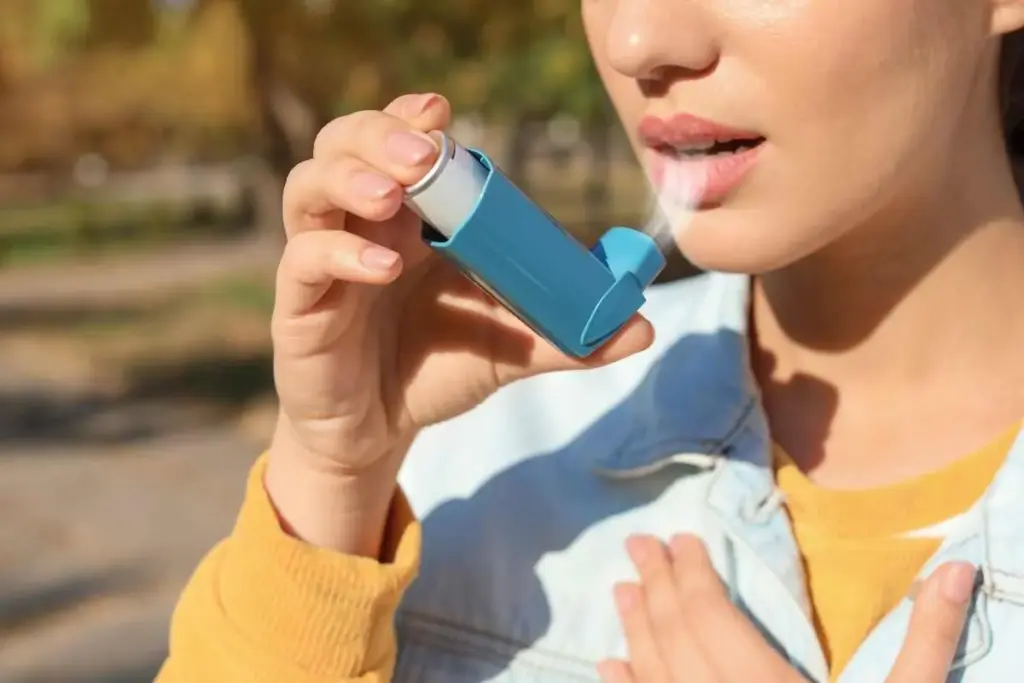
For those with asthma or COPD, breathing can be tough every day. Bronchodilators are key in helping relax airway muscles, making breathing easier. At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch respiratory care and offer proven treatments.
Bronchodilators target the main cause of airway blockage. They give quick relief and help control symptoms over time. We’ll look at the different types of bronchodilators and how they work, showing their role in managing breathing issues.
Key Takeaways
- Bronchodilators relax airway smooth muscle, improving breathing for asthma and COPD patients.
- These medications offer immediate relief and long-term symptom control.
- Different classes of bronchodilators target specific aspects of airway obstruction.
- Effective respiratory care is key for managing chronic conditions.
- Liv Hospital provides trusted, evidence-based treatment options for international patients.
Understanding Bronchodilators and Airway Function
To understand how bronchodilators work, we first need to grasp their role in airway function and overall respiratory health. Bronchodilators are medications that help open up the airways, making breathing easier. They are key in managing respiratory conditions like asthma and COPD.
What Are Bronchodilators?
Bronchodilators relax the muscles around the airways, causing them to widen. This widening improves airflow to the lungs, helping patients with respiratory conditions breathe better. They are usually given through inhalers or nebulizers, which send the medication straight to the lungs.
The use of bronchodilators is a cornerstone in managing obstructive airway diseases. By understanding what bronchodilators are and how they work, patients can better manage their respiratory health.
Bronchodilation vs. Bronchoconstriction
The terms bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction refer to the opposite processes in the airways. Bronchodilation widens the airways, improving airflow and making breathing easier. On the other hand, bronchoconstriction narrows the airways, leading to difficulty breathing and is often associated with respiratory conditions like asthma.
Understanding the difference between bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction is key to seeing how bronchodilators work. Bronchodilators counteract bronchoconstriction by relaxing the airway muscles, improving airflow.
Common Conditions Requiring Bronchodilator Therapy
Bronchodilators are used to treat various respiratory conditions, mainly those with airway obstruction. The most common conditions requiring bronchodilator therapy include:
- Asthma: A chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes recurring episodes of wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A progressive lung disease that makes it difficult to breathe. COPD includes conditions like emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
- Chronic Bronchitis: A type of COPD characterized by chronic inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
By understanding what bronchodilators are used for, it’s clear they play a vital role in managing these conditions. Bronchodilators help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with these respiratory diseases.
How Do Bronchodilators Work: Mechanism of Action
Bronchodilators help manage breathing problems by relaxing airway muscles. They do this through different ways. These medicines are key in treating asthma and COPD. Let’s see how they work.
Beta-2 Agonists: Primary Bronchodilators
Beta-2 agonists are the main bronchodilators used today. They act on beta-2 receptors on airway muscles. This action increases cAMP, leading to muscle relaxation and wider airways. They work fast, making them great for sudden breathing tightness.
A study in the
Journal of Respiratory Medicine
shows their vital role in treating breathing issues.
Anticholinergic Agents
Anticholinergic agents work differently by blocking cholinergic nerves. This stops the airways from tightening. They’re good for those who can’t use beta-2 agonists.
Methylxanthines
Methylxanthines are another type of bronchodilator. They stop phosphodiesterase enzymes from breaking down cAMP. This keeps airway muscles relaxed. They also have anti-inflammatory effects.
Here’s a comparison of bronchodilator classes:
| Bronchodilator Class | Mechanism of Action | Primary Use |
| Beta-2 Agonists | Activate beta-2 receptors, increasing cAMP | Relieving acute bronchospasm |
| Anticholinergic Agents | Block cholinergic nerve effects | Alternative for beta-2 agonist intolerance |
| Methylxanthines | Inhibit phosphodiesterase enzymes | Sustained bronchodilation and anti-inflammatory effects |
Knowing how these bronchodilators work is key to better treatment. Tailoring treatment to each patient’s needs can greatly improve their health.
Types and Clinical Applications of Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators are divided into short-acting and long-acting types. They help manage diseases like COPD and asthma. These medicines relax airway muscles, making breathing easier.
Short-acting bronchodilators, like albuterol, offer quick relief. Long-acting ones, such as salmeterol and formoterol, control symptoms over time. Each type has its own uses and benefits.
Short-Acting Bronchodilators
Short-acting bronchodilators work fast to ease breathing. They are used when symptoms suddenly get worse. They quickly relax airway muscles, helping with wheezing and shortness of breath.
“Short-acting bronchodilators are key for quick relief in asthma and COPD,” say doctors. They are perfect for emergency situations because they act fast.
Long-Acting Bronchodilators
Long-acting bronchodilators, such as salmeterol and formoterol, control symptoms for longer. They reduce how often symptoms get worse and improve life quality for those with chronic respiratory diseases.
We often give long-acting bronchodilators with other medicines for better symptom control. Their long-lasting effect keeps airways open, making breathing easier for patients.
Potential Adverse Effects and Contraindications
While bronchodilators are mostly safe, they can have side effects. Common issues include tachycardia and hypokalemia. It’s important to watch for these, mainly when starting treatment or changing doses.
Who can’t take bronchodilators varies by drug and patient health. Some can’t take them if they’re allergic to the drug. Always check a patient’s history before starting treatment.
A study shows, “choosing the right patient and monitoring them closely are vital to avoid risks with bronchodilators.” This stresses the need for tailored treatment plans for respiratory conditions.
Conclusion: Benefits and Future Directions in Bronchodilator Therapy
Bronchodilators have changed how we treat asthma and COPD. They relax the muscles around airways, making it easier to breathe. The benefits of bronchodilators are clear. They offer quick relief and long-term symptom control, greatly improving patients’ lives.
Research is moving forward, aiming to create better bronchodilators. New medications and ways to deliver them are being explored. These advancements could lead to even better results for patients.
Healthcare providers can improve treatment plans by knowing the strengths and weaknesses of bronchodilators. Looking ahead, new bronchodilators will be key in managing respiratory diseases. They promise to bring more effective treatments to those in need.
FAQ
What are bronchodilators?
Bronchodilators are medications that relax the smooth muscles around the airways, widening them to improve airflow and ease breathing.
What is the difference between bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction?
Bronchodilation is the widening of the airways, while bronchoconstriction is the narrowing of airways due to muscle contraction, making breathing difficult.
What are bronchodilators used for?
They are used to treat respiratory conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchitis to relieve wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
How do beta-2 agonists work as bronchodilators?
Beta-2 agonists stimulate beta-2 adrenergic receptors in airway smooth muscles, causing relaxation and airway dilation.
What is the mechanism of action of anticholinergic agents as bronchodilators?
Anticholinergics block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, preventing parasympathetic-induced bronchoconstriction and allowing airways to relax.
What is the role of short-acting bronchodilators in respiratory care?
Short-acting bronchodilators (SABAs) provide rapid relief from acute asthma or COPD symptoms and are used as “rescue” inhalers.
How do long-acting bronchodilators differ from short-acting bronchodilators?
Long-acting bronchodilators (LABAs) provide prolonged airway relaxation, usually for maintenance therapy, whereas short-acting bronchodilators act quickly but briefly.
What are the possible side effects of bronchodilators?
Common side effects include tremors, rapid heart rate, palpitations, headache, nervousness, dry mouth, and throat irritation.
Are there any contraindications for using bronchodilators?
Contraindications include hypersensitivity to the drug, severe heart disease, certain arrhythmias, uncontrolled hypertension, and in some cases, hyperthyroidism.
Is bronchodilation sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Bronchodilation is primarily sympathetic, mediated by beta-2 adrenergic receptor activation.
How do methylxanthines work as bronchodilators?
Methylxanthines (like theophylline) relax airway smooth muscles, reduce inflammation, and inhibit phosphodiesterase enzymes, leading to increased cAMP and bronchodilation.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26432616/