
Feeling chest pain when taking a deep breath can be scary and affect your daily life. At Liv Hospital, we know this symptom can come from many things. It could be something simple like inflammation in the chest wall or something serious like heart disease.Listing the common causes of discomfort when breathing deeply, from muscle strain to lung inflammation issues.
Chest pain when you breathe deeply can mean different health issues. These include costochondritis, injuries, heart problems, or lung infections. Knowing what’s causing it is key to finding the right treatment.
We value getting the right diagnosis and caring for our patients. Our team is committed to giving you the best care. We aim to address your concerns and create a treatment plan that works for you.
Key Takeaways
- Chest pain when taking a deep breath can result from various causes, including minor and serious conditions.
- Common causes include chest wall inflammation, trauma, and cardiovascular disease.
- Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered care with high-quality medical expertise.
- Understanding the cause of chest pain is key to effective treatment.
Causes of Discomfort When Breathing Deeply
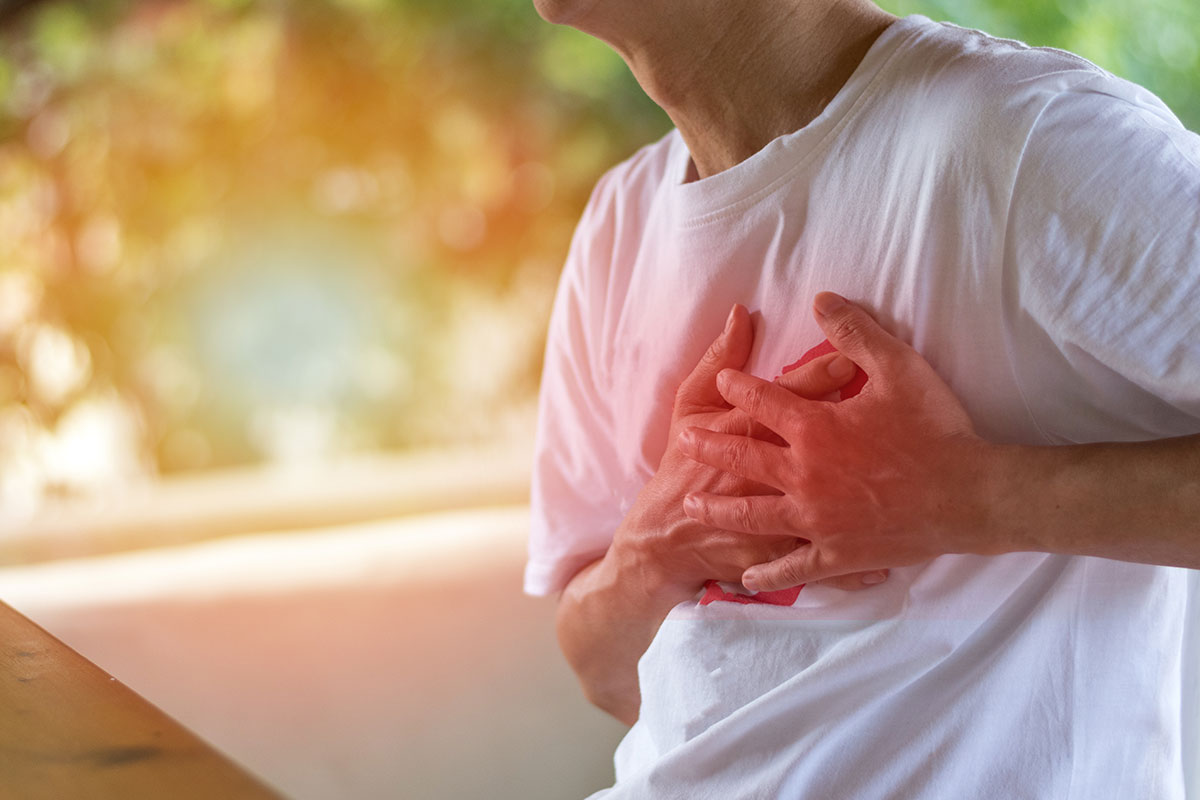

Chest tightness or pain when breathing deeply is a common issue. It can come from many causes, from mild to severe. When we take a deep breath, our chest expands. This can irritate or make worse conditions affecting the lungs, pleura, pericardium, or rib cartilage.
“The relationship between breathing and chest pain is complex, involving multiple anatomical structures,” as medical professionals often note. Knowing about the types of pain and how we breathe normally is key to finding the cause of discomfort.
Types of Pain During Inhalation
Pain during deep breathing can be different for everyone. Some feel sharp, stabbing pain, while others experience a dull ache or tightness in the chest. The type of pain can hint at its cause. For example, sharp pain that gets worse with deep breathing might point to pleurisy or costochondritis.
How Normal Breathing Works
Normal breathing uses many parts, like the diaphragm, rib cage, and lungs. When we inhale, the diaphragm goes down, and the rib cage opens up. This lets air fill the lungs easily and without pain. But, if there’s inflammation or damage, breathing can hurt.
Issues like pneumonia or pleurisy can make breathing painful. These conditions cause inflammation in the lungs or pleura. Knowing how these work helps doctors figure out why breathing deeply hurts.
Inflammatory Conditions of the Chest Wall
Inflammation in the chest wall can cause sharp pains that get worse with deep breaths. This discomfort is linked to certain inflammatory conditions affecting the chest’s structures.
Pleurisy and costochondritis are two common conditions causing chest pain when breathing deeply. Knowing about these can help find the cause of pain and get the right medical care.
Pleurisy: Inflammation of the Lung Lining
Pleurisy is when the pleura, the thin membrane around the lungs, gets inflamed. This can lead to sharp chest pain that gets worse with deep breathing or coughing. The pain from pleurisy is sharp and stabbing, often in one chest area.
Costochondritis: When Rib Cartilage Becomes Inflamed
Costochondritis is inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum. It causes pain along the sternum, getting worse with deep breathing or movement. The pain is usually in the area where the rib cartilage meets the sternum.
Both pleurisy and costochondritis can make daily activities hard because of deep breathing. It’s key to see a healthcare professional for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
Heart-Related Causes of Breathing Pain
The heart and lungs work together closely. Problems with the heart can cause pain when you breathe deeply. It’s important to get these issues checked out quickly.
Pericarditis: Inflammation Around the Heart
Pericarditis is when the membrane around the heart gets inflamed. This can make your chest hurt more when you breathe deeply or lie down. The pain feels sharp and stabbing, but it might feel better when you sit up and lean forward.
Symptoms of pericarditis include fever, tiredness, and coughing, along with chest pain. If you notice these signs, you should see a doctor right away.
Angina and Heart Attack Symptoms
Angina and heart attacks are serious and can cause chest pain. Angina happens when the heart doesn’t get enough blood, usually when you’re stressed or active. It gets better when you rest.
A heart attack happens when the heart doesn’t get enough blood for a long time. This can damage or kill heart muscle. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, and feeling very tired.
If you have severe chest pain or pressure that lasts, get emergency help right away.
Pulmonary Conditions That Cause Painful Breathing
Breathing is essential for life, but some lung issues can make it painful. Feeling pain when you take a deep breath might signal a serious problem. It’s important to get medical help if this happens.
Pulmonary Embolism: Blood Clots in the Lungs
A pulmonary embolism is a serious condition where a blood clot blocks a lung. It can cause sudden, severe chest pain that gets worse with deep breaths. If you have trouble breathing, a fast heart rate, or sharp chest pain, get help right away.
Pneumonia and Respiratory Infections
Pneumonia and other lung infections can cause lung inflammation, leading to breathing pain. These infections can be from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Symptoms include coughing, fever, and shortness of breath. Knowing the cause is key to the right treatment.
Lung Cancer and Breathing Pain
Lung cancer can also cause chest pain, often if the tumor affects the lung’s lining. The pain might feel like a dull ache or sharp stabbing that gets worse with deep breaths or coughing. Finding and treating lung cancer early is critical for better outcomes.
If you have ongoing or severe chest pain while breathing deeply, see a doctor. They can find out what’s causing it and help you get better.
Musculoskeletal Sources of Chest Pain
Chest pain can come from different musculoskeletal issues. This includes rib fractures and muscle strain. These problems can cause a lot of pain, making it worse when you breathe deeply or move.
Rib Fractures and Bruising
Rib fractures are a common reason for chest pain, often after an injury. When a rib breaks, it can hurt a lot, getting worse with deep breaths or coughing. Bruises around the ribcage can also cause discomfort, though it’s usually less severe than a fracture.
Many people feel pain when they breathe deeply because of rib fractures. Proper care and rest can help manage the pain. But, it’s important to see a doctor to check for other problems.
Intercostal Muscle Strain
Intercostal muscle strain happens when the muscles between the ribs get stretched or torn. This can be due to overuse, injury, or sudden twisting. The pain from this strain can be sharp and gets worse with movement or deep breathing.
Straining these muscles can cause chest pain that might seem like something more serious. But, with rest and physical therapy, the pain can get better.
Spinal Problems Affecting Breathing
Spinal issues, like herniated discs or spinal stenosis, can also cause chest pain. When the spine is affected, it can lead to pain that radiates to the chest, often due to compressed or irritated nerves.
In some cases, spinal problems can make pain worse with certain movements or deep breathing. It’s important to get these issues checked and treated properly.
Understanding the musculoskeletal causes of chest pain is key to managing and treating it. By figuring out the specific cause, whether it’s rib fractures, muscle strain, or spinal problems, we can provide the right care to ease the pain.
|
Condition |
Common Causes |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
|
Rib Fractures |
Trauma, injury |
Sharp pain with deep breathing, tenderness |
|
Intercostal Muscle Strain |
Overuse, injury, sudden twisting |
Sharp pain with movement, deep breathing |
|
Spinal Problems |
Herniated discs, spinal stenosis |
Pain radiating to the chest, worsening with movement |
Positional Pain: Why Breathing Hurts When Lying Down
The way we lie down can make chest pain worse. Some health issues get more painful in this position. It’s important to find out why to treat it right.
Cardiac vs. Respiratory Causes
Chest pain that gets worse when lying down can be from the heart or lungs. Pericarditis, which is inflammation around the heart, can make pain worse. Pleurisy, inflammation of the lung lining, can also cause more pain when lying down.
It’s key to know the difference to get the right treatment. Heart problems might include shortness of breath or irregular heartbeats. Lung issues might include coughing or trouble breathing deeply.
Recommended Sleeping Positions
Changing how you sleep can help with chest pain. If lying down hurts, trying different ways might help. Sleeping on your side with knees bent or slightly raised can ease pressure on the chest and heart.
- Elevated Position: Extra pillows can lift the upper body. This reduces pressure on the heart and lungs.
- Side Sleeping: A pillow between your knees can keep your spine straight and ease chest strain.
Knowing why chest pain gets worse when lying down is key to managing it. By figuring out if it’s heart or lung related, you can take steps to feel better.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Approaches
Chest pain can be really tough to deal with. But, there are many home remedies and self-care methods that can help. These methods can work together with medical treatment to ease your discomfort.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Options
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain meds can help with chest pain. Drugs like ibuprofen can reduce inflammation and ease pain. But, always check the dosage and talk to a doctor first, if you have health issues or take other meds.
Common OTC Pain Relief Options:
|
Medication |
Dosage |
Precautions |
|---|---|---|
|
Ibuprofen |
200-400 mg every 4-6 hours |
Avoid if allergic to NSAIDs or have kidney issues |
|
Acetaminophen |
325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours |
Do not exceed 3000 mg in 24 hours; caution with liver disease |
Breathing Exercises and Techniques
Breathing exercises can help reduce stress and ease chest pain. Diaphragmatic breathing, or belly breathing, is very effective. It involves breathing deeply into your lungs, letting your belly rise.
Steps for Diaphragmatic Breathing:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent, or sit comfortably.
- Place one hand on your belly and the other on your chest.
- Inhale slowly through your nose, letting your belly rise while your chest stays steady.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth, letting your belly fall.
- Repeat for several minutes, focusing on your belly rising and falling.
By adding these home remedies and self-care methods to your daily routine, you can manage chest pain better. But, always watch for worsening symptoms or red flags and seek medical help if needed.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
Knowing when to go to the emergency room is key for your health. Some symptoms mean you need help right away to avoid serious problems.
Red Flag Symptoms That Require Immediate Care
Some symptoms are red flags because they might mean serious health issues. These include:
- Severe chest pain or pressure that doesn’t go away
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus
- Severe headache or sudden confusion
- Loss of consciousness or fainting
If you or someone else has these symptoms, call emergency services or go to the nearest ER right away.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
When you get to the emergency room, doctors will quickly check you out. They will:
- Ask about your symptoms and medical history
- Do a physical exam
- Run tests (like ECG, blood tests, and imaging)
- Start treatment to make you stable
Being ready with your symptoms and medical history helps doctors diagnose you faster and more accurately.
Quick medical help can greatly improve your chances of getting better in emergencies.
Going to the emergency room can be scary. But knowing what to expect and when to go can really help your care.
Conclusion: Managing and Preventing Painful Breathing
To manage and prevent painful breathing, it’s key to know the causes and take action. By tackling the root issues and using self-care, people can cut down on painful breathing.
Dealing with chest pain when breathing deeply needs a full plan. Knowing the causes, like inflammation, heart problems, or muscle issues, helps. This knowledge lets people take steps to avoid painful breathing.
To stop painful breathing, adopt healthy habits and watch your body position, like when sleeping. Good sleeping positions and breathing exercises can ease pain. If your heart hurts when you breathe in, get medical help to check for serious issues.
Being proactive in managing and preventing painful breathing can reduce chest pain. This mix of self-care, awareness, and sometimes medical help is essential.
FAQ
Why does it hurt when I take a deep breath?
Taking a deep breath can hurt for many reasons. It might be because of inflammation, infection, or trauma to the chest, lungs, or heart. Knowing the cause is key to finding the right solution.
What are the common causes of chest pain when breathing deeply?
Chest pain when breathing deeply can come from several sources. It might be due to inflammation, heart problems, or lung issues. These include pleurisy, costochondritis, pericarditis, angina, heart attacks, pulmonary embolism, pneumonia, and lung cancer.
What is pleurisy and how does it cause chest pain?
Pleurisy is when the pleura gets inflamed. This leads to sharp pains that get worse with each breath. It can be very uncomfortable and might be linked to an infection or other issues.
Can musculoskeletal issues cause chest pain when breathing?
Yes, musculoskeletal problems can cause chest pain. This includes rib fractures, intercostal muscle strain, and spinal issues. These can be due to trauma, overuse, or spinal problems.
Why does breathing hurt when lying down?
Breathing can hurt when lying down because of heart and lung problems. The position can make some conditions worse. It’s important to know the cause to find the right solution.
What are some home remedies for managing chest pain?
Home remedies for chest pain include over-the-counter pain relief and breathing exercises. These can help, but it’s important to know when to seek medical help.
When should I seek emergency medical attention for chest pain?
Seek emergency help if you have severe chest pain, trouble breathing, or other serious symptoms. Recognizing these signs quickly is very important.
Does Advil help with chest pain?
Advil and other over-the-counter pain meds might help with some chest pain. But, it’s vital to know the cause and talk to a doctor for the right treatment.
What can cause chest pain and shortness of breath?
Chest pain and shortness of breath can be caused by many things. This includes heart problems, lung issues, and musculoskeletal problems. Knowing the cause is key to finding the right solution.
How can I prevent painful breathing?
To prevent painful breathing, understand the causes and take steps to prevent them. By being proactive, you can reduce chest pain from deep breathing.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448150/










