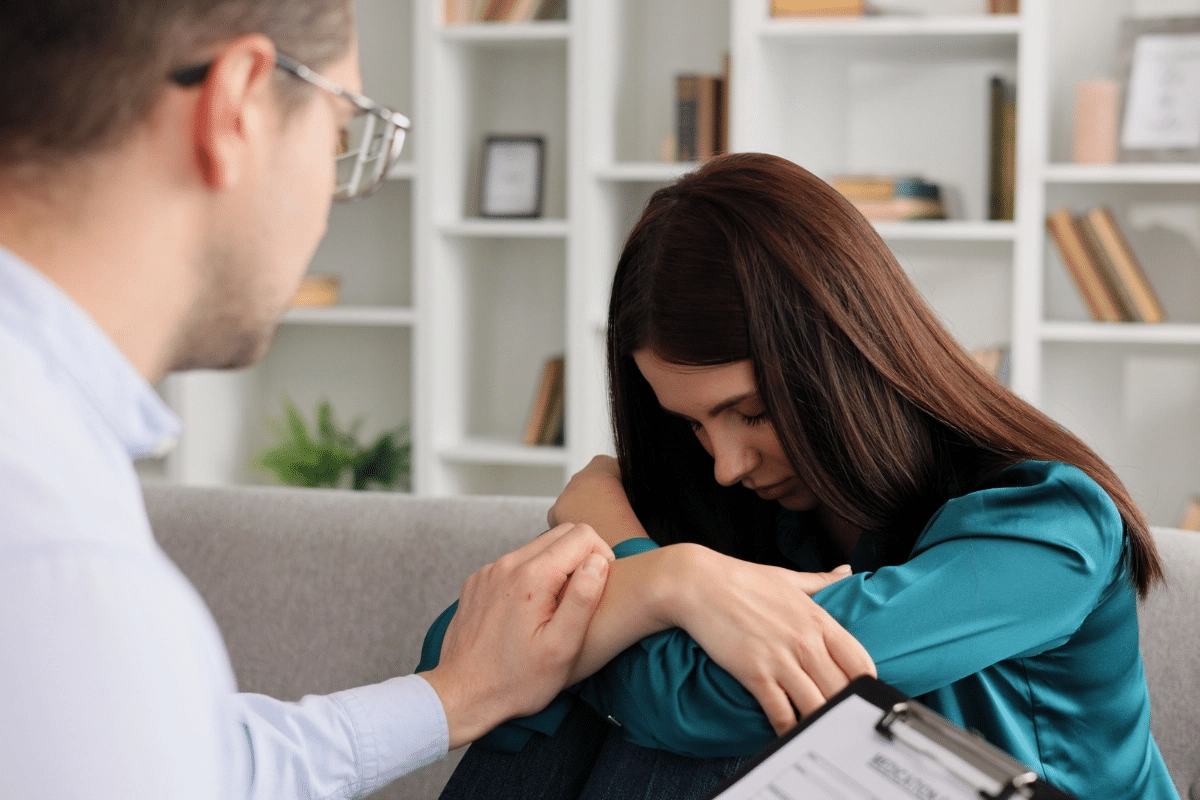
At Liv Hospital, we understand the link between mental health conditions and disability benefits. About one quarter of Social Security Disability Insurance applicants say mental health illnesses are their main issue.is mental health a disabilityIs a Frozen Shoulder a Disability
The Social Security Administration knows many mental health disorders can get you disability benefits. These include neurocognitive disorders, schizophrenia spectrum, and depressive disorders.
We’ll look at what it takes to get SSDI and SSI benefits. We’ll also cover the SSA’s evaluation process and how these benefits differ.
Key Takeaways
- Mental health conditions are a big part of disability claims.
- The SSA recognizes many mental health disorders for disability benefits.
- Knowing the rules for SSDI and SSI benefits is key.
- The SSA checks how serious your mental health issues are.
- SSDI and SSI have different rules and ways to apply.
Mental Health Conditions as Recognized Disabilities
The SSA recognizes many mental health disorders as possible disabilities for benefits. This is key to seeing how mental health can really affect someone’s work and daily life.
Legal Definition of Disability Under Social Security
To get disability benefits from Social Security, you must have a condition that meets their definition of disability. The SSA says a disability is a medical issue that makes it hard to do work that pays well. It must be severe enough to stop you from working and earning a living.
Key criteria for disability include:
- The inability to perform work-related activities due to a medical condition.
- A condition that significantly impairs one’s ability to engage in substantial gainful activity.
- A condition that lasts or is expected to last for at least one year or result in death.
How Mental Health Fits Within Disability Framework
Mental health disorders are listed in the SSA’s Blue Book. This book lists mental health conditions that might qualify for benefits. These include depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety, and more.
The SSA has a five-step process to check if mental health claims are valid:
- Determining if the individual is working and earning above a certain threshold.
- Assessing the severity of the mental health condition.
- Evaluating if the condition meets or equals a listing in the Blue Book.
- Assessing the individual’s residual functional capacity (RFC).
- Determining if the individual can perform other jobs in the national economy.
To show how mental health conditions are checked, here’s a table:
|
Mental Health Condition |
SSA Listing |
Criteria for Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
|
Depressive Disorders |
12.04 |
Symptoms such as depressed mood, loss of interest, and changes in appetite or sleep. |
|
Bipolar Disorder |
12.04 |
Symptoms including manic or hypomanic episodes, depressed mood, and significant distress or impairment. |
|
Anxiety Disorders |
12.06 |
Symptoms such as excessive anxiety, fear, or avoidance behaviors that significantly impair functioning. |
It’s important to know how mental health conditions are seen as disabilities under Social Security laws. By looking at how severe the condition is and its effect on daily life and work, the SSA decides if you’re eligible for benefits.
Qualifying Mental Health Conditions for Disability Benefits

The SSA knows about many mental health issues that can make it hard to work. These include depression and anxiety disorders. These problems can really affect how well someone can do daily tasks.
Depression and Mood Disorders
Depression is a big reason for disability all over the world. If it’s very bad, it might get you SSDI benefits. To qualify, depression must make it hard to do basic work tasks.
Key factors in evaluating depression include:
- Severity and frequency of symptoms
- Impact on daily life and work-related activities
- Response to treatment
Anxiety and Panic Disorders
Anxiety disorders, like panic disorder, can be very tough. They might get you disability benefits if they’re severe. The SSA looks at how bad the symptoms are and how they affect your daily life.
“Anxiety disorders can significantly impair an individual’s ability to engage in substantial gainful activity, making them eligible for disability benefits.”
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder makes you feel really high or really low. It can make it hard to keep a job. This is why it might get you social security disability for bipolar depression.
The SSA looks at how often and how bad the mood swings are. They also consider how it affects your daily life.
Schizophrenia and Psychotic Disorders
Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders mess with your thinking, feelings, and actions. Symptoms like hearing things that aren’t there or thinking things that aren’t true can be very disabling.
To qualify for disability benefits, individuals with schizophrenia must demonstrate significant functional limitations.
Most mental health disability claims are for depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorders. The SSA checks your medical records and how these conditions affect your life.
SSDI vs. SSI: Understanding the Differences
It’s important to know the difference between SSDI and SSI for mental health benefits. Both are run by the Social Security Administration. But they help in different ways and have different rules for who can get them.
SSDI is for people who have worked and paid Social Security taxes. It’s like a safety net for when they can’t work anymore. SSI, on the other hand, is for those with little income and resources. It’s based on need.
SSDI Eligibility Requirements for Mental Health Conditions
To get SSDI for mental health issues, you need to have worked and earned Social Security credits. How many credits you need depends on your age when you got sick. Usually, you need 40 credits, with 20 in the last 10 years.
Mental health conditions like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia can qualify for SSDI. But only if they really stop you from working.
SSI Qualification Criteria for Mental Health Disabilities
For SSI, it’s about how much money you make and have. You must not have much income or resources. And your mental health issue must be severe enough to stop you from working.
The SSA has a five-step process for both SSDI and SSI claims. They check if you can do work tasks and how bad your mental health is. It’s very important to have good medical proof for your claim.
Knowing the differences and what each program needs helps those with mental health issues. It makes it easier to get the disability benefits they need.
The Social Security Blue Book and Mental Disorders
Understanding the SSA’s Blue Book for mental disorders is key for those seeking disability benefits. The SSA’s Blue Book is a detailed guide. It lists impairments that might qualify someone for disability benefits.
Section 12.00: Mental Disorders Listing
The SSA’s Blue Book has a special section for mental disorders. It lists mental health conditions that could qualify for disability benefits. These include depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorders.
Mental Health Conditions Listed in the Blue Book
|
Mental Health Condition |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Depressive, Bipolar, and Related Disorders |
Conditions such as major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder that significantly impact mood and functioning. |
|
Anxiety and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders |
Disorders like generalized anxiety disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder that cause significant distress and impairment. |
|
Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders |
Conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) that develop after a traumatic event. |
Meeting vs. Equaling a Listing
To get disability benefits, your mental health condition must meet or equal a Blue Book listing. Meeting a listing means your condition fits all the Blue Book criteria. Equaling a listing means your condition is as severe, even if it doesn’t fit all the criteria.
For example, if you have major depressive disorder, your symptoms must match the Blue Book criteria. If they do, you might be considered disabled.
Medical evidence is vital in deciding if your mental health condition meets or equals a listing. This includes medical records, psychiatric evaluations, and assessments of how your condition affects your daily life.
Is Mental Health a Disability? Statistical Evidence
Mental health awareness is growing fast. More people are applying for disability benefits because of mental health issues. This shows we need to look at the facts behind these claims.
Prevalence of Mental Health Disability Claims
Mental health problems are a big reason for disability claims. About one quarter of SSDI applicants say mental health issues are their main problem. This shows how important mental health is in deciding if someone is disabled.
The number of mental health disability claims is going up. This is because more people are talking about mental health and feeling less ashamed about it.
Approval Rates for Mental Health Disability Applications
How often mental health disability claims get approved can change a lot. It depends on the mental health issue and the medical proof given. Let’s dive into the numbers to understand better.
|
Mental Health Condition |
SSDI Approval Rate |
SSI Approval Rate |
|---|---|---|
|
Depression and Mood Disorders |
45% |
42% |
|
Anxiety and Panic Disorders |
38% |
35% |
|
Bipolar Disorder |
50% |
48% |
Bipolar disorder seems to get approved more often than depression and anxiety. This shows how important it is to have good medical records. It also shows the need for applicants to know what their condition needs.
Applying for disability can be tough. But with the right help and proof, people with mental health issues can get the benefits they deserve.
Applying for Disability Benefits with Mental Health Conditions
Applying for disability benefits with mental health conditions needs careful planning and paperwork. The Social Security Administration (SSA) has clear rules for mental health disabilities. Knowing these rules can really help your application.
Required Documentation and Medical Evidence
The SSA needs detailed medical proof for mental health disability claims. This includes:
- Reports from psychiatrists or psychologists that confirm the mental health condition.
- A detailed list of treatments, like medications and therapies.
- Proof of how the condition affects daily life and work.
Table: Required Documentation for Mental Health Disability Claims
|
Document Type |
Description |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Diagnostic Reports |
Medical records confirming the diagnosis of a mental health condition. |
High |
|
Treatment History |
Details of treatments received, including medications and therapies. |
High |
|
Functional Limitations |
Assessment of how the mental health condition affects daily life and work capabilities. |
High |
The Role of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals are key in the application process. They provide the needed medical proof. They also share how severe the condition is and its impact on daily life.
Consultative Examinations for Mental Conditions
At times, the SSA might ask for a consultative examination (CE). This is to get more info about the mental health condition. A healthcare professional chosen by the SSA does this exam. It’s needed when the current medical evidence isn’t enough.
Knowing about consultative exams helps applicants get ready. It ensures they have all the right documents for a successful claim.
Challenges in Proving Mental Health Disability
Proving mental health disability is hard because mental illnesses are not visible. Unlike physical disabilities, mental health issues don’t have clear signs. This makes it tough for people to show how they are limited.
Subjective Nature of Symptoms
Mental health symptoms are hard to measure because they depend on what the person says and what doctors think. This makes it hard to agree on what someone’s disability is.
To tackle this, it’s key to:
- Keep detailed medical records of symptoms and how they respond to treatment.
- Get thorough checks from mental health experts.
- Show how symptoms affect daily life and work.
Documenting Functional Limitations
It’s important to show how mental health issues limit daily activities. This includes how they affect social life and work.
Ways to document these limitations include:
- Keeping a journal of daily symptoms and challenges.
- Getting statements from family, friends, or coworkers about changes in behavior or ability.
- Having mental health professionals assess the impact of symptoms.
Addressing Credibility Concerns
People with mental health disabilities often face doubts about their conditions. To overcome this, it’s important to gather and present strong evidence.
To boost credibility, claimants should:
- Provide consistent and detailed medical records.
- Stick to treatment plans and therapies.
- Cooperate fully with assessments and exams.
By understanding these challenges and using strategies to overcome them, people with mental health conditions can improve their chances of getting the benefits they need.
Continuing Disability Reviews for Mental Health Conditions
The Social Security Administration (SSA) regularly checks if people with mental health conditions are eligible for benefits. These checks, called Continuing Disability Reviews (CDRs), help decide if someone is disabled according to SSA rules.
Frequency of Reviews for Mental Health Disabilities
How often CDRs happen depends on the mental health condition’s severity and stability. Generally, the SSA reviews:
- Within 6 to 18 months for cases involving significant medical improvement
- Every 3 years for cases where the condition is considered stable but potentially reversible
- Every 7 years for cases where the condition is deemed less likely to improve
During these reviews, the SSA looks at the person’s current health, treatment, and work ability. People getting benefits must give new medical info and might need a special exam.
Maintaining Benefits During Mental Health Fluctuations
For those with mental health issues, symptoms and ability to work can change. To keep getting benefits, it’s key to:
- Keep detailed records of symptoms, treatment, and how the condition affects daily life and work capabilities
- Follow the treatment plan and tell the SSA about any changes
- Inform the SSA of any hospitalizations or significant changes in condition
If someone’s condition gets worse, they should tell the SSA. Benefits might stay the same if the condition is disabling, even with some improvement.
|
Review Frequency |
Condition Severity |
Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
|
6-18 months |
Significant medical improvement possible |
Re-evaluation of disability status |
|
3 years |
Stable but potentially reversible |
Assessment of ongoing disability |
|
7 years |
Less likely to improve |
Periodic confirmation of continued eligibility |
Knowing about CDRs and talking openly with the SSA can help those with mental health conditions keep their benefits. Being informed and proactive makes it easier to deal with reviews.
Working While Receiving Mental Health Disability Benefits
The Social Security Administration (SSA) lets people work while getting mental health disability benefits. This is good for those who want to go back to work or start a new job. It helps them manage their mental health while working.
Trial Work Period Provisions
The SSA has a trial work period (TWP) for those who want to try working. During this time, they can get full SSDI benefits, no matter how much they earn. They just need to tell the SSA about their work. The TWP can last up to nine months, spread out over 60 months.
Trial Work Period Example: Say someone with anxiety disorder disability starts working part-time. They can keep getting SSDI benefits during the TWP. This lets them see if they can work without losing money right away.
Substantial Gainful Activity Limitations
After the TWP, the SSA checks if the person is making too much money. In 2023, making over $1,470 a month is too much for non-blind people. If they make too much, they might lose their benefits. But the SSA looks at the job, how it’s done, and how it affects their disability.
- Earnings above the SGA threshold may result in benefit termination.
- Beneficiaries can appeal decisions if they believe their condition affects their work capability.
Return-to-Work Success Rates for Mental Health Beneficiaries
Studies show that success rates for mental health beneficiaries vary. Success depends on the mental health condition, treatment, and support. Those getting SSDI for depression and anxiety or SSI for anxiety have different chances.
Success Factors: Having good support, like mental health experts and job training, helps a lot. We suggest looking into these resources to improve job chances.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how mental health and disability benefits are connected. The Social Security Administration (SSA) sees mental health issues as possible disabilities.
People with mental health problems like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia might get SSDI or SSI. The SSA’s Blue Book lists mental disorders that can qualify for benefits. This includes depression and anxiety.
To apply for disability for bipolar depression or other mental health issues, you need to show strong medical evidence. You must also prove how your condition limits your daily activities.
Knowing the difference between SSDI and SSI is key. Mental health experts play a big role in the application process. This knowledge can greatly affect your claim’s success.
By acknowledging mental health as a disability, we can offer SSDI and SSI benefits. This helps people with mental health issues get the support they need. It improves their life quality.
FAQ
What mental health conditions are considered disabilities under Social Security?
The Social Security Administration (SSA) lists many mental health conditions as disabilities. These include depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. They are found in Section 12.00: Mental Disorders of the SSA’s Blue Book.
How do I qualify for SSDI benefits with a mental health condition?
To get SSDI benefits, your mental health condition must meet the SSA’s disability criteria. You also need to have worked and paid Social Security taxes. The SSA checks how severe your condition is and how it affects your work ability.
What is the difference between SSDI and SSI benefits for mental health disabilities?
SSDI benefits are based on your work history and Social Security taxes. SSI benefits, on the other hand, are for those who need them and don’t have to work. Both consider mental health conditions as disabilities, but have different rules.
How does the SSA evaluate mental health disability claims?
The SSA looks at how severe your condition is and how it affects your daily life. They also review medical evidence from doctors. They use a five-step process to decide if you’re disabled, including checking if your condition matches a Blue Book listing.
Can I receive disability benefits for anxiety or panic disorder?
Yes, you can get disability benefits for anxiety or panic disorders if they’re severe. The SSA looks at how often and how intense your symptoms are. They also consider any work limitations caused by your condition.
What documentation is required to apply for disability benefits with a mental health condition?
You’ll need detailed medical records to apply for benefits. This includes your diagnosis, treatment history, and how your condition affects your daily life and work. Mental health professionals are key in providing this information.
How often are continuing disability reviews conducted for mental health conditions?
Reviews for mental health conditions happen at different times. They’re more frequent for conditions expected to improve, like every 6 to 18 months. For more severe or stable conditions, reviews are less often.
Can I work while receiving mental health disability benefits?
Yes, but there are rules. You can try working during a trial work period without losing benefits right away. But, you must not earn too much or you could lose your benefits.
How do I maintain my benefits during fluctuations in my mental health?
To keep your benefits, keep up with treatment and document your condition’s impact. Also, tell the SSA about any changes. This ensures your benefits stay if your condition remains disabling.
What is the role of a consultative examination in the disability application process?
A consultative examination is an SSA-chosen doctor’s assessment. It’s used when existing medical evidence isn’t enough. It helps the SSA make a better decision on your disability claim.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ssa.gov/disability/professionals/bluebook/12.00-MentalDisorders-Adult.htm