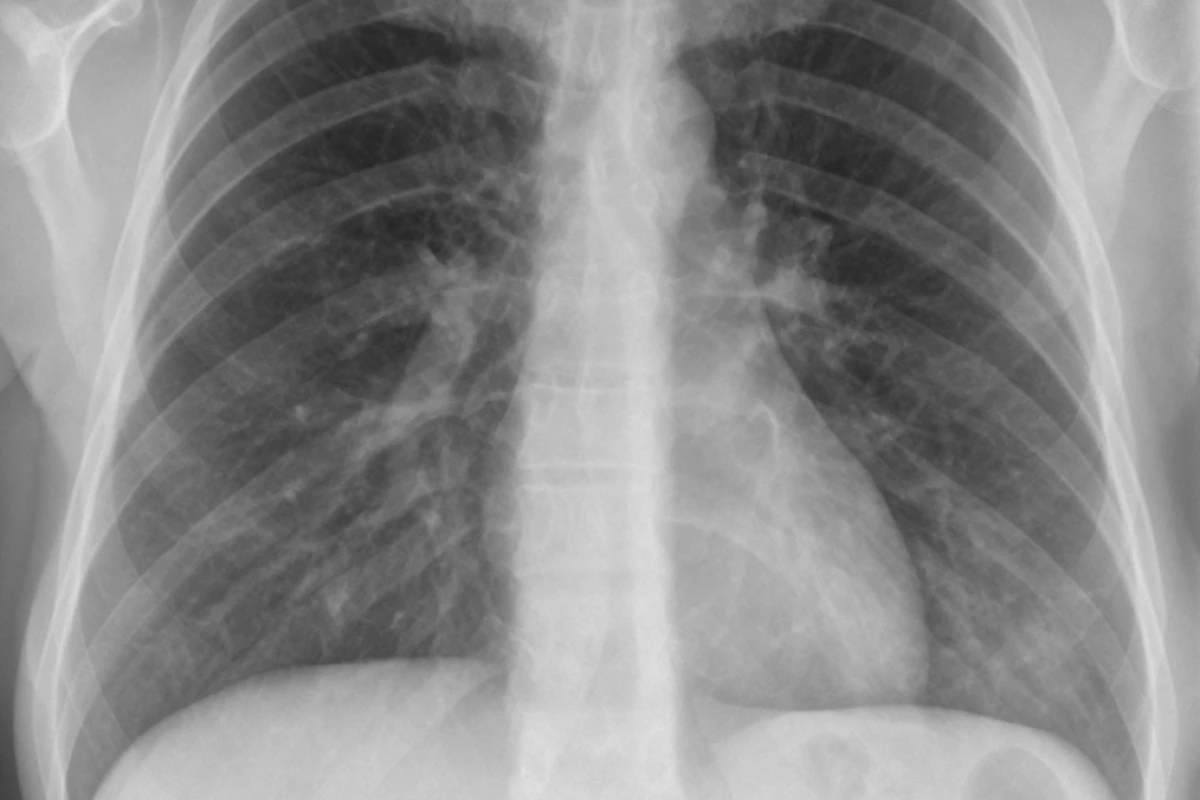
It’s important to know if a cold can develop into pneumonia. This knowledge helps protect your respiratory health. A common cold might seem mild, but it can turn serious.We explain the risk factors and specific conditions where can a cold turn into pneumonia as a secondary infection, especially in high-risk patients.
A viral infection can weaken your immune system. This makes it easier for pneumonia to develop. Spotting warning signs early and getting medical help quickly is key. It can prevent serious health issues.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the connection between a cold and pneumonia is critical for early intervention.
- A weakened immune system can lead to secondary infections like pneumonia.
- Early recognition of warning signs is vital for timely medical evaluation.
- Pneumonia can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- Seeking medical attention early can prevent serious complications.
Understanding the Common Cold and Pneumonia

It’s important to know the difference between a common cold and pneumonia. Both are infections of the respiratory system. But they have different causes and symptoms.
What Causes the Common Cold
The common cold is usually caused by viruses. Rhinoviruses are the most common. Other viruses like coronaviruses and adenoviruses can also cause cold symptoms. These viruses spread easily through the air, close contact, and surfaces.
When we get a cold, our body fights the virus. But sometimes, the virus can cause more problems, mainly for people who are more vulnerable.
What Causes Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by different things, like bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacteria causing pneumonia. Viral pneumonia can be caused by the same viruses that cause colds, and other viruses like influenza.
Pneumonia is a complex condition that needs proper diagnosis and treatment.
Key Differences Between Colds and Pneumonia
Colds and pneumonia both affect the respiratory system. But their symptoms and severity are different. A cold usually has mild symptoms like a runny nose, sneezing, and a sore throat. Pneumonia has more severe symptoms, like high fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Knowing the difference between a cold and pneumonia is important. Pneumonia can be serious, leading to complications, mainly in older adults, young children, and those with weakened immune systems.
Can a Cold Turn Into Pneumonia?
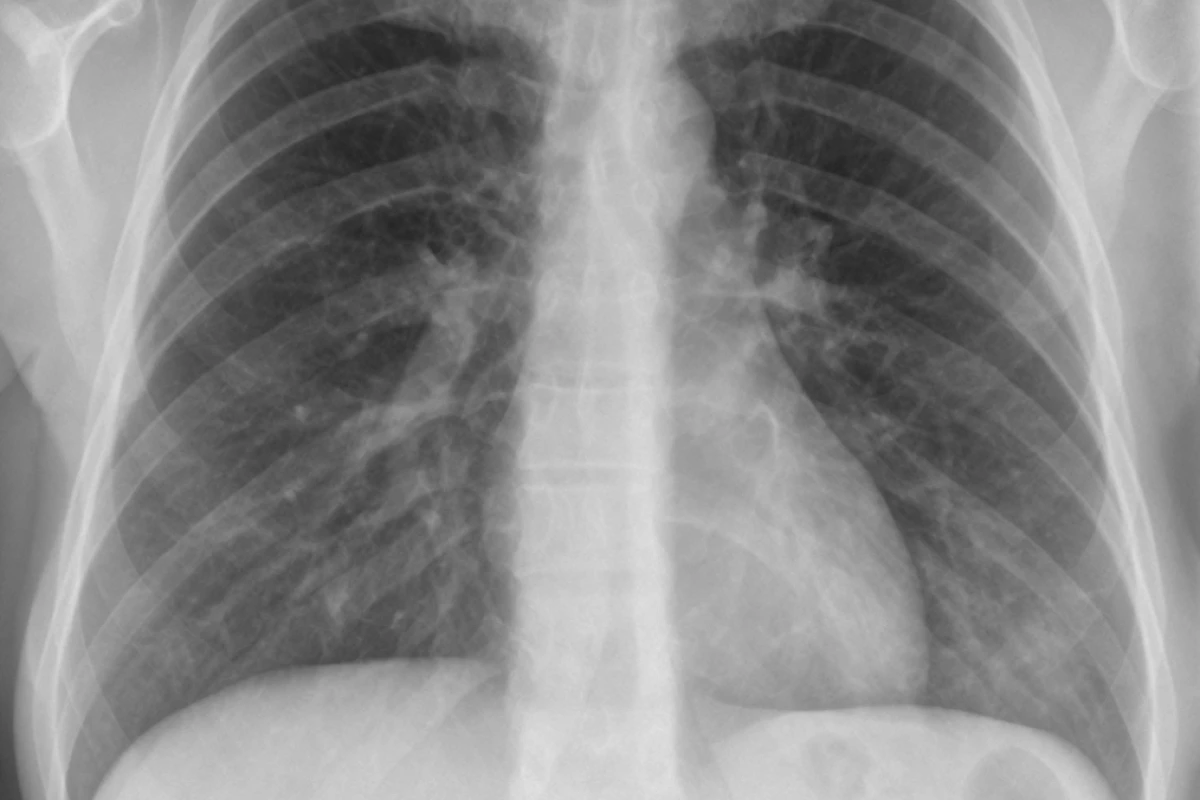
When we catch a cold, our immune system is tested. Sometimes, this can lead to more serious problems like pneumonia. The link between colds and pneumonia is complex, involving weakened immune defenses and secondary infections.
The Connection Between Colds and Pneumonia
A cold can turn into pneumonia if our immune system is weak. This happens when the initial virus weakens the lungs’ defenses, making them open to more infections.
Research shows that a cold-weakened immune system is more at risk for pneumonia. This is because the body is busy fighting the first infection. It can’t defend against new pathogens as well.
Superimposed Pneumonia Explained
Superimposed pneumonia is when a secondary infection hits after a cold. This happens when bacteria attack the lungs, taking advantage of the weakened state. It leads to a more serious infection that needs quick medical help.
Research on Cold-to-Pneumonia Progression
Studies show that turning from a cold to pneumonia is a big worry, mainly for the elderly and those with chronic conditions. Research stresses the need to watch symptoms and get medical help if they get worse or show signs of pneumonia.
Knowing the risks and factors of cold-to-pneumonia progression helps us take steps to prevent it. By recognizing warning signs and acting fast, we can lower the risk of complications and improve health outcomes.
How Respiratory Infections Progress
Respiratory infections start in the upper respiratory tract, like the nose and throat. They can then move to the lower respiratory tract, which includes the lungs.
From Upper to Lower Respiratory Tract
When an infection starts, it can spread to the lower respiratory tract. This includes the trachea, bronchi, and lungs. It can spread through direct invasion or by aspirating infected secretions.
The lower respiratory tract is usually free from harmful bacteria. But, if an infection from the upper tract reaches it, it can cause serious issues. This includes bronchitis or pneumonia.
The Role of the Immune System
The immune system is key in fighting off respiratory infections. When a pathogen enters, the immune system works to get rid of it.
A strong immune system can usually handle infections in the upper respiratory tract. But, if it’s weak or the pathogen is strong, the infection can move to the lower tract. This can lead to serious conditions like pneumonia.
It’s important to understand how the immune system works in respiratory infections. By keeping our immune system healthy, we can prevent infections from getting worse. This helps in preventing serious conditions.
Types of Pneumonia That Can Develop After a Cold
It’s important to know about the different pneumonias that can come after a cold. Each type has its own signs and treatments. Understanding these can help in getting better.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is caused by viruses like the flu and RSV. It shows symptoms like fever, cough, and body aches. Treatment includes antiviral meds and rest, along with staying hydrated and managing fever.
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is caused by bacteria, like Streptococcus pneumoniae. It often starts after a cold or flu, hitting those with weak immune systems hard. Symptoms include high fever, chills, and a productive cough. Antibiotics are key in treating it.
Atypical Pneumonia
Atypical pneumonia, or walking pneumonia, is caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It’s usually milder and can cause a persistent cough, headache, and fatigue. Antibiotics are often used, but it can also get better with rest and care.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia happens when food or liquids are inhaled into the lungs. This can occur during a cold, if swallowing is hard or if someone is unconscious. Symptoms include coughing, breathing trouble, and chest pain. Treatment focuses on the cause and antibiotics if needed.
The table below shows the main features of each pneumonia type that can follow a cold:
|
Type of Pneumonia |
Cause |
Symptoms |
Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Viral Pneumonia |
Viruses (e.g., influenza, RSV) |
Fever, cough, body aches |
Antiviral medications, supportive care |
|
Bacterial Pneumonia |
Bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae) |
High fever, chills, productive cough |
Antibiotics |
|
Atypical Pneumonia |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
Persistent cough, headache, fatigue |
Antibiotics, supportive care |
|
Aspiration Pneumonia |
Inhalation of foreign material |
Coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain |
Addressing underlying cause, antibiotics |
Risk Factors for Developing Pneumonia After a Cold
It’s important to know what increases the risk of getting pneumonia after a cold. Some groups are more likely to face this problem. Knowing these risks helps in preventing and treating it early.
Age-Related Risks
Age is a big factor in getting pneumonia after a cold. Young children and older adults are more at risk. This is because their immune systems are not fully developed or are weakening.
Children under 5, and even more so those under 2, are at high risk. Their immune systems are just starting to grow. Adults over 65 also face a higher risk. This is because their immune function naturally weakens with age.
Chronic Health Conditions
People with ongoing health issues are also more likely to get pneumonia after a cold. Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and chronic lung disease make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
|
Chronic Condition |
Increased Risk |
|---|---|
|
Heart Disease |
Higher risk due to possible heart failure and poor circulation |
|
Diabetes |
More likely to get infections because of high blood sugar |
|
Chronic Lung Disease |
Lung function is compromised, making it tough to fight off respiratory infections |
Compromised Immune Systems
Those with weakened immune systems are more likely to get pneumonia after a cold. This includes people with immunodeficiency diseases like HIV/AIDS, those undergoing chemotherapy, or taking immunosuppressive drugs.
These individuals need to watch their health closely during and after a cold. They should seek medical help right away if they notice any complications.
Environmental Factors That Increase Risk
Many environmental factors can raise the risk of getting pneumonia after a cold. Knowing these can help us protect ourselves better.
Cold Weather and Respiratory Infections
Cold weather often leads to more respiratory infections, like pneumonia. Low temperatures can weaken our immune system, making us more likely to get sick. Also, cold air dries out our nose and throat, making it harder to fight off germs.
Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
Good indoor air quality is key to our respiratory health. Poor air can trap harmful germs, raising the risk of infections. Keeping air clean with proper ventilation and filters can lower this risk. Also, staying away from pollutants like smoke and chemicals helps our lungs stay healthy.
Exposure to Pollutants and Irritants
Being around pollutants and irritants can also up our pneumonia risk. Air pollution, for example, can make breathing harder and weaken our lungs. Using air purifiers, avoiding polluted areas, and wearing masks can help. Also, keeping away from dust and mold is good for our breathing.
By knowing and tackling these environmental risks, we can lower our chance of getting pneumonia after a cold. This means watching the weather, keeping air clean indoors, and avoiding pollutants and irritants.
Recognizing When a Cold Might Be Developing Into Pneumonia
Understanding when a cold might turn into pneumonia is key. A cold can sometimes lead to pneumonia, a serious infection. We’ll look at the signs, how doctors diagnose it, and when to get help.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Some symptoms suggest a cold is turning into pneumonia. Look out for increased shortness of breath, chest pain, high fever, and a persistent cough with discolored mucus. If you notice these, watch them closely and get medical help if they get worse or if you feel really sick.
Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors use several ways to diagnose pneumonia. A chest X-ray shows lung inflammation. Blood tests help find the cause, like bacteria or viruses. Sometimes, a sputum test is done to check the mucus for infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help is important. If you have trouble breathing, chest pain, or a fever that doesn’t go away, get help right away. Also, if you’re at risk, like older adults or those with chronic conditions, see your doctor at the first sign of trouble.
Being aware of these signs and knowing when to get help can prevent serious complications. It ensures you get the right treatment on time.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Preventing and treating pneumonia need a full plan. We’ll look at ways to stop pneumonia when you have a cold. We’ll also talk about how to keep your immune system strong and the best treatments for different pneumonias.
Preventing Pneumonia During a Cold
To avoid pneumonia, follow some key steps. Good hygiene is key; wash your hands often, more so during cold and flu season. Also, getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal disease can help prevent pneumonia.
Living a healthy lifestyle is also important. Eat well, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Don’t smoke and avoid secondhand smoke, as it harms your lungs and raises your risk of infections.
Strengthening Your Immune System
A strong immune system fights off infections, like pneumonia. Nutritional support is essential; make sure you get enough vitamins and minerals, like vitamin C and D, and zinc. These boost your immune system.
Regular physical activity and stress management also help keep your immune system strong. Yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can lower stress, which weakens your immune system.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia varies by type and severity. Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics. Viral pneumonia may need antiviral medications. Sometimes, you might need to stay in the hospital, depending on how bad your symptoms are or if you’re at high risk.
|
Type of Pneumonia |
Treatment Approach |
Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
|
Bacterial Pneumonia |
Antibiotics |
Completing the full course of antibiotics is key |
|
Viral Pneumonia |
Antiviral medications, supportive care |
Rest, hydration, and watching your symptoms are important |
|
Atypical Pneumonia |
Antibiotics or antivirals depending on cause |
Getting the right diagnosis is vital for good treatment |
It’s also important to follow up with your healthcare provider. This ensures the infection is gone and helps with any lingering symptoms or worries.
Conclusion
It’s important to know how colds and pneumonia are connected. This knowledge helps us avoid serious health issues and get help when we need it. A cold can turn into pneumonia, which is more serious, for some people.
We can spot the signs of pneumonia early. This lets us act fast to prevent it. Keeping our immune system strong and avoiding harmful environments are good ways to fight off pneumonia after a cold.
In short, knowing about the link between colds and pneumonia is key to keeping our lungs healthy. By being proactive and informed, we can lower the chance of getting pneumonia. This is how we protect our health and get the right care if pneumonia does happen.
FAQ
Can a cold turn into pneumonia?
Yes, a cold can turn into pneumonia if your immune system is weak or if you have health issues.
What are the warning signs that a cold is developing into pneumonia?
Look out for a cough that won’t go away, trouble breathing, chest pain, fever, chills, and feeling really sick. If these symptoms get worse or don’t get better, see a doctor.
How can I prevent pneumonia when I have a cold?
To avoid pneumonia, wash your hands often, stay away from others, rest well, drink lots of water, and eat healthy foods. This helps keep your immune system strong.
Are some people more at risk of developing pneumonia after a cold?
Yes, some people are more at risk. This includes older adults, young kids, people with heart disease, diabetes, or lung problems, and those with weak immune systems.
Can a cold directly cause pneumonia?
A cold itself usually doesn’t cause pneumonia. But, it can make your immune system weaker. This makes it easier for other infections, like pneumonia, to start.
What types of pneumonia can develop after a cold?
After a cold, you might get viral pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, or aspiration pneumonia. Each has its own cause and treatment.
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, chest X-rays, and blood and sputum tests to diagnose pneumonia. These help figure out the cause and type.
What are the treatment options for pneumonia?
Treatment varies by pneumonia type and severity. Antibiotics treat bacterial pneumonia, while antiviral meds might be used for viral pneumonia. Rest, hydration, and oxygen therapy are also key.
Can pneumonia be treated at home?
Mild pneumonia might be treated at home with rest, fluids, and meds. But, severe cases need hospital care, including oxygen and IV antibiotics.
How can I strengthen my immune system to prevent pneumonia?
Keep your immune system strong by eating well, exercising, sleeping enough, not smoking, and managing stress. Getting flu and pneumococcal disease vaccines also helps prevent pneumonia.
Does cold weather increase the risk of pneumonia?
Cold weather might make respiratory problems worse and weaken your immune system. But, pneumonia is caused by pathogens, not cold weather itself.
Can indoor air quality affect the risk of developing pneumonia?
Yes, bad indoor air quality can irritate your respiratory system and increase infection risk, including pneumonia.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1500245