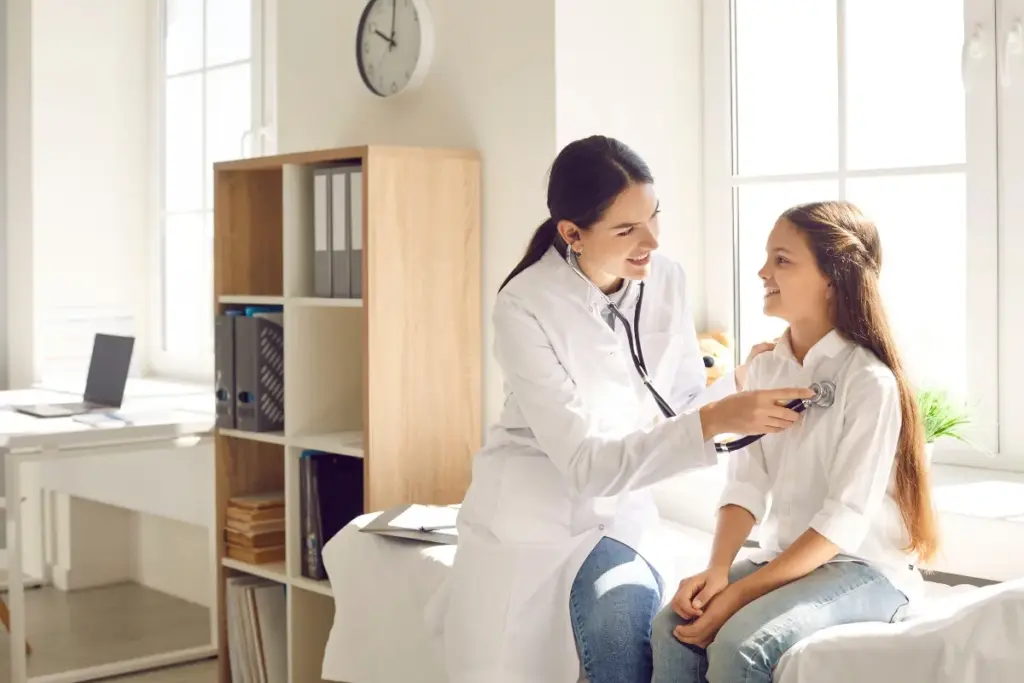
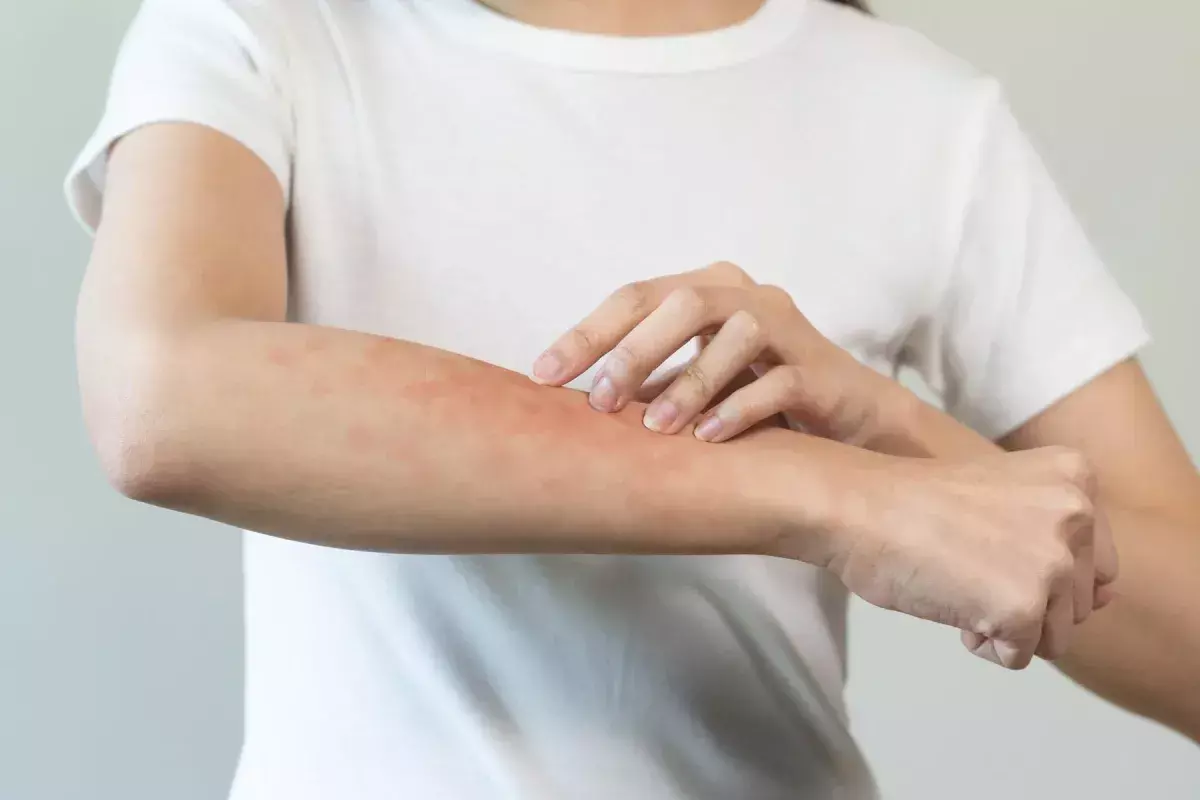
Hives, also known as urticaria, are itchy, raised bumps on the skin. They can show up anywhere on the body. About 20 percent of people will get hives at some time.
These welts happen when histamine is released, causing a histamine rash. Knowing what causes hives is key to finding relief and curing hives.
At Liv Hospital, we offer trusted advice and care. We help you find what triggers hives and offer proven medical solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Hives are itchy, raised bumps that can appear anywhere on the body.
- They affect approximately 20 percent of people at some point in their lives.
- The release of histamine is a primary cause of hives.
- Understanding the causes of hives is critical for finding relief.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered care to help identify triggers and find relief.
Understanding Hives (Urticaria)

Hives, or urticaria, are a common skin condition that can cause significant discomfort and distress. We will explore what hives are, how common they are, and their characteristic symptoms.
What Are Hives and How Common Are They?
Hives are itchy, raised bumps that appear on the skin, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. They can occur anywhere on the body and are known for their ability to change shape, disappear, and reappear. Urticaria affects a significant portion of the population at some point in their lives.
Studies suggest that acute urticaria is more common than chronic urticaria, with the former often being triggered by allergic reactions or infections. Understanding the prevalence and causes of hives is essential for effective management.
| Prevalence | Description |
| Acute Urticaria | More common, often triggered by allergic reactions or infections. |
| Chronic Urticaria | Less common, lasting more than six weeks, often with unknown causes. |
Recognizing Hive Symptoms and Appearance
The symptoms of hives include raised, itchy bumps that can vary in color, often appearing red or white. These bumps can merge to form larger areas, known as plaques. The itchiness associated with hives can range from mild to severe.
Hives can appear anywhere on the body and may change in shape and size over time. They are not contagious and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, if they are part of an allergic reaction.
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the appearance of hives is key for diagnosis and treatment. If you experience persistent or severe hives, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and care.
How Can a Person Get Hives: Common Triggers

Knowing what causes hives is key to managing them. Hives, or urticaria, can come from many sources. It’s important to find out what triggers them to ease symptoms and stop them from coming back.
Food and Medication Triggers
Some foods and medicines can lead to hives. Food allergies are a big reason, with common culprits being nuts, shellfish, eggs, and dairy. Eating these foods can cause an allergic reaction, leading to hives.
- Nuts and seeds
- Shellfish and fish
- Eggs and dairy products
- Certain fruits and vegetables
Medications can also cause hives. NSAIDs like ibuprofen and aspirin can trigger hives in some. Antibiotics, such as penicillin, can also cause allergic reactions.
Environmental and Physical Triggers
Environmental factors can also trigger hives. Temperature extremes, whether hot or cold, can cause hives in some people. Being in the sun or cold can also lead to hives.
Physical triggers include skin pressure, vibrations, and water. Some people get hives from physical urticaria, where hives are caused by a physical stimulus.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress is a known hives trigger. Emotional stress can release histamine and other chemicals, causing blood vessels to leak and leading to hives. Reducing stress through relaxation and stress management can help.
By knowing these triggers, people can avoid or manage them. This can help reduce the number of hives they get.
Types of Hives and Their Characteristics
Hives can show up in different ways, from short-term to long-lasting. They can appear anywhere on the body. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Acute vs. Chronic Urticaria
Acute urticaria means hives that last less than six weeks. On the other hand, chronic urticaria lasts more than six weeks. This longer form often needs a more detailed treatment plan.
For more details on hives, check out Allergy & Asthma Network. They offer a deep dive into urticaria.
Location-Specific Hives
Hives can pop up in many places, like the face, groin, feet, and knees. Each spot has its own set of problems. For example, face hives can be upsetting because they’re visible. Hives in the groin can be itchy and uncomfortable.
| Location | Characteristics | Common Concerns |
| Face | Visible, often causing swelling around the eyes and lips | Aesthetic concerns, severe swelling risk |
| Groin Area | Can be itchy and uncomfortable, irritated by clothes | Discomfort, infection risk from scratching |
| Feet (Sole or Bottom) | Can be painful, hurts when walking or standing | Mobility issues, pain |
| Knees | May be itchy or painful, affects mobility | Discomfort, daily activity impact |
Knowing the specific traits and challenges of hives in different spots helps us tailor treatments. This way, we meet each patient’s unique needs.
Effective Treatments and Prevention Strategies
To ease the discomfort of hives, knowing the treatment options is key. Hives, or urticaria, can be managed with medical treatments and self-care.
Medical Treatments for Hives
Medical treatments aim to relieve symptoms and find the cause. Antihistamines are often the first choice, as they help reduce itching and hives. For severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to lessen inflammation.
For chronic or severe hives, other treatments like immunosuppressants or biologics might be needed. Always talk to a healthcare professional to find the best treatment.
| Medication Type | Use | Benefits |
| Antihistamines | Relieve itching and reduce hives | Fast relief, available over-the-counter |
| Corticosteroids | Reduce inflammation | Effective for severe cases, reduces swelling |
| Immunosuppressants | Treat chronic hives | Can be effective for long-term management |
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Home remedies can also help with hives. A cool compress can ease itching and swelling. Oatmeal baths are also soothing.
Avoiding triggers and good skin care can prevent hives. Keeping a diary to track hives can help find what triggers them.
- Avoid tight clothing that can irritate the skin
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps and moisturizers
- Stay cool to reduce sweating and irritation
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many hives cases can be managed at home, some need medical help. If you have trouble breathing, a fast heartbeat, or dizziness, go to the emergency room. Also, if hives don’t get better with treatment, see a doctor.
Knowing when to seek help is important for managing hives and avoiding complications.
Conclusion:
Understanding hives and their causes is key to managing them well. Knowing what triggers hives helps prevent outbreaks. It also helps find the right medical care when needed.
There are many ways to treat hives, from medical treatments to home remedies. A mix of these can help ease symptoms. It’s important to avoid triggers, take prescribed meds, and make lifestyle changes to control outbreaks.
Living with hives can be tough, but it’s not impossible. With the right information and support, people can live full lives. We suggest talking to doctors to create a personal plan. This way, they can get the care and support they need to do well.
FAQ:
What are hives, and how common are they?
Hives are raised, itchy welts on the skin that affect roughly 20% of people at some point in their lives.
What causes hives to appear on the skin?
Hives occur when the body releases histamine in response to triggers like infections, allergies, or physical stimuli, causing blood plasma to leak from small vessels.
Can certain foods trigger hives?
Yes, common food triggers include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, eggs, and certain fruits, as well as food additives like dyes and preservatives.
Are hives a sign of a serious underlying condition?
While usually harmless, chronic hives (lasting over 6 weeks) can sometimes be a sign of underlying issues like thyroid disease, lupus, or other autoimmune conditions.
How can I treat hives at home?
You can manage hives at home with over-the-counter antihistamines, cool compresses, and soothing baths using colloidal oatmeal or baking soda.
When should I seek medical attention for hives?
Seek emergency care immediately if hives are accompanied by difficulty breathing, swelling of the tongue or throat, dizziness, or a feeling of faintness.
Can stress cause hives to appear?
Yes, emotional stress can trigger the release of chemicals like acetylcholine and histamine, which can cause “stress hives” or worsen an existing outbreak.
Can hives be white, or are they always red?
Hives are typically red or pink on light skin but can also appear as skin-colored or white “wheals,” and may look gray or purple on darker skin tones.
What is the difference between acute and chronic urticaria?
Acute urticaria lasts for less than six weeks and is often tied to a specific trigger, while chronic urticaria persists for six weeks or longer and is frequently idiopathic (unknown cause).
Can hives occur on specific areas of the body, like the face or feet?
Hives can appear anywhere on the body, including the face and feet, and are sometimes accompanied by angioedema, which is deeper swelling often found around the eyes and lips.
References:
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia