Knowing if asthma is an obstructive or restrictive lung disease is key for the right treatment. Asthma causes airway inflammation and makes breathing hard, but it can get better. This is different from restrictive lung diseases.
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tests and have top pulmonologists. They use pulmonary function tests (PFTs), like spirometry, to tell disease types apart.
Knowing the difference between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases helps us give better care. Asthma narrows airways, making it tough to breathe out.
Key Takeaways
- Asthma is classified as an obstructive lung disease due to airway inflammation and narrowing.
- Obstructive lung diseases, like asthma, make it harder to exhale.
- Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are key in diagnosing and differentiating lung diseases.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced diagnostic capabilities and expert pulmonologists.
- Understanding lung disease types is essential for effective treatment.
Understanding Lung Disease Classifications

It’s important to know about lung disease types to treat them well. Lung diseases are mainly divided into obstructive and restrictive types. Each type has its own signs and needs for care.
Difficulty Exhaling: Obstructive Lung Diseases
Obstructive lung diseases make it hard to breathe out. Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) are common examples. In asthma, airways get inflamed and clogged with mucus, making it hard to breathe out.
These diseases can really affect your life. They need careful management. For more on asthma, check out Healthline’s article.
Limited Lung Expansion: Restrictive Lung Diseases
Restrictive lung diseases make it hard for lungs to fully expand. This includes conditions like pulmonary fibrosis and obesity-related lung disease. These diseases limit lung growth, making deep breathing hard.
Managing restrictive lung diseases is different from obstructive ones. Knowing the exact disease is key to a good treatment plan.
Is Asthma an Obstructive or Restrictive Disease?
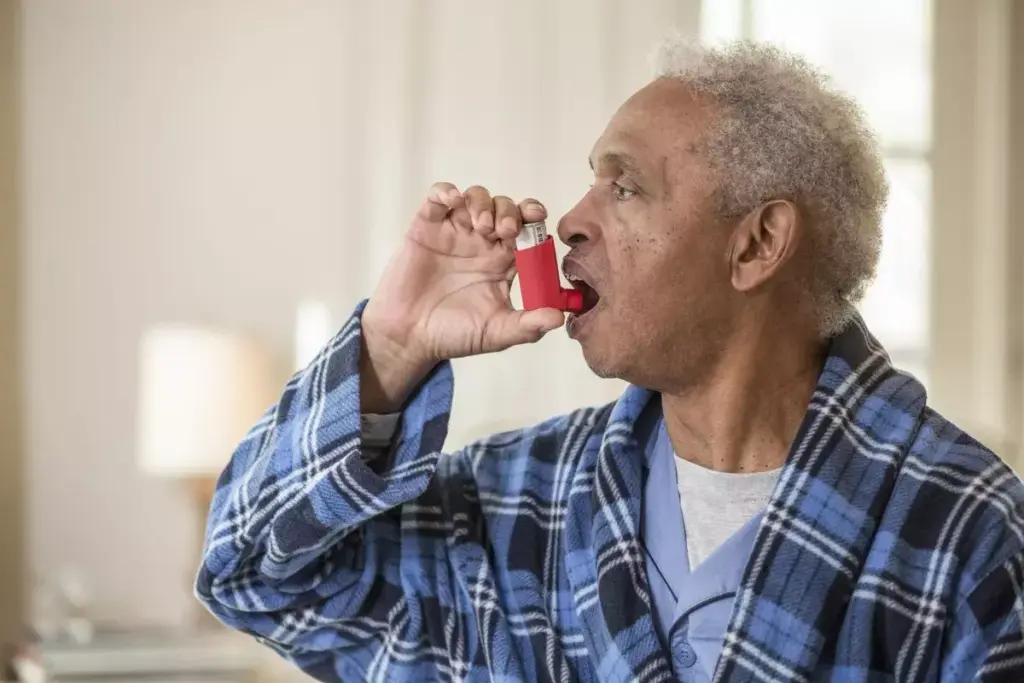

Understanding if asthma is obstructive or restrictive is key to treating it. Asthma is an obstructive lung disease. It’s caused by inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness, and reversible airflow obstruction.
Mechanism of Airway Obstruction in Asthma
Asthma blocks airways in several ways. First, inflammation of the airway walls causes swelling and more mucus. This makes airways more sensitive and reactive.
Second, bronchoconstriction tightens airway muscles, narrowing passages. This constriction is often triggered by allergens or irritants.
Asthma Attacks: Inflammation, Mucus, and Bronchoconstriction
During an asthma attack, inflammation, mucus, and bronchoconstriction block airways. This leads to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
The severity of asthma attacks varies. Understanding these mechanisms is key to managing them. Treatments aim to reduce inflammation, relieve bronchoconstriction, and improve airflow.
| Characteristics | Obstructive Lung Disease (Asthma) | Restrictive Lung Disease |
| Primary Feature | Airflow obstruction | Limited lung expansion |
| Common Symptoms | Wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath | Shortness of breath, difficulty taking deep breaths |
| Causes | Inflammation, bronchoconstriction, mucus production | Inflammation, fibrosis, muscle weakness |
Diagnosing and Differentiating Lung Disease Types
It’s key to know the difference between lung diseases to treat them right. Lung diseases fall into two main groups: obstructive and restrictive. Doctors use special tools to figure out which one a patient has.
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) Explained
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) check how well the lungs work. PFTs help tell apart obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. Spirometry is a common PFT that looks at how much and fast air moves in and out.
It checks things like Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC). The FEV1 to FVC ratio is key for spotting obstructive diseases like asthma.
“Pulmonary function tests give us important info on lung health,” says a top pulmonologist. They help doctors figure out if a lung disease is obstructive or restrictive. For example, a low FEV1/FVC ratio points to obstructive diseases. But a normal or high ratio with low FVC means it’s restrictive.
Other Common Lung Conditions
Asthma is just one of many obstructive lung diseases. COPD and emphysema are others. COPD comes from long-term exposure to harmful substances. Emphysema damages the alveoli, making it hard to breathe out.
Restrictive lung diseases, like pulmonary fibrosis and obesity, are different. Obesity-related restrictive lung disease is a big health problem. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors give better care.
In short, figuring out lung disease types needs a detailed approach, including PFTs. Knowing the exact lung disease helps doctors create better treatment plans for patients.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the difference between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. This knowledge helps in making the right diagnosis and treatment. We’ve looked into how asthma is classified as an obstructive lung disease and its differences with other conditions.
Asthma is an obstructive lung disease because it causes reversible airflow blockage. Spirometry tests are key in diagnosing lung issues and managing patient care. For more details on asthma and its diagnosis, check out Liv Hospital’s insightful article.
Healthcare providers can give better care by understanding asthma and other lung diseases. They can offer treatments that really help patients. Knowing how obstructive lung diseases work is essential for effective management.
FAQ:
Is asthma classified as an obstructive or restrictive lung disease?
Asthma is classified as an obstructive lung disease because it narrows the airways and limits airflow.
What is the difference between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases?
Obstructive diseases block airflow out of the lungs, while restrictive diseases reduce lung expansion and volume.
How do pulmonary function tests (PFTs) help diagnose lung conditions?
PFTs measure lung volume, airflow, and gas exchange to identify obstructive or restrictive patterns.
Is COPD obstructive or restrictive?
COPD is an obstructive lung disease, causing chronic airflow limitation.
Can obesity cause restrictive lung disease?
Yes, obesity can restrict lung expansion, leading to a restrictive pattern in breathing.
Is emphysema an obstructive or restrictive lung disease?
Emphysema is obstructive, as it damages alveoli and reduces airflow out of the lungs.
How do asthma attacks occur?
Asthma attacks occur when airway inflammation, mucus, and bronchospasm combine to block airflow.
What is the role of spirometry in diagnosing lung conditions?
Spirometry measures airflow and lung capacity to detect and monitor obstructive or restrictive lung disease.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7126962/