Learn to read your allergy skin test on back results. Follow the best guide on interpreting swelling size for accurate diagnosis.
Understanding the results of an allergy skin test on your back is key. It helps diagnose allergic contact dermatitis. It also finds out what allergens cause your symptoms.
At Liv Hospital, we use patch testing to find out what might cause allergic reactions. We apply small patches with possible allergens to your back. These patches stay there for 48 hours.
By correctly reading your patch test results, we can make a treatment plan just for you. This plan helps you manage your allergies better. It also improves your life quality.
Key Takeaways
- Patch testing is the best way to find out about allergic contact dermatitis.
- The test involves applying patches with possible allergens to the back for 48 hours.
- Understanding your patch test results well is key to managing allergies effectively.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch dermatological care and support for international patients.
- Our team is committed to providing world-class healthcare that puts patients first.
What Is an Allergy Skin Test on Back
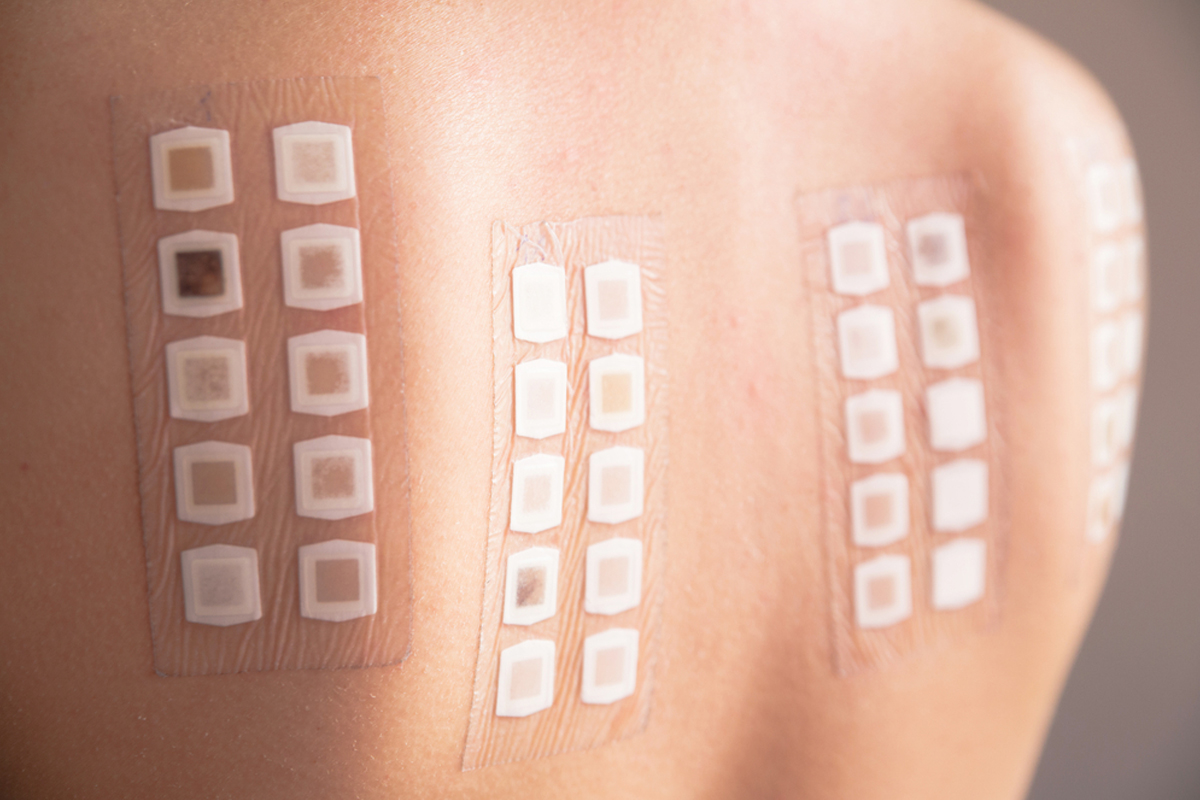
Allergic contact dermatitis can be diagnosed with a skin test on the back. This test applies possible allergens to the skin. It’s very good at finding out what causes allergic reactions, helping in treatment and prevention.
The Purpose of Patch Testing
Patch testing aims to find out what allergens cause allergic contact dermatitis. Small amounts of possible allergens are put on the back skin. Then, the skin’s reaction is watched for a few days.
This test is key for:
- Diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis
- Finding out what allergens cause the reaction
- Creating treatment and prevention plans
Detecting Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction. It means the immune response is delayed. Patch testing spots this by exposing the skin to possible allergens and watching for signs like redness or swelling.
The back is the best place for patch testing because it’s flat and has little hair. This makes the test more accurate, with a success rate of 70 to 80 percent.
Advantages of Back Location Testing
The back is great for patch testing for several reasons:
- It’s flat, which helps the patch stick better to the skin.
- It has little hair, which means less chance of the test being messed up.
- It’s big, so you can test many allergens at once.
Using the back for patch testing helps doctors find out what causes allergic contact dermatitis. This leads to better treatment and care plans.
The Science Behind Delayed Hypersensitivity Reactions
The immune system reacts to certain allergens in a way that leads to delayed hypersensitivity reactions. This is key to allergic contact dermatitis. It happens when the skin reacts badly to substances it comes into contact with.
These reactions are mediated by T-cells, important immune cells. They help fight off foreign substances. Unlike immediate reactions, which happen fast, delayed reactions take longer to show up.
Type IV Allergic Reactions
Type IV allergic reactions, or delayed hypersensitivity, are a big part of allergic contact dermatitis. They involve T-cells, antigen-presenting cells, and other immune cells working together.
Difference Between Immediate and Delayed Reactions
It’s important to know the difference between immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Immediate reactions show up fast, with symptoms like hives and itching. Delayed reactions, on the other hand, take longer to appear. They show up as red, raised, or blistering areas 48 to 96 hours after exposure.
|
Reaction Type |
Time to Onset |
Symptoms |
Mediators |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Immediate Hypersensitivity |
Minutes |
Hives, itching, swelling |
IgE antibodies |
|
Delayed Hypersensitivity |
Hours to days |
Redness, vesicles, blistering |
T-cells |
The Cellular Process of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis starts with T-cells getting activated by specific allergens. This leads to the release of cytokines and chemokines. These molecules help orchestrate an immune response, causing the symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis.
Positive patch test reactions show up as red, raised, or blistering areas. This is a sign of an allergic reaction. Knowing how these reactions work is key to understanding patch test results and managing allergic contact dermatitis well.
Preparing for Your Patch Test
Knowing how to prepare for your patch test is key to getting accurate results. We offer important tips to help you before and during the test.
Pre-Test Instructions
Before your test, it’s important to follow some steps. Avoid using topical corticosteroids on your back for at least a week before. This is because they can mess with the test results. Also, try to stay away from UV light, like tanning beds and too much sun, as it can change how your skin reacts.
Medications to Avoid
Some medicines can change how your patch test comes out. Oral corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs can make it seem like you’re not allergic when you are. Tell us about any medicines you’re taking so we can figure out if you need to stop them before the test.
What to Wear During Testing
When you’re getting tested, wear loose, comfy clothes that won’t bother the test area or make the patches move. Stay away from tight clothes that might rub against the patches and cause irritation or make them fall off.
By following these tips, you can make sure your patch test results are right. If you have any questions or worries about getting ready for your test, we’re here to help.
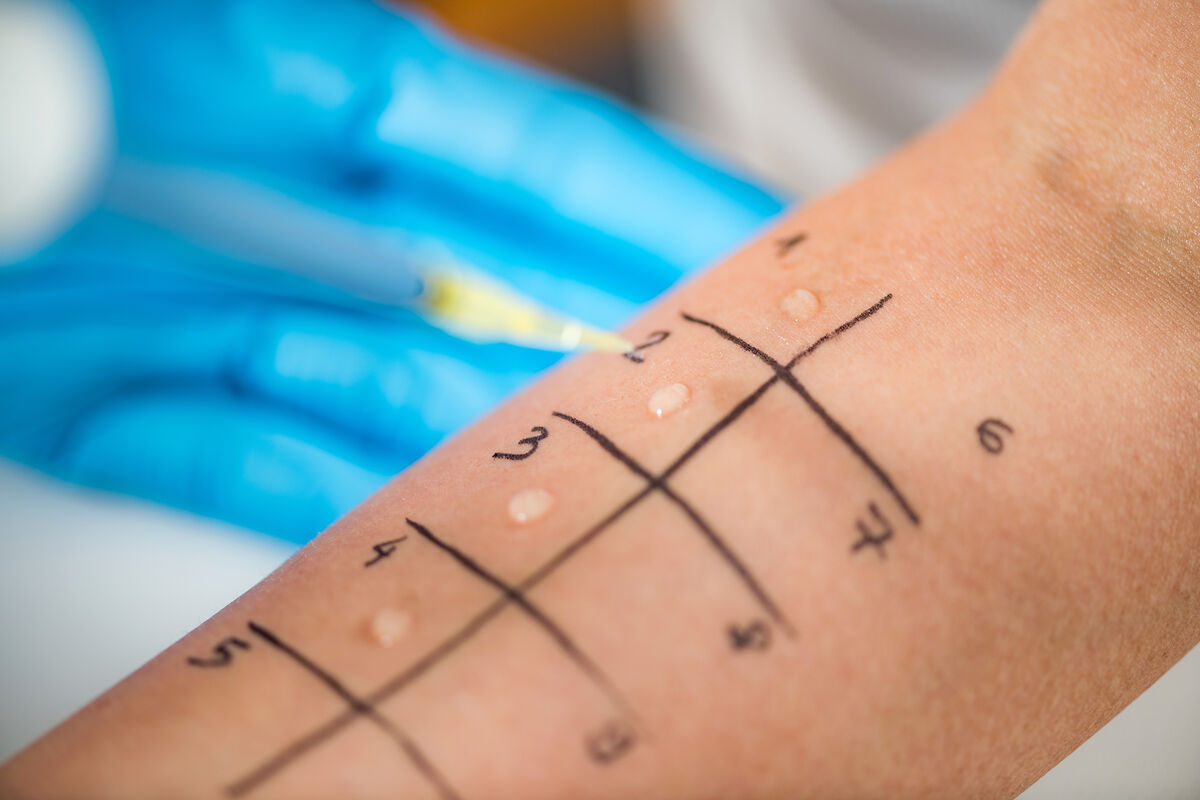
The Application Process for Back Patch Testing
To do a back patch test, we have a clear process. We put patches with possible allergens on the back with special tape.
The patches stay on for 48 hours. During this time, the patient should avoid certain activities. This helps make the test more accurate, as dermatologists advise.
Aluminum and Polyethylene Chambers
The allergens go in small aluminum or polyethylene chambers. These keep the allergen close to the skin, making the reaction easier to track.
Aluminum chambers are often used because they’re strong and safe for the skin. Polyethylene chambers are better for people who can’t handle certain metals.
Common Allergens in Standard Series
The standard test includes common allergens. These include metals like nickel and preservatives in products. Fragrances are also tested.
- Metals (nickel, cobalt, chromium)
- Preservatives (parabens, formaldehyde releasers)
- Fragrances (balsam of Peru, fragrance mix)
Testing these common allergens helps find out what causes skin reactions. It helps patients avoid these allergens.
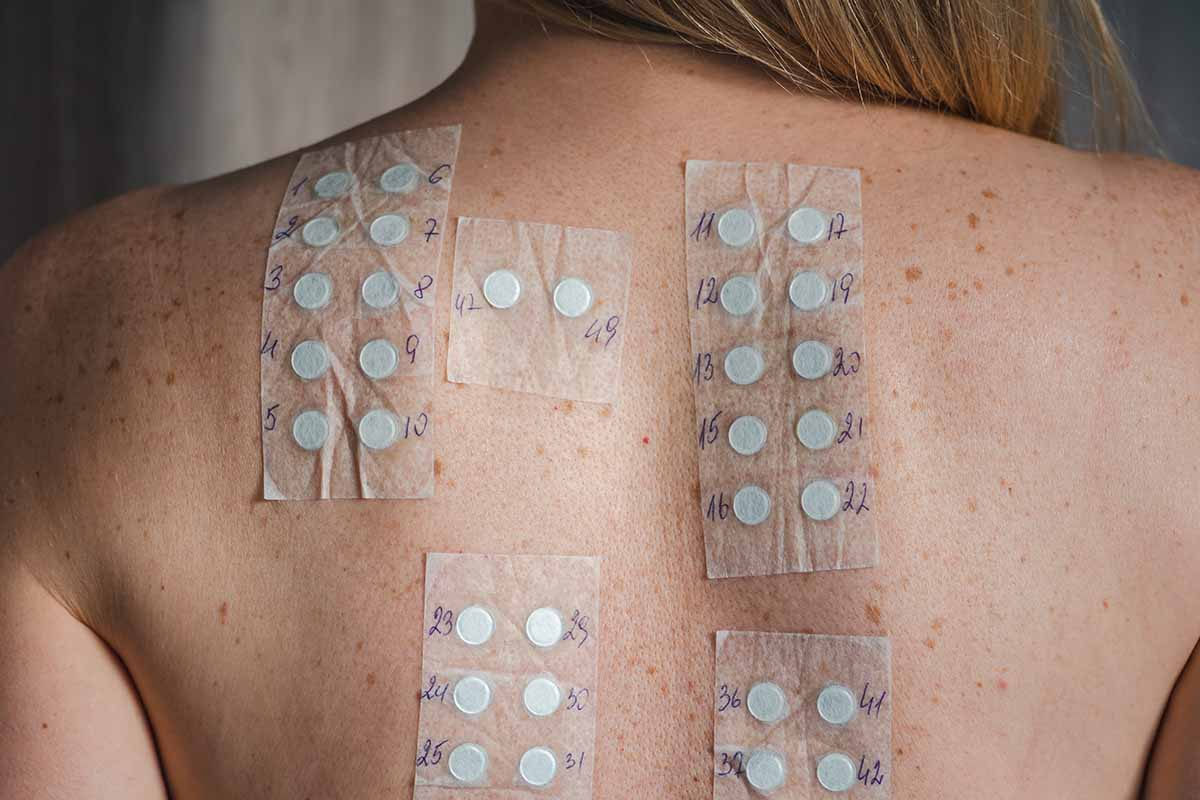
Placement Patterns on the Back
The patches are placed carefully on the back. This ensures they’re spread out and don’t irritate the skin. They’re arranged in a grid, with each one labeled.
Dermatologists say the way patches are placed is key. It helps get accurate results. This helps diagnose allergies and find the right treatments.
Living With Patch Tests on Your Back
Living with patch tests on your back needs some adjustments. We know patch tests can be tough, but with the right tips, you can do it comfortably. This way, the test will be successful.
Activity Restrictions
When you have patch tests, avoid activities that make you sweat a lot. This means no intense workouts, sauna visits, or anything that might make the patches fall off. Keeping sweat down is important for the patches to stay put and get accurate results.
Here’s a list of activities to skip during the test:
- Strenuous exercise or gym workouts
- Sauna or hot tub visits
- Contact sports or activities that might cause the patches to loosen
Showering and Water Exposure Guidelines
You can shower with patch tests, but follow some rules. Use lukewarm water instead of hot to prevent sweating. Use gentle, lukewarm water. When showering, don’t soak the patches or use harsh soaps that could irritate your skin or make the patches fall off.
|
Activity |
Guideline |
|---|---|
|
Showering |
Use lukewarm water, avoid harsh soaps |
|
Swimming |
Avoid swimming pools, specially those with high chlorine levels |
|
Bathing |
Prefer showers over baths to minimize water exposure |
Managing Discomfort and Itching
Some people feel a bit uncomfortable or itchy with patch tests. If you do, try not to scratch too much. Scratching can make the patches fall off or irritate your skin more. Instead, use a cold compress or an anti-itch cream that your doctor says is okay.
By following these tips, you can make your patch test successful and feel better. If you have any worries or questions, talk to your doctor for help.
The Patch Test Reading Schedule
The timing of patch test readings is key to spotting delayed hypersensitivity reactions. It helps get accurate diagnoses. When you have an allergy patch test on your back, the reading schedule is very important.
Initial Reading at 48 Hours
The patches are removed after 48 hours for the first reading. This early check lets doctors see how your skin reacts to allergens. It’s a big step in figuring out what’s causing your reaction.
Final Reading at 96 Hours
The final reading is at 96 hours, or four days after the patches go on. This second check is important because some reactions take time to show up. It helps doctors catch reactions that might not be seen right away.
Why Multiple Readings Are Necessary
Having multiple readings is important to understand all reactions to allergens. Some reactions happen right away, while others take longer. By checking at 48 and 96 hours, doctors get a full picture of your skin’s reactions. This leads to better diagnoses and treatment plans.
To show the patch test reading schedule and what it means, here’s a table:
|
Reading Time |
Purpose |
Significance |
|---|---|---|
|
48 Hours |
Initial Assessment |
Observes early reactions to allergens |
|
96 Hours |
Final Assessment |
Identifies delayed hypersensitivity reactions |
It’s important to know and follow the patch test reading schedule. This way, you and your doctor can find out what allergens you’re reacting to. You can then avoid them to lower the chance of allergic contact dermatitis.
Understanding the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group Grading System
When it comes to patch test results, a standard approach is key. The ICDRG grading system is a widely accepted method for this. It helps clinicians assess allergic reactions in a consistent way.
The ICDRG grading system sorts patch test reactions by severity. It ranges from no reaction to very strong reactions. This system is vital for making sure patch test results are interpreted the same way everywhere.
Negative Reactions (0)
A score of 0 means no visible reaction at the patch test site. This shows the person is not allergic to the tested substance.
Doubtful Reactions (?+)
A ?+ score means a faint or minimal reaction. It’s not clear-cut. More testing might be needed to understand this reaction.
Weak Positive Reactions (+)
A + score shows a clear but mild reaction. This means the person has an allergic response to the tested substance.
Strong Positive Reactions (++)
++ scores indicate a more pronounced allergic response. This shows a significant allergy to the tested substance.
The ICDRG grading system also covers extreme positive reactions (+++) and irritant reactions. Knowing these different grades is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
To better understand the ICDRG grading system, here’s a table that summarizes the different reaction grades:
|
Grade |
Description |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Negative Reaction |
|
?+ |
Doubtful Reaction |
|
+ |
Weak Positive Reaction |
|
++ |
Strong Positive Reaction |
|
+++ |
Extreme Positive Reaction |
Healthcare professionals use the ICDRG grading system for consistent patch test result interpretation. This leads to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans for patients with allergic contact dermatitis.
Identifying Positive Patch Test Results Visually
Seeing positive patch test results is key in finding allergies. It’s important to know what allergic reactions look like.
Characteristics of Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions show up as red, raised, or blistering skin areas. These happen when the body reacts to certain allergens.
Common signs include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Swelling where the allergen was applied
- Vesiculation or blistering in severe cases
Redness, Swelling, and Vesiculation
Reactions can be mild or severe. Some people might just have a little redness, while others could have swelling and blisters. Knowing the difference is key for a correct diagnosis.
The pattern and how severe the reaction is can tell us a lot about the allergy.
|
Reaction Severity |
Characteristics |
Clinical Implication |
|---|---|---|
|
Mild |
Redness, minimal swelling |
May indicate a low-level allergy or sensitivity |
|
Moderate |
Redness, swelling, possible vesiculation |
Suggests a significant allergic reaction |
|
Severe |
Marked redness, swelling, vesiculation, or blistering |
Indicates a strong allergic reaction requiring avoidance of the allergen |
Reaction Patterns and Their Meaning
The way a reaction spreads can also tell us a lot. If it goes beyond where the allergen was applied, it might mean the allergy is more intense.
By looking closely at the signs and patterns of positive patch test reactions, doctors can make accurate diagnoses. They can then help manage allergies better.
Distinguishing True Allergic Reactions from False Results
It’s important to tell real allergic reactions from false positives in patch testing. When looking at patch test results on the back, we need to know the difference. This helps us spot true allergies and not confuse them with other skin issues.
Irritant Reactions vs. Allergic Responses
Irritant reactions are not allergies. They happen when something irritates the skin, not when the immune system reacts. We must look closely at the reaction to figure out why it’s happening.
Key differences between irritant reactions and allergic responses:
- Irritant reactions show up sooner after exposure.
- Allergic reactions take longer, usually at 48 or 96 hours.
- Irritant reactions can look like widespread redness or burns. Allergic reactions are more focused, with redness, swelling, or blisters.
Staining Effects from Substances Like PPD Hair Dye
Some things, like PPD hair dye, can stain the skin. This might look like an allergic reaction. But it’s actually just the dye leaving a mark.
Using Alcohol Swabs to Remove Staining
If you think staining is what you’re seeing, try an alcohol swab. It can remove dye marks, like from PPD. This shows the mark isn’t an allergic reaction.
Pressure or Tape Reactions
Pressure or tape reactions can look like allergies too. They happen when the patch test chamber or its adhesive presses on the skin. They go away when the patch is taken off.
Knowing these details helps us accurately spot real allergic reactions. This way, we can give better advice on how to handle allergies.
Common Allergens and Their Typical Reactions
Knowing about common allergens is key to handling allergic contact dermatitis. Some substances are more likely to trigger allergic reactions. It’s important to know which ones to avoid.
Metals
Metals like nickel, cobalt, and chromium are common allergens. Nickel is often in jewelry and buckles. Cobalt is in medical gear and jewelry. Chromium is in leather and construction materials.
Reactions can be mild or severe. They can cause redness or even severe dermatitis.
Preservatives and Fragrances
Preservatives and fragrances in personal care products can also cause allergies. Preservatives like parabens and formaldehyde releasers keep products fresh. Fragrances make them smell good.
But, they can irritate sensitive skin. This can lead to skin irritation and dermatitis.
Rubber Accelerators
Rubber accelerators in rubber products can also cause allergic reactions. Thiurams and mercaptobenzothiazole make rubber last longer. But, they can irritate skin, mainly in people who wear rubber gloves a lot.
Topical Medications
Some topical medications can also be allergens. Neomycin and bacitracin are in antibiotic ointments. They can cause allergic reactions in some people.
This shows why it’s important to test even skin medications. It helps prevent allergic reactions.
By knowing about these allergens and their effects, we can manage and prevent allergic contact dermatitis. Avoiding these substances is key to keeping our skin healthy and preventing allergic reactions.
What to Do After Receiving Your Results
When you get your patch test results, it’s important to understand what they mean. Knowing how your results affect you is key to managing your allergy and avoiding future problems.
Understanding Clinical Relevance
Clinical relevance is about how allergens impact your daily life. We’ll help you understand your results. This means figuring out which products, environments, or materials cause your reactions.
Getting your results right is critical. For example, if you react to nickel, it’s not about avoiding all nickel products. It’s about finding common sources like jewelry or clothes and avoiding them.
Allergen Avoidance Strategies
Staying away from allergens is essential to avoid allergic reactions. Keep a record of your reactions and what causes them. This helps you spot patterns and make smart choices about your environment and products.
If you’re allergic to fragrances, choose fragrance-free options. For metal allergies, like nickel or cobalt, pick hypoallergenic jewelry or clothes.
Finding Allergen-Free Products
Finding products without allergens can be tough, but there are ways to help. Talk to your doctor or dermatologist for advice. Many groups also list safe products for people with allergies.
Here’s a table with common allergens and safe alternatives:
|
Allergen |
Common Sources |
Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
|
Nickel |
Jewelry, clothing buckles |
Hypoallergenic jewelry, nickel-free clothing |
|
Fragrances |
Perfumes, scented lotions |
Fragrance-free products |
|
Cobalt |
Jewelry, medical equipment |
Cobalt-free alternatives |
When Additional Testing Is Needed
Sometimes, your first test results might not fully explain your symptoms. Or, new symptoms might show up. In these cases, we might suggest more testing. This could be to check for other allergens or to look at old results again.
Conclusion
Patch testing is a key tool for finding out what causes allergic contact dermatitis. We’ve looked at how to do an allergy skin test on the back. It’s important to know how to read these tests to find out what allergens cause problems.
Following the steps in this article helps people understand patch testing better. It’s vital to do multiple tests to get accurate results. These are usually done at 48 and 96 hours, using a specific grading system.
Managing allergic contact dermatitis means knowing what to avoid. Patch testing helps find out what to steer clear of. We suggest using patch testing to help diagnose and treat this condition.
FAQ
What is an allergy skin patch test, and how is it performed?
An allergy skin patch test, also known as patch testing, is a way to find out what causes allergic skin reactions. It involves putting patches with possible allergens on your back.
What is the purpose of patch testing, and what does it detect?
Patch testing aims to find out what causes allergic reactions. It helps doctors treat and prevent these reactions. It finds the substances that cause allergic contact dermatitis.
How do I prepare for a patch test, and what instructions should I follow?
Before a patch test, you’ll get instructions. You should avoid certain medicines, like topical corticosteroids. You’ll also learn what to wear during the test.
What happens during the application process for back patch testing?
Small chambers with possible allergens are applied to your back. They are held in place with special tape to prevent them from falling off.
How should I care for the patch test area on my back, and what activities should I avoid?
Take care to avoid activities that might irritate the test area. This includes avoiding too much sweating or direct water. It’s also important to manage any discomfort or itching.
What is the patch test reading schedule, and why are multiple readings necessary?
The test is read twice, first at 48 hours and then at 96 hours. This is because some reactions take longer to show up.
How are patch test results interpreted using the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group grading system?
The grading system rates reactions from 0 (negative) to extreme positive. It helps doctors and researchers understand the results in the same way.
What are the characteristics of a positive patch test result, and how can I identify them?
A positive result shows as red, raised areas. These might swell, vesiculate, or even blister. The severity and pattern of the reaction can tell you about the allergy.
How can I distinguish between true allergic reactions and false results, such as irritant reactions or staining effects?
Irritant reactions can look like true allergies. Some substances, like PPD hair dye, can stain or cause other effects that might be mistaken for positive reactions.
What are some common allergens associated with allergic contact dermatitis, and what are their typical reactions?
Common allergens include metals like nickel and chromium. Also, preservatives and fragrances in personal care products can cause reactions. Rubber accelerators in rubber products can also trigger allergies.
What steps should I take after receiving my patch test results, and how can I manage my allergies?
After getting your results, understand what they mean. Avoid products with the allergens found. Look for hypoallergenic or allergen-free alternatives.
What is a positive patch test, and what does it indicate?
A positive patch test means you have an allergic reaction to something. The reaction shows as redness, swelling, and other skin symptoms.
What does it mean if an allergy patch test turns black, and is it related to the test result?
If the test turns black, it might be due to substances like PPD hair dye staining. This is not a true allergic reaction and can be distinguished from one.
References
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/24912-allergy-skin-test





