.
How Asthma Can Induce GERD
Asthma can also make GERD worse in several ways:
- Pressure Changes During Breathing: Asthma makes breathing hard, changing chest pressure. This can cause stomach acid to flow up into the esophagus.
- Medication Side Effects: Some asthma meds can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter. This increases the risk of stomach acid reflux.
It’s key for doctors to understand how GERD and asthma affect each other. This helps in making treatments that work for both conditions.
Conclusion: Identifying and Managing GERD-Related Asthma
It’s key to understand how gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and asthma are connected. Studies show that about 70% of people see better asthma symptoms with anti-reflux meds. This shows why it’s important to handle GERD-related asthma well.
Managing GERD can really help control asthma. We can make lifestyle changes, take meds, or even surgery in some cases. PPIs are often used to cut down stomach acid and ease GERD symptoms. This can also lessen asthma attacks.
The relationship between reflux and asthma goes both ways. GERD can make asthma worse, and asthma can make GERD symptoms like heartburn worse. Knowing this, doctors can create better treatment plans for both conditions. This helps patients get better overall.
By tackling GERD and asthma together, we can improve life for those with these issues. We should teach patients about lifestyle changes and sticking to their meds, like PPIs. This helps manage symptoms and lowers the chance of asthma and GERD problems.
FAQ
What is the relationship between GERD and asthma?
Can acid reflux trigger asthma symptoms?
How does asthma contribute to the development or worsening of GERD?
What are the strategies for managing GERD-related asthma?
Can managing GERD help improve asthma symptoms?
Is it necessary to test for GERD if I have asthma?
Can asthma cause heartburn?
How does gastroesophageal reflux disease affect asthma?
Can reflux cause asthma attacks?
What lifestyle changes can help manage GERD and asthma?
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30037641/