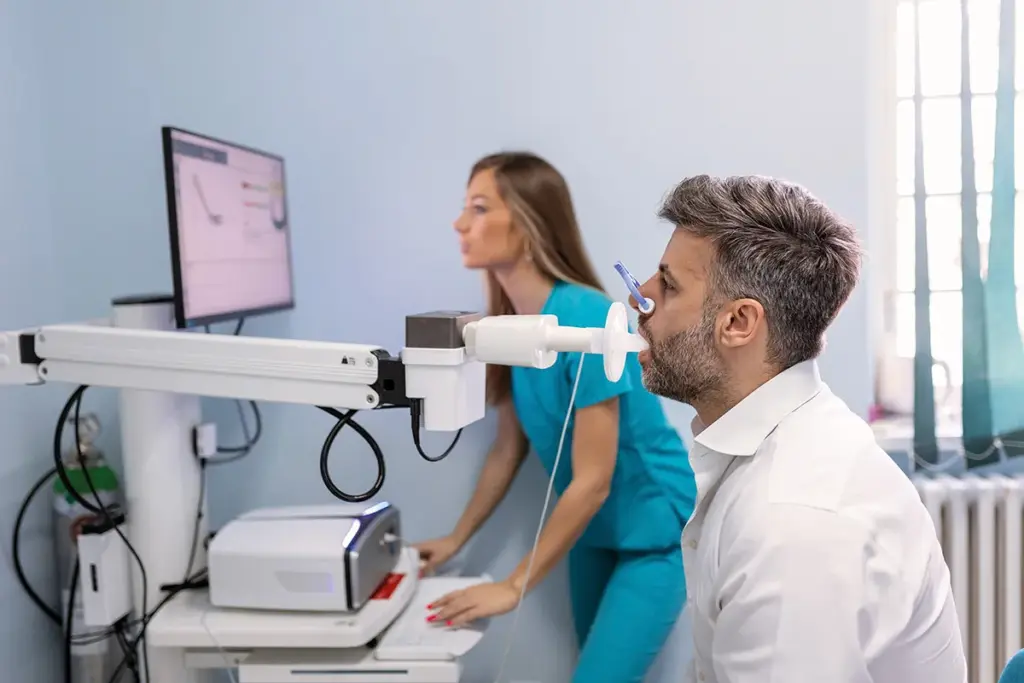
Spirometry is a key test that checks how much air you breathe in and out. It’s a simple test that doctors use to see how well your lungs work. It helps find problems like asthma and COPD.
This test looks at how much air you can breathe in and out. It also checks how fast you can breathe out. By using a spirometer, spirometry gives doctors important info about your lungs. A healthcare expert will guide you through the test.
The results from spirometry, like Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) and Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1), are very helpful. They help doctors figure out what’s wrong and if treatments are working.
Key Takeaways
- Spirometry measures lung function by assessing the volume and flow rate of air inhaled and exhaled.
- It is a non-invasive diagnostic tool used to evaluate respiratory health.
- Spirometry helps diagnose conditions such as asthma, COPD, and other respiratory diseases.
- The test involves breathing into a tube attached to a spirometer.
- Measurements obtained from spirometry guide treatment decisions and disease management.
Understanding Spirometry and Lung Volume Measurements
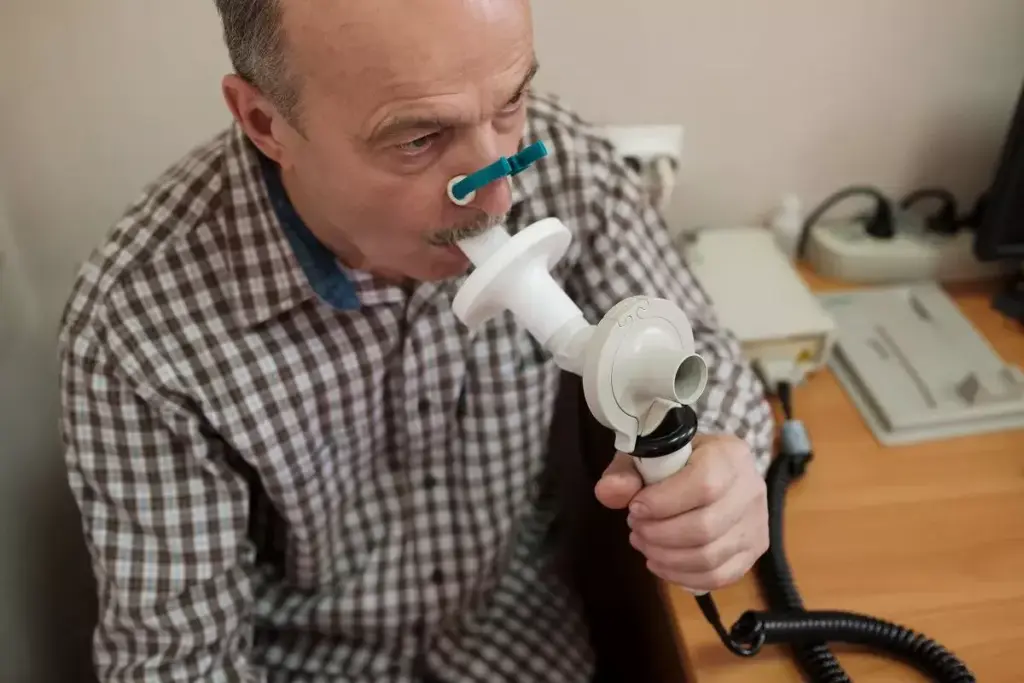
Spirometry is key for diagnosing and managing lung diseases. It’s a test that checks how well your lungs work. It gives important data on lung volumes and capacities.
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) and Expiratory Volume (FEV1)
Spirometry looks at important values like Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) and Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1). FVC is how much air you can push out after a deep breath. FEV1 is the air you blow out in the first second of a forced breath. These numbers help check lung health.
The steps to do spirometry are simple:
- Take a deep breath to fill your lungs.
- Push out air as hard and fast as you can.
- Measure how much air you blow out.
FEV1/FVC Ratio and Other Key Measurements
The FEV1/FVC ratio is a key number from spirometry. It’s FEV1 divided by FVC. This ratio is vital for spotting lung diseases. A low ratio might mean you have COPD or asthma.
Other spirometry results include:
- FVC: Shows the total air you can exhale.
- FEV1: Measures air exhaled in the first second.
- FEV1/FVC ratio: Helps figure out lung disease types.
Knowing these numbers helps doctors better diagnose and treat lung issues. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
What Is a Spirometer Used For in Respiratory Diagnostics
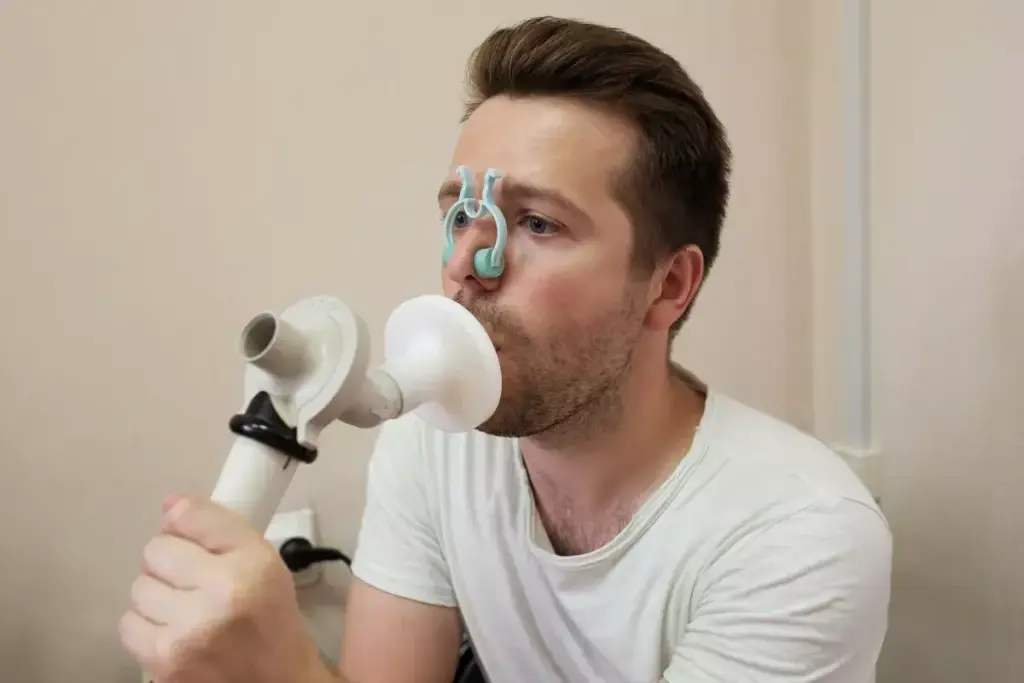
In respiratory diagnostics, spirometry is key for checking lung health. It helps diagnose and manage diseases like asthma and COPD.
Detecting Early-Stage Lung Diseases
Spirometry catches lung diseases early, like asthma, COPD, and cystic fibrosis. This is when treatment works best. It checks lung function to spot these conditions early.
According to the Medical organization, it’s used to diagnose asthma and find respiratory disease in breathless patients.
Early detection through spirometry can significantly improve patient outcomes. It lets doctors start the right treatment early. This can slow disease growth and improve life quality.
Monitoring COPD, Asthma, and Other Respiratory Conditions
Spirometry is not just for diagnosis. It also tracks how respiratory diseases progress. Regular tests help doctors see if treatments are working.
| Respiratory Condition | Spirometry Measurement | Clinical Significance |
| Asthma | FEV1/FVC Ratio | Indicates airway obstruction |
| COPD | FEV1 | Assesses severity of airflow limitation |
| Cystic Fibrosis | FVC | Monitors lung function decline |
Using spirometry for both diagnosis and monitoring helps doctors give better care to patients with respiratory issues.
How Spirometry Works: The Testing Procedure
Spirometry is a key tool for checking lung health. It involves a simple test. A patient breathes deeply into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer. This lets doctors see how well the lungs are working.
Spirometer Components and Technology
Most spirometers show graphs like volume-time curves and flow-volume loops. These are key for spotting breathing problems. The tech in spirometry has improved a lot. Advanced spirometers use smart sensors and software to give detailed reports.
Open Circuit Spirometry Systems and Their Advantages
Open circuit spirometry systems measure lung function without a closed circuit. This makes tests more comfortable for patients. The advantages include easy use and accurate results during different breathing tests.
Knowing how spirometry works helps doctors diagnose and treat breathing issues better. Using advanced spirometers and open circuit systems makes tests more accurate and comfortable.
Conclusion: The Value of Spirometry in Modern Healthcare
Spirometry is a key tool in healthcare. It gives us important information about lung health. It’s vital for diagnosing and treating lung diseases.
This test measures lung function and spots lung diseases early. It’s a must-have in respiratory medicine. It helps doctors diagnose asthma, detect respiratory diseases, and check how well airways respond.
Healthcare experts use spirometry to check lung health without harm. It’s a powerful tool in respiratory care. As we improve in this field, spirometry’s role stays important.
In short, spirometry is key to top-notch healthcare, even for patients from abroad. Its role in today’s healthcare is clear. We keep counting on spirometry for lung health checks.
FAQ:
What is spirometry and how does it work?
A lung function test that measures how much and how quickly you can inhale and exhale using a spirometer.
What does spirometry measure?
Lung volumes, airflow rates, forced vital capacity (FVC), and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1).
What is the significance of the FEV1/FVC ratio in spirometry?
It detects airway obstruction; a low ratio indicates conditions like asthma or COPD.
How is spirometry performed?
You inhale fully, then exhale forcefully into a spirometer, usually repeating 2–3 times for accuracy.
What is a spirometer used for?
To assess lung function, diagnose respiratory diseases, monitor treatment, and evaluate surgical risk.
What are the benefits of open circuit spirometry systems?
They provide accurate measurements, reduce CO2 rebreathing, and allow continuous monitoring of lung volumes and airflow.
What is the purpose of spirometry in respiratory diagnostics?
To diagnose lung diseases, assess severity, monitor progression, and guide treatment decisions.
How does spirometry contribute to modern healthcare?
It enables early detection of respiratory conditions, improves patient management, and supports preventive and therapeutic strategies.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3945631/























